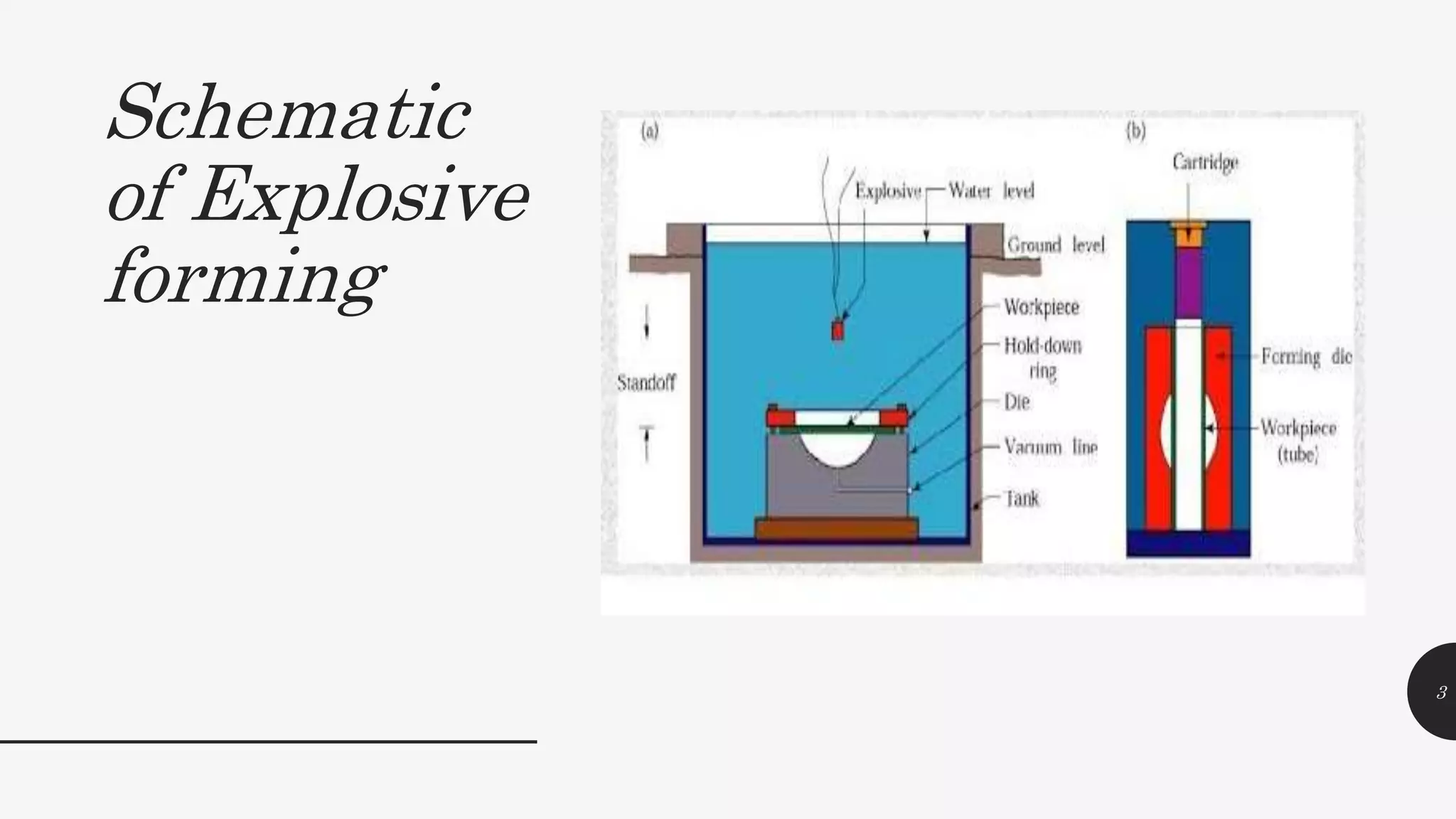
