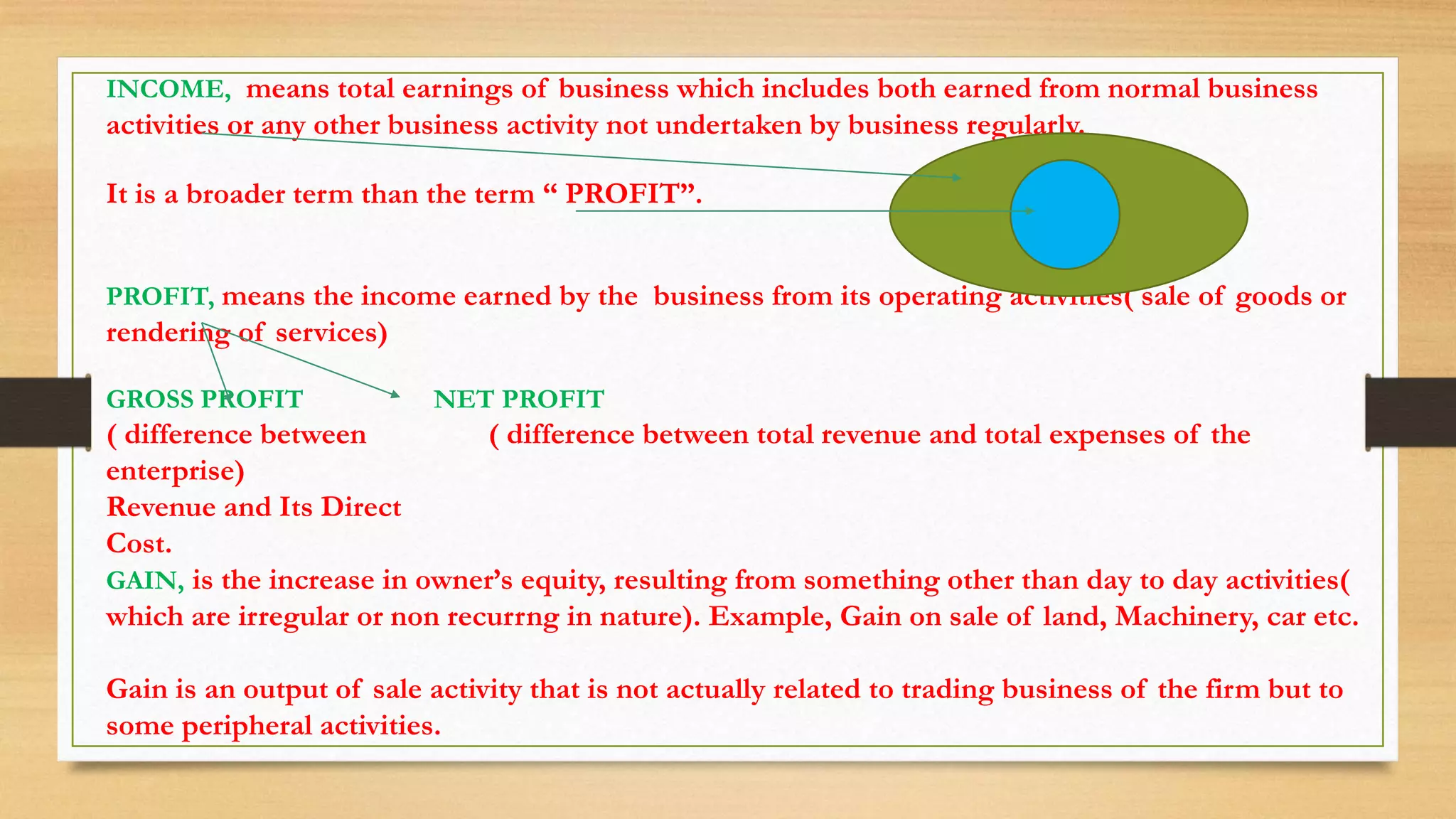
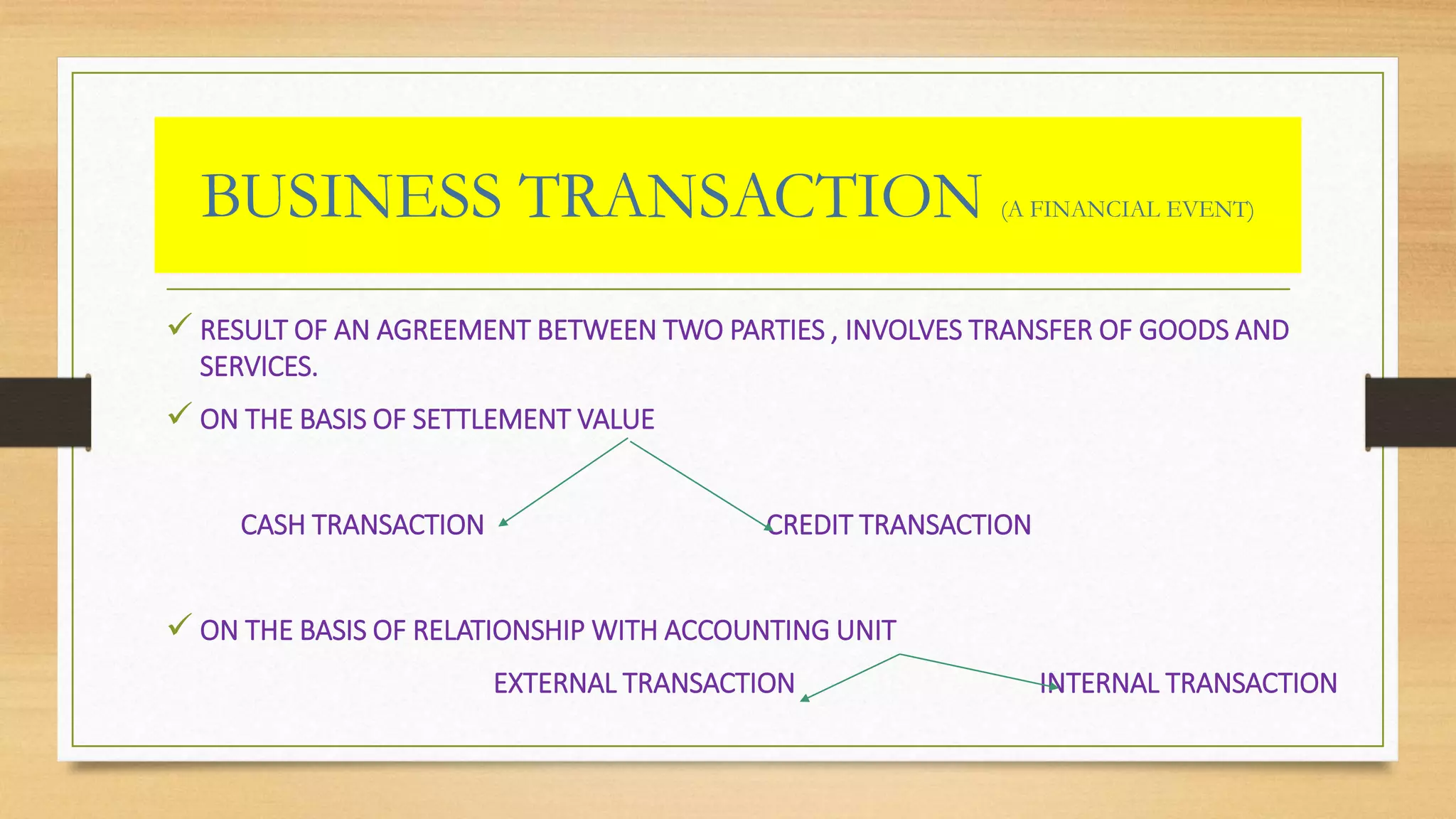
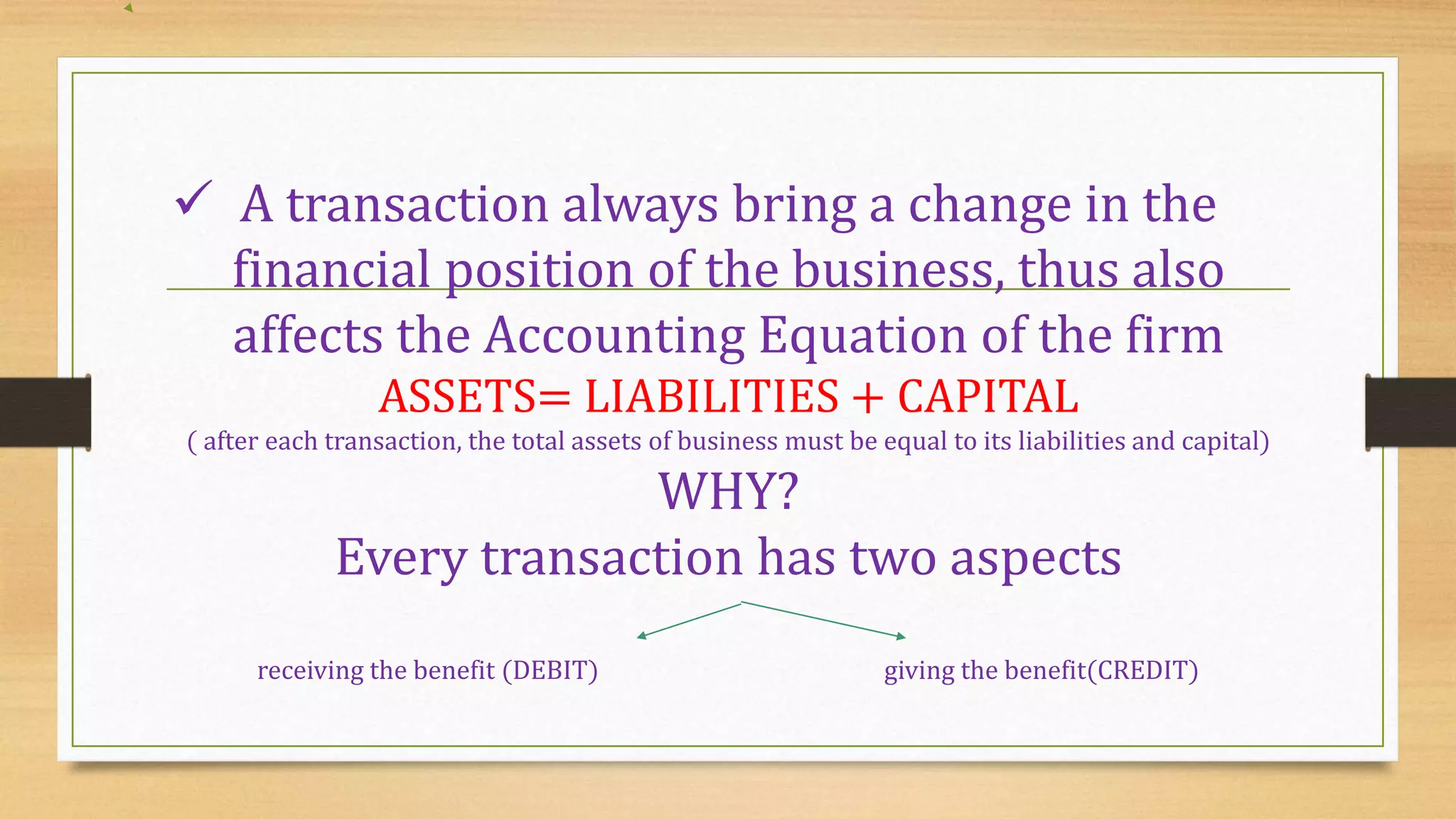
This document defines key accounting terms related to income, expenses, assets, liabilities, and financial statements. It explains that income is broader than profit, with profit referring specifically to earnings from operating activities. It also distinguishes various types of expenses, assets, liabilities, and transactions that appear in basic accounting records and financial statements.



![DRAWINGS
(amount withdrawn by the Owner for personal use.)
In the form of CASH In the form of GOODS, at Purchase Cost.
[DEBITED TO DRAWINGS A/c]
In balance Sheet, CAPITAL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicaccountingterms-220729111325-968cbf74/75/BASIC-ACCOUNTING-TERMS-pptx-7-2048.jpg)










