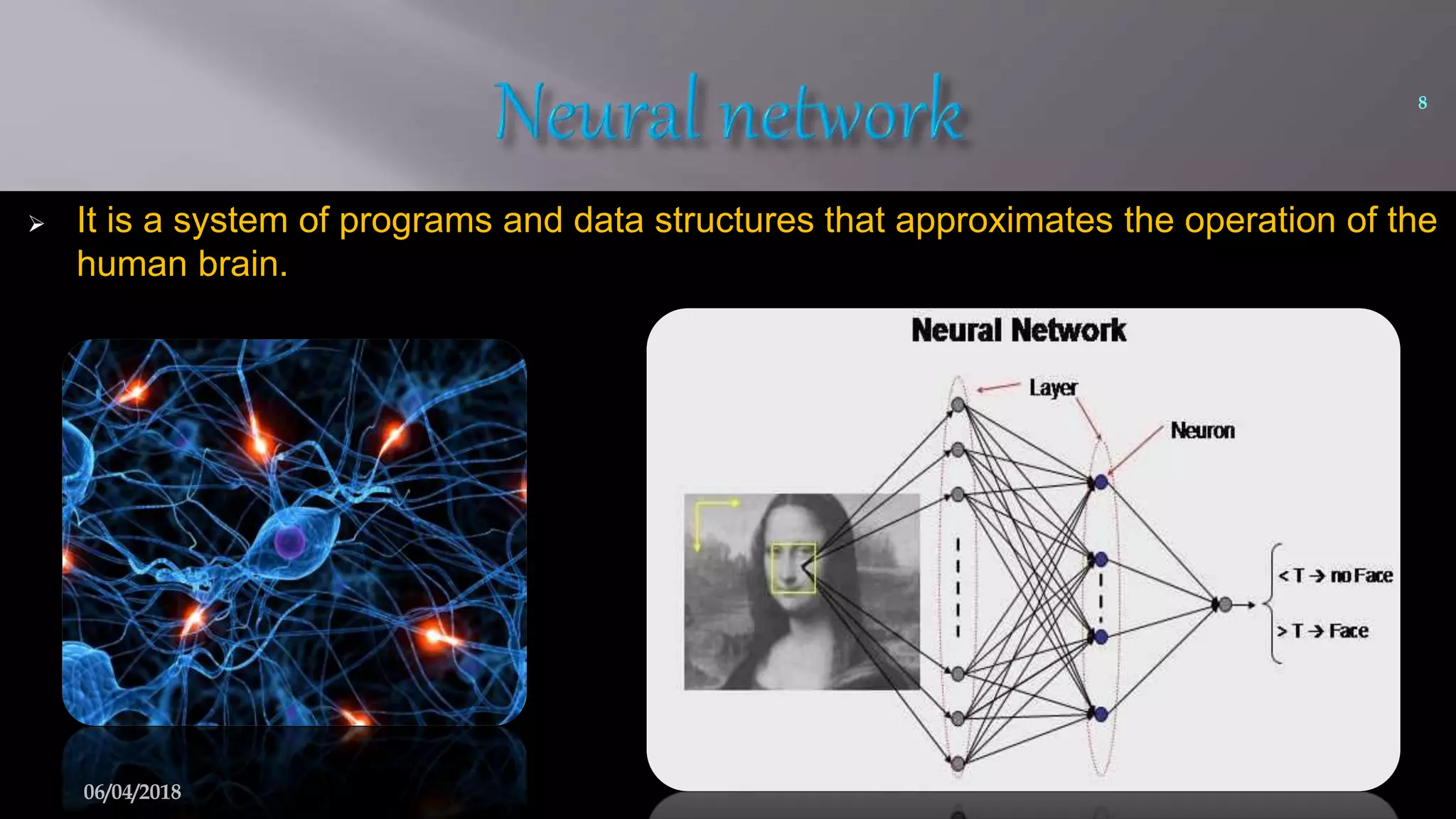
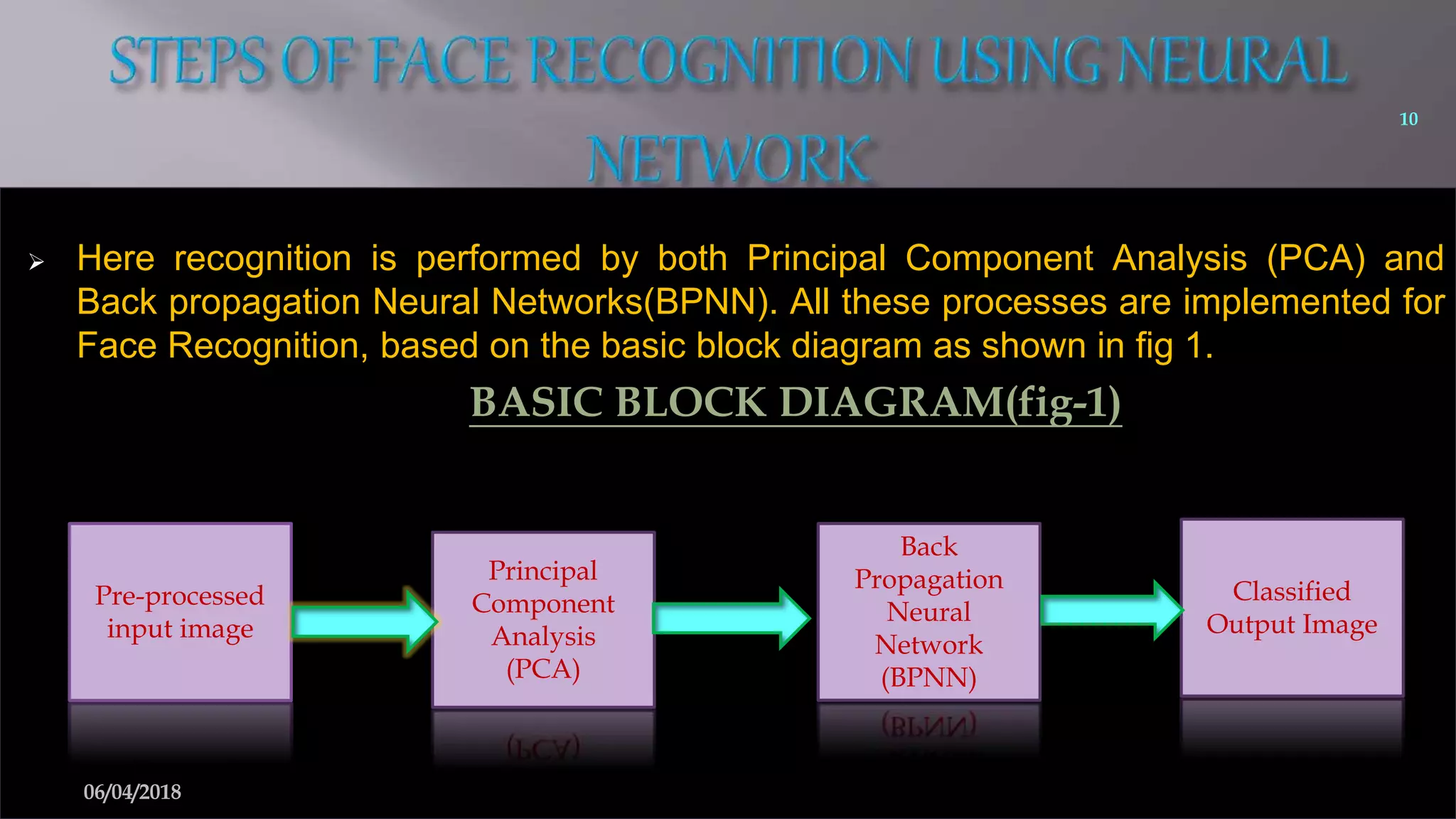
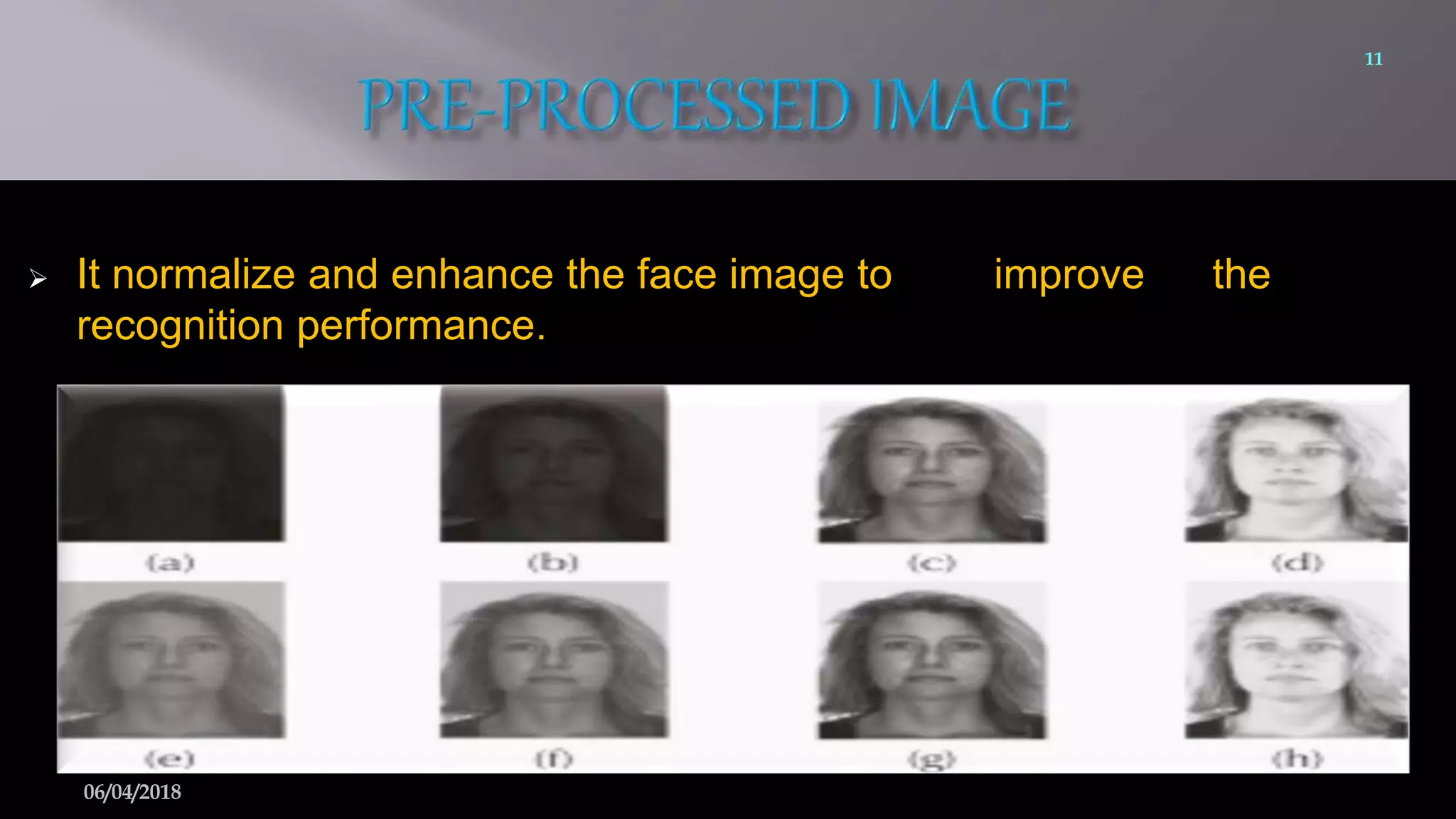