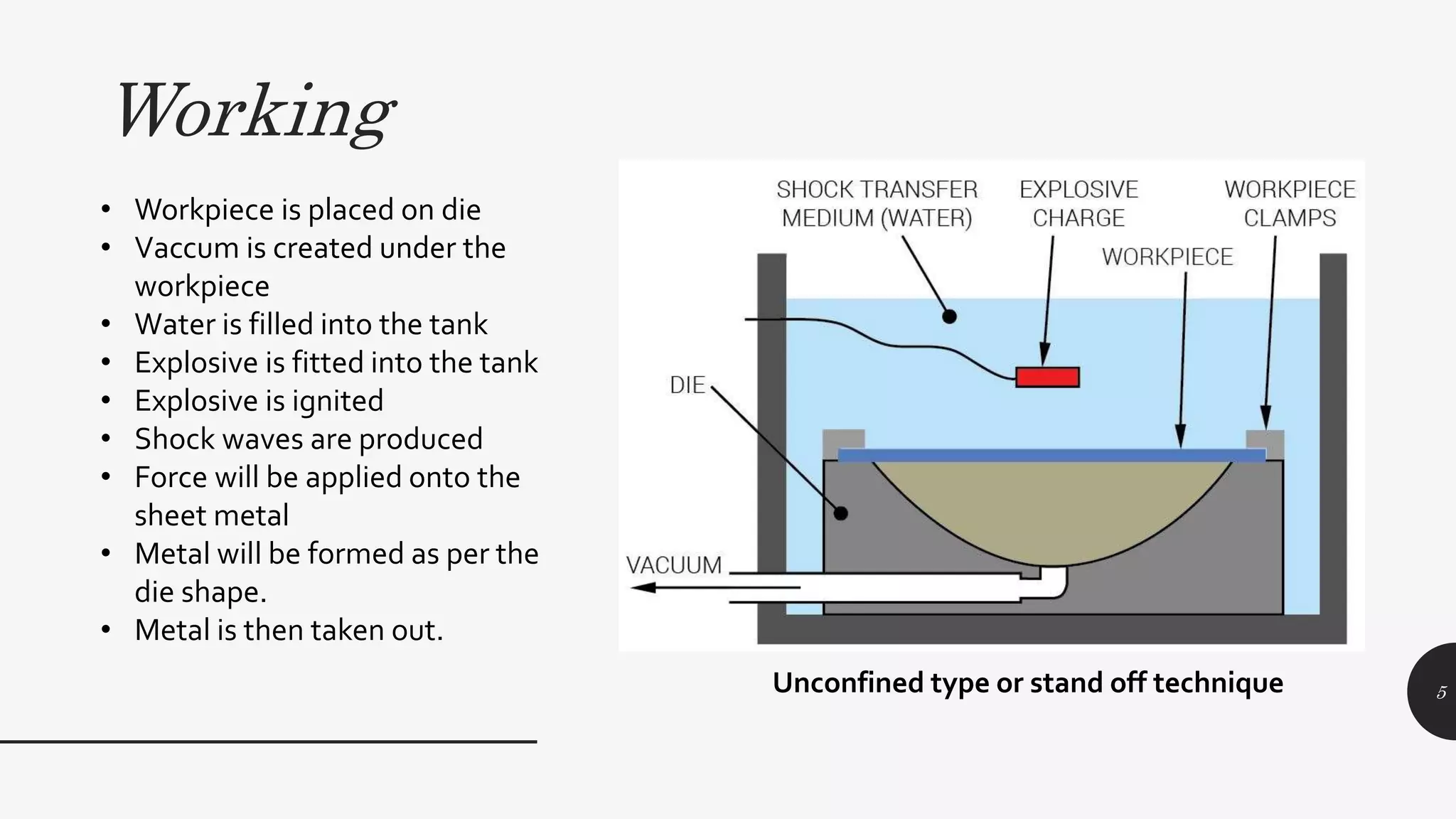
