This document provides an overview of key differences between Indian GAAP and US GAAP. It defines GAAP as the common set of accounting principles, standards and procedures used to compile financial statements. Some major differences discussed include underlying assumptions, financial statement presentation formats, treatment of investments, consolidation of subsidiaries, accounting for foreign currency transactions, and accounting for expenses such as depreciation, pre-operating expenses, and employee benefits. The document also explains some accounting concepts and terms referenced in discussing the differences between Indian and US GAAP.


![DEFINITION: The common set of accounting principles,
standards and procedures that companies use
to compile their financial statements. GAAP
are a combination of authorities standards
[set by policy boards] and simply the
commonly accepted ways of recording and
reporting accounting information.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-3-320.jpg)

![GAAP WAS ESTABLISHED BY Securities
and exchange
commission [SEC]
Financial accounting standards
board [FASB]
Governmental accounting
standards board [GASB]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-5-320.jpg)






![CASH FLOW STATEMENT
• Cash flow statement in
financial statements is
mandatory only for
listed companies[AS-3]
• Cash flow statement is
mandatory for 3yearscurrent year & 2
immediate preceding
years irrespective of
whether the company is
listed/not[AS-95]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-12-320.jpg)


![ Subsidiary company- A company controlled
by holding company i:e the company holding
more than 51% of shares.
Consolidation- It refers to the
aggregation[collection] of financial statements
of a group company as consolidated financial
statements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-16-320.jpg)
![CONSOLIDATION OF SUBSIDIARY
ACCOUNTS
• Consolidation of
accounts of subsidiary
companies is not
mandatory[AS-21]
• Consolidation of results
of subsidiary companies
is mandatory, hence
eliminating material,
inter company
transactions & giving a
true picture of the
operations &
profitability [AS-94]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-17-320.jpg)
![What is prudence?
• It is a good judgement or wisdom gained by
experience & knowledge, expressed in a
realistic & frugal attitude. It is not the same as
grave caution or wariness concerned only with
preserving status quo[existing state of affairs].
If there is no real cause for fear, prudence lies
in avoiding excessive deliberations & in the
readiness to sacrifice today’s gain for
tomorrow’s greater gain.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-19-320.jpg)

![FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSACTIONS
• Exchange
• Capitalization of
fluctuations on
exchange fluctuation
liabilities incurred for
arising from
fixed assets can be
liabilities incurred for
capitalized[AS-11]
acquiring fixed
assets does not
exist[AS-52]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-22-320.jpg)
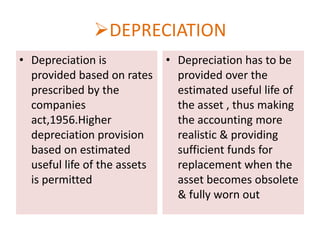
![EXPENDITURE DURING
CONSTRUCTION PERIOD
• All incidental
expenditure on
construction of assets
during project stage are
accumulated &
allocated to the cost of
asset
• Such expenses are
divided into 2 heads
direct & indirect. While
direct expense is
accumulated &
allocated to the cost of
asset, indirect are
charged to revenue[AS7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-23-320.jpg)
![RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT
EXPENDITURE
• R&D to be charged to
P/L, except equipment
& machinery which are
capitalized &
depreciated[AS-8]
• All R&D costs are
expenses except
intangible assets
purchased from others
& tangible assets that
have alternative future
uses which are
capitalized &
depreciated[AS-2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-24-320.jpg)



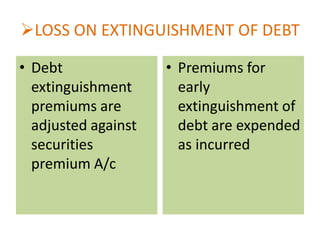
![EXTRAORDINARY ITEMS & PRIOR
PERIOD ITEMS
• Extraordinary &
prior period items
are disclosed
without netting off
for tax effects[AS-5]
• Adjustments for tax
effects are required
to be made while
reporting the prior
period items[AS-16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-28-320.jpg)
![GOODWILL
• Goodwill is
capitalized &
charged to earnings
over 5-10yrs period
• Goodwill &
intangible assets are
amortized, but they
are tested at least
annually for
impairment[AS-142]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-29-320.jpg)


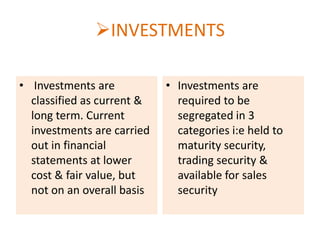
![INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATED
COMPANIES
• Investments in
associate companies is
initially recorded at
cost, identifying
goodwill/capital reserve
arising at the time of
acquisition[AS-23]
• Investments in
associates are
accounted under equity
method in group
accounts but would be
held at cost in the
investor’s own A/c[AS115]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-33-320.jpg)
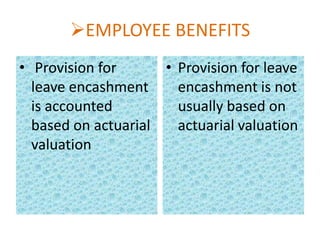
![PREOPERATIVE EXPENSES
• Direct revenue
expenses like
preliminary &
indirect like
incidental, are
allowed to be
capitalized
• Expenses have to be
charged to revenue
& assets are
capitalized as a
normal
organization[AS-7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fa-gaap-140125033656-phpapp01/85/Fa-gaap-34-320.jpg)