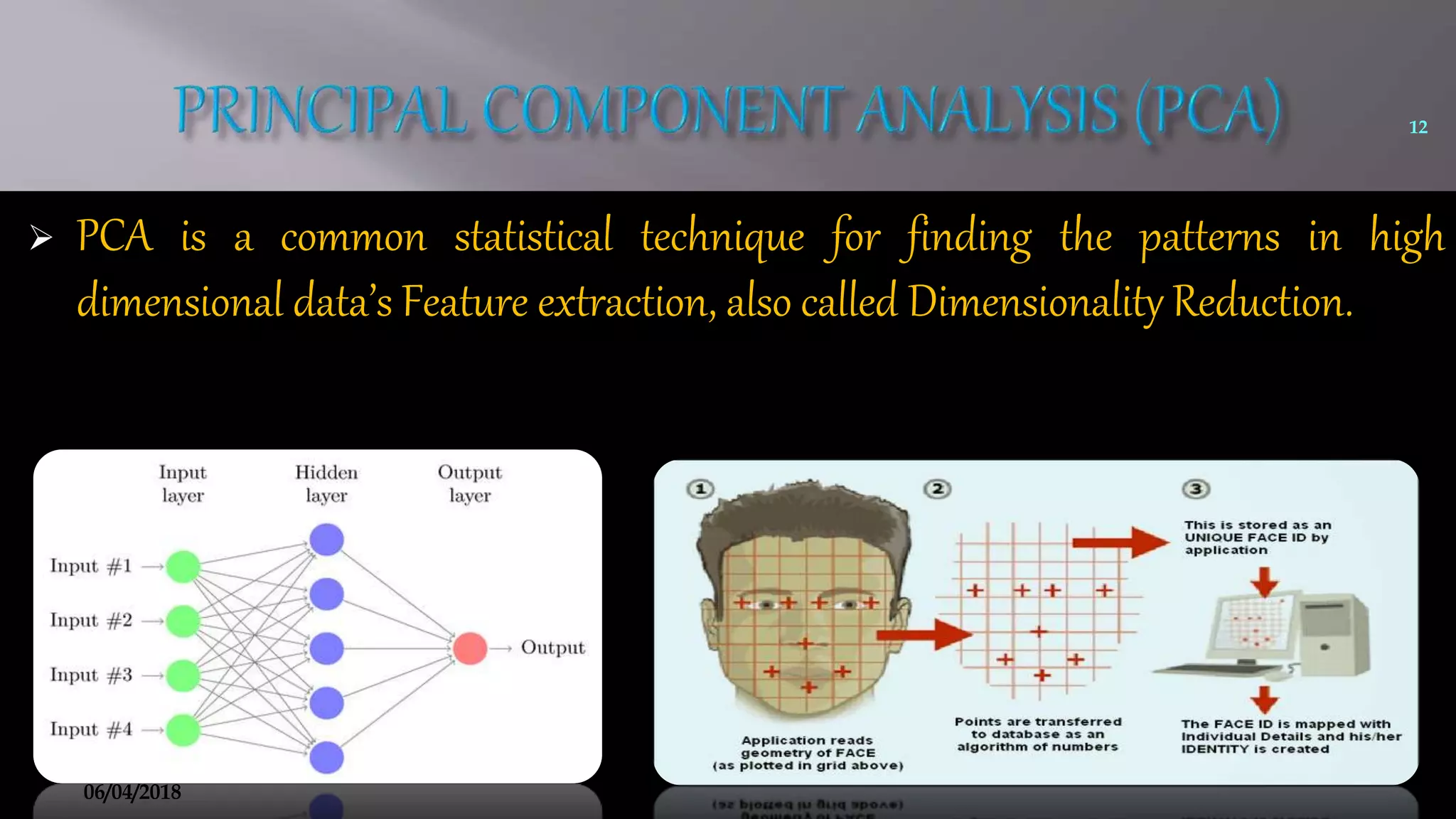
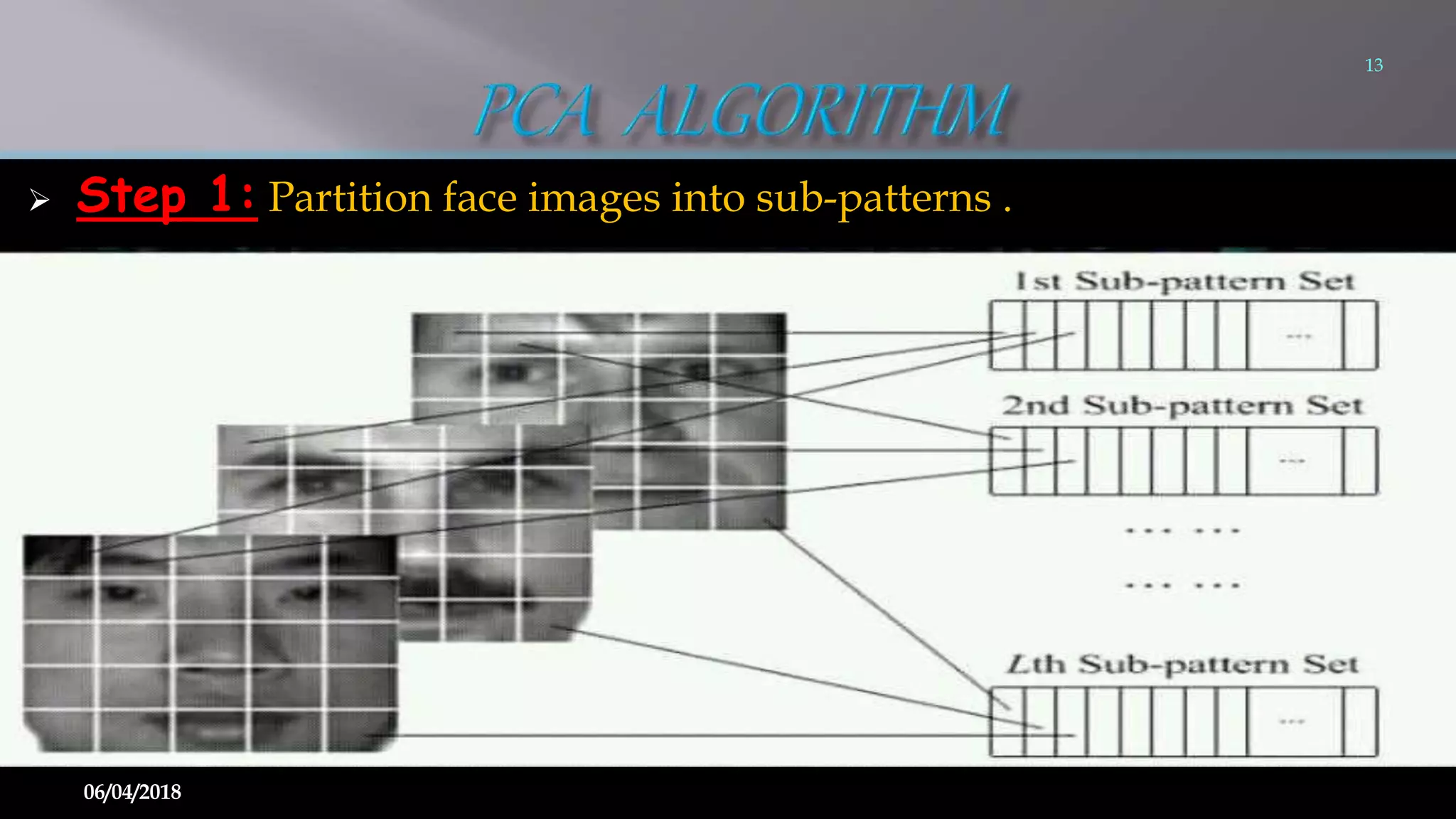
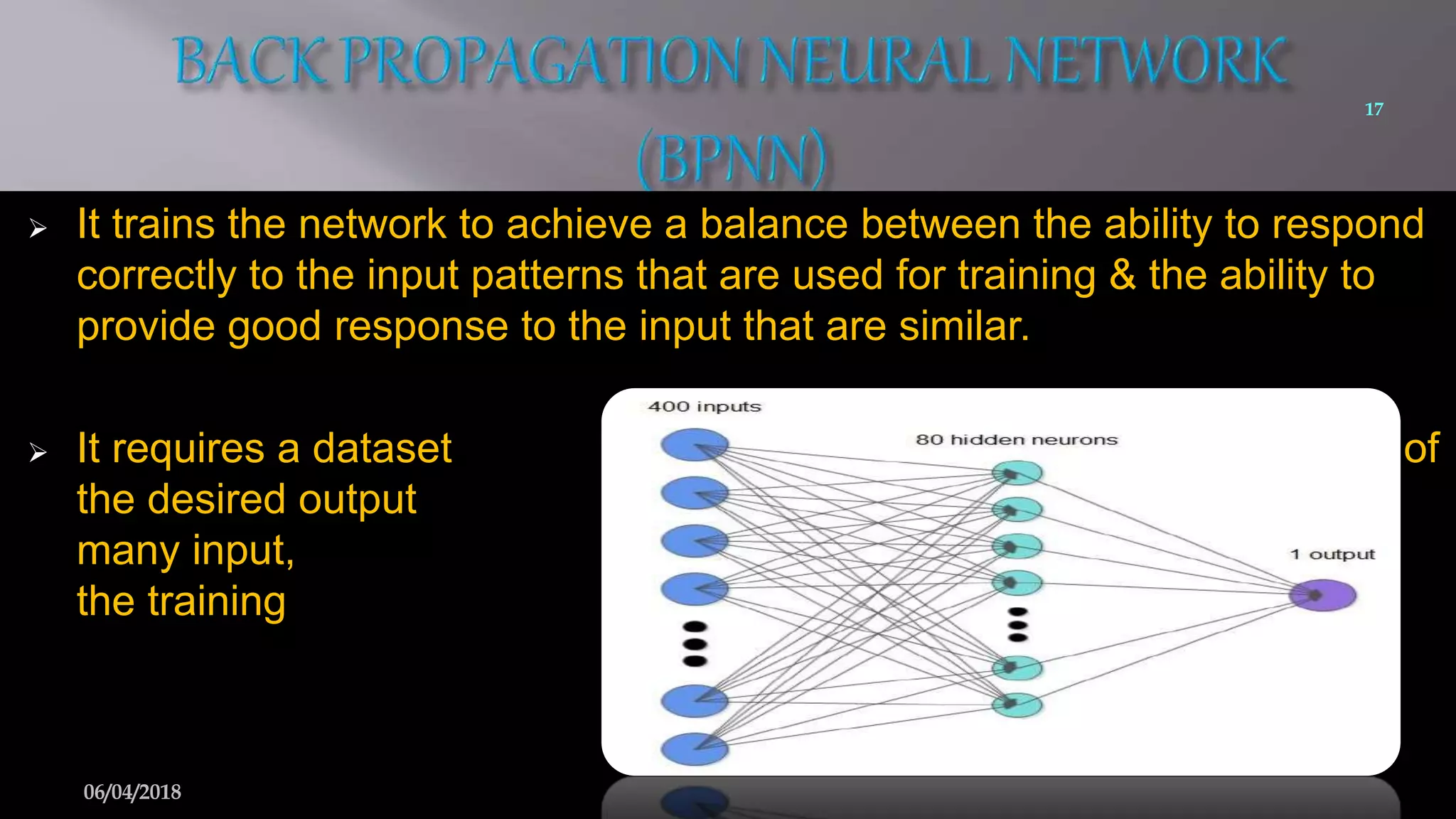