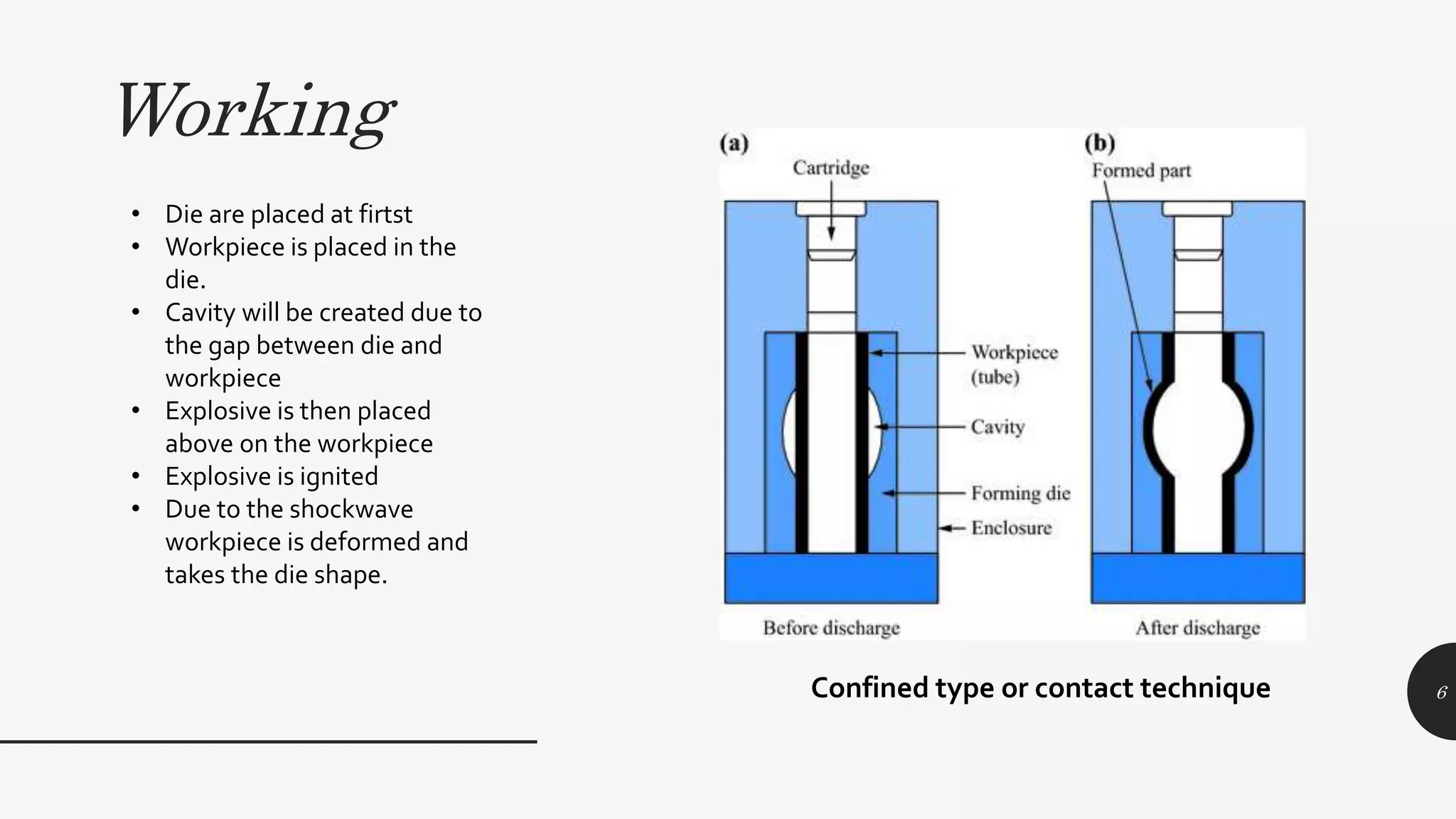
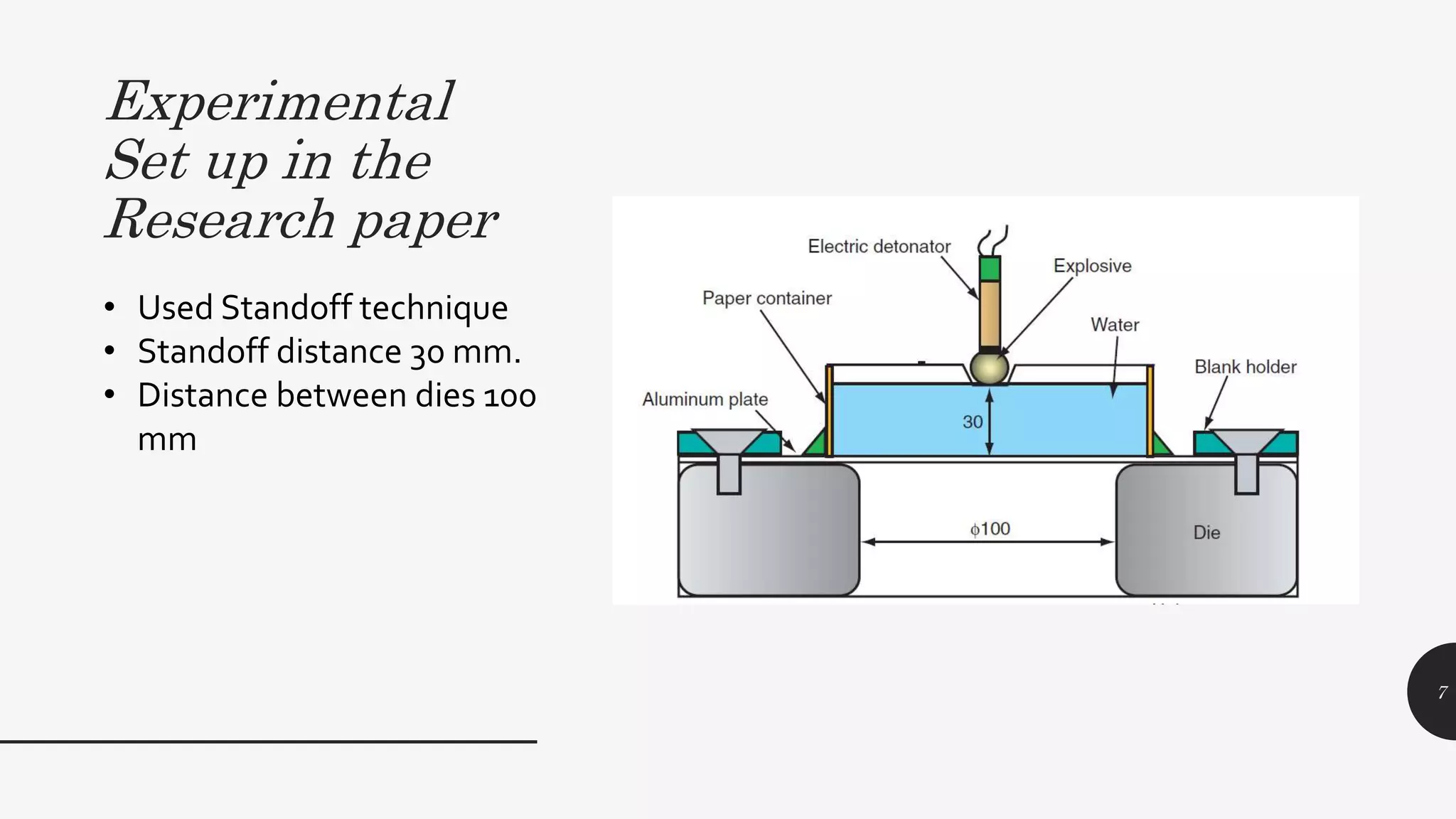
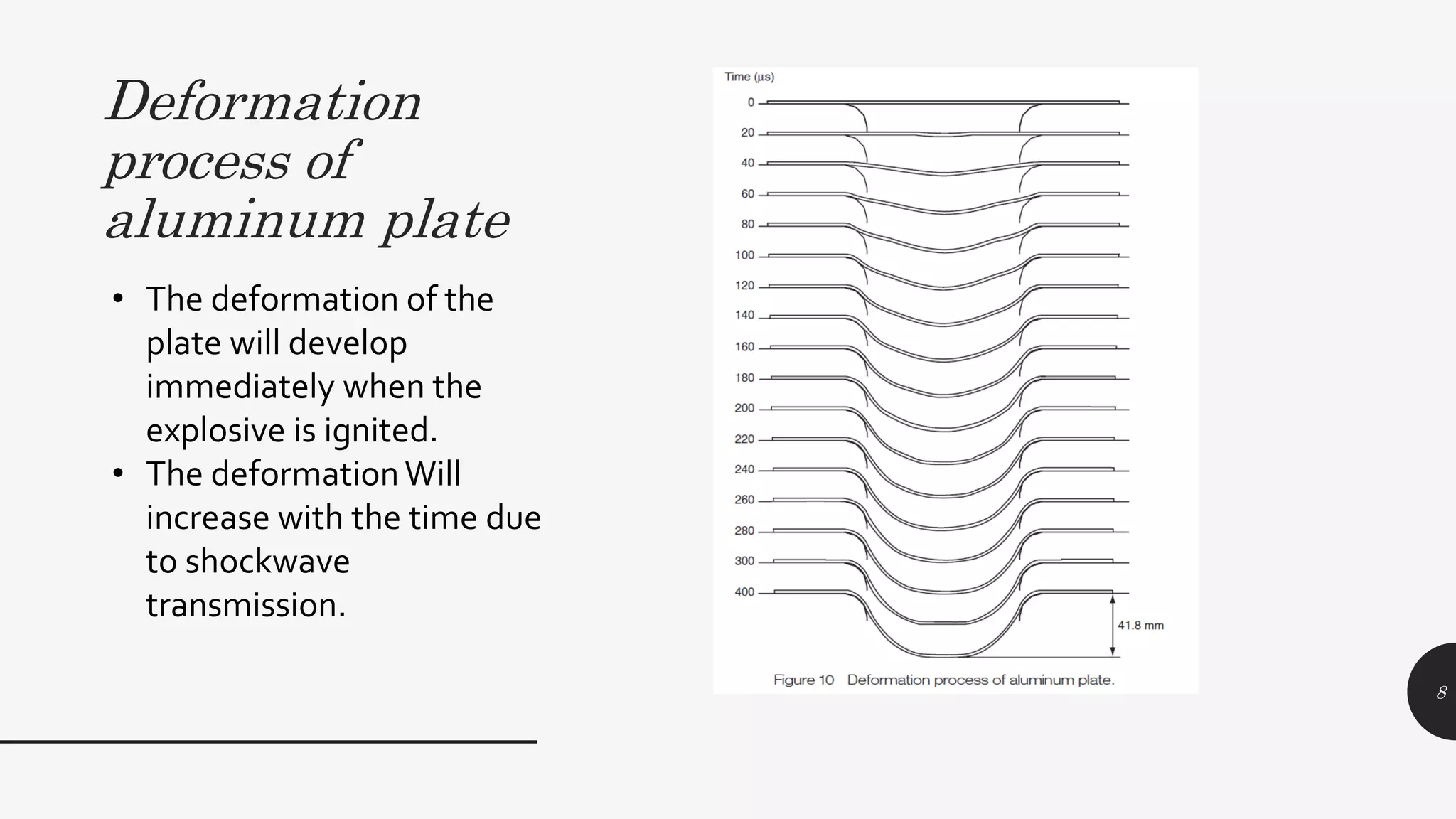
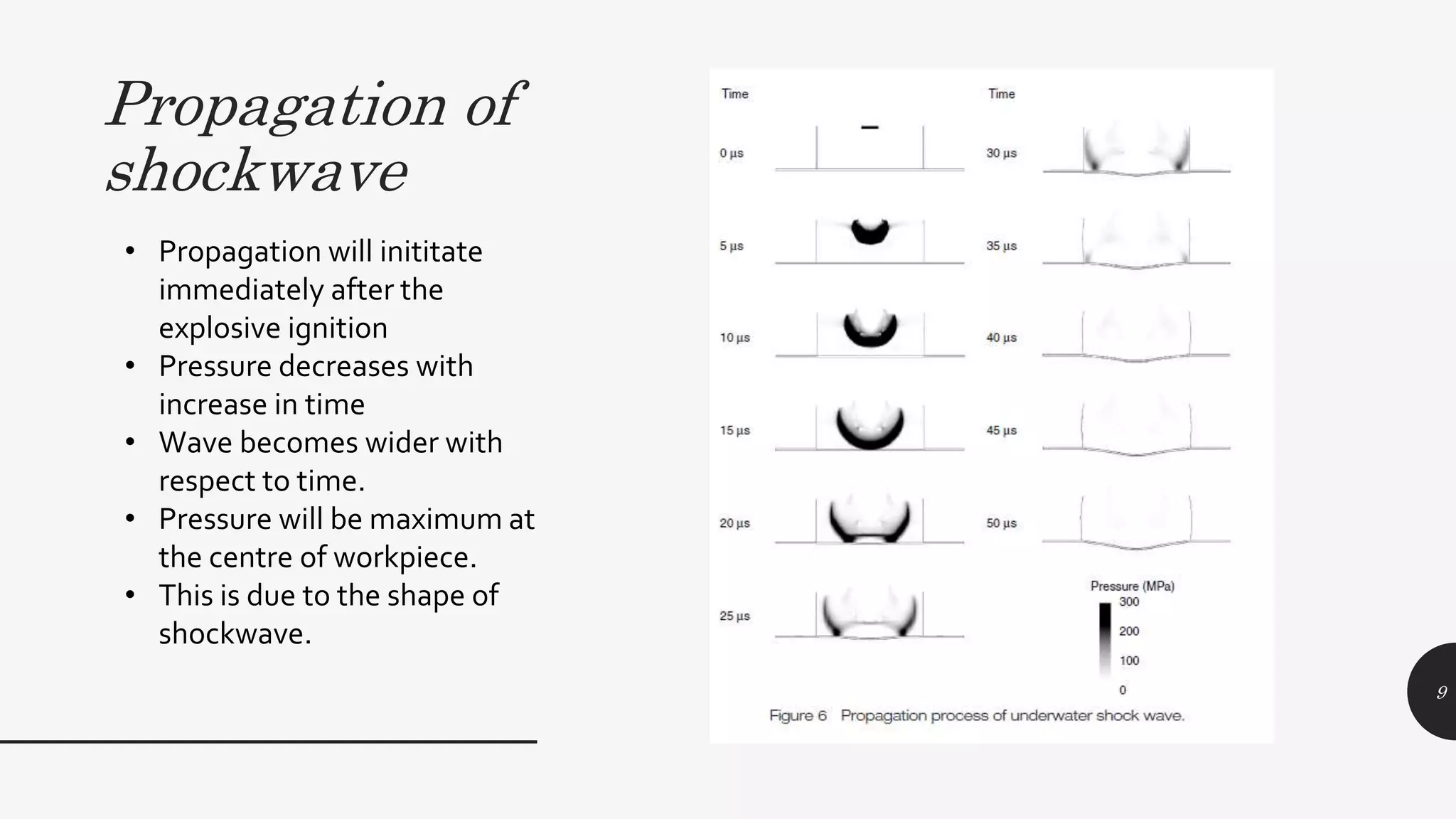