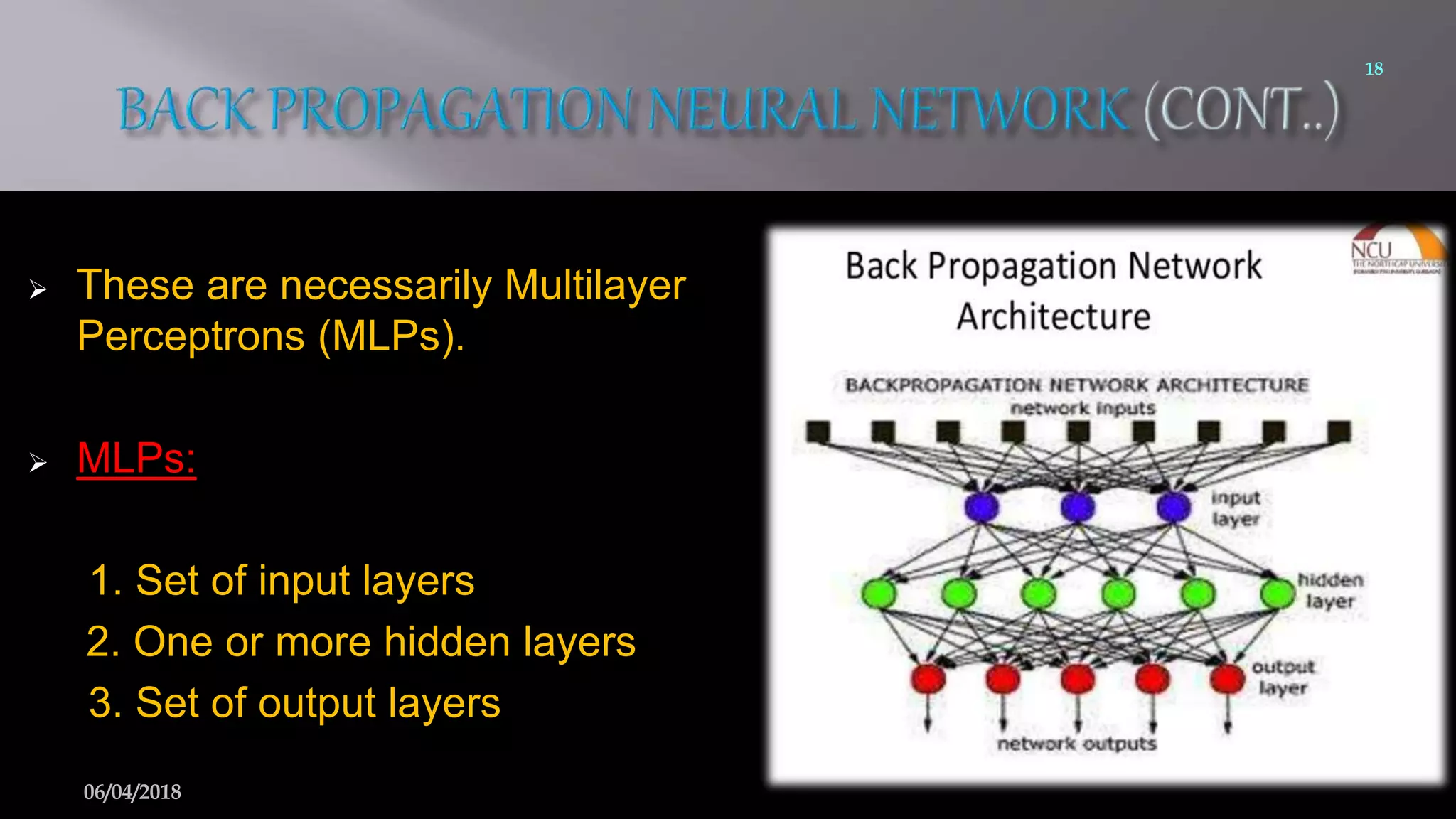
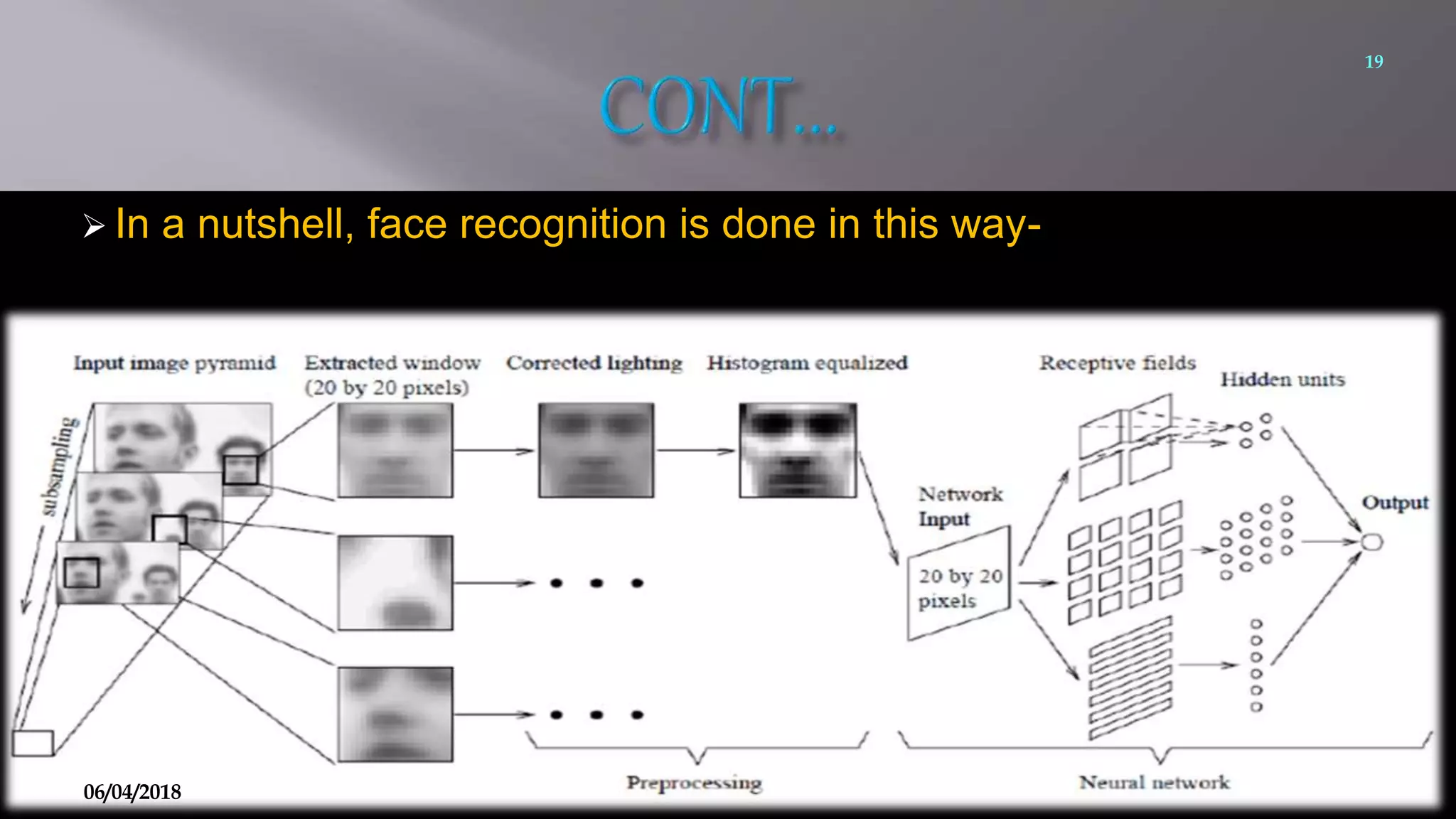
This document summarizes a seminar on face recognition using neural networks. It discusses the history of face recognition, how neural networks can be used for face recognition, and the basic process which involves pre-processing images, using principal component analysis for feature extraction, and comparing images to a database using backpropagation neural networks. Some advantages are that it is non-intrusive and can use existing hardware, while disadvantages include issues with identical twins and environment. Applications discussed include security, criminal identification, and credit card verification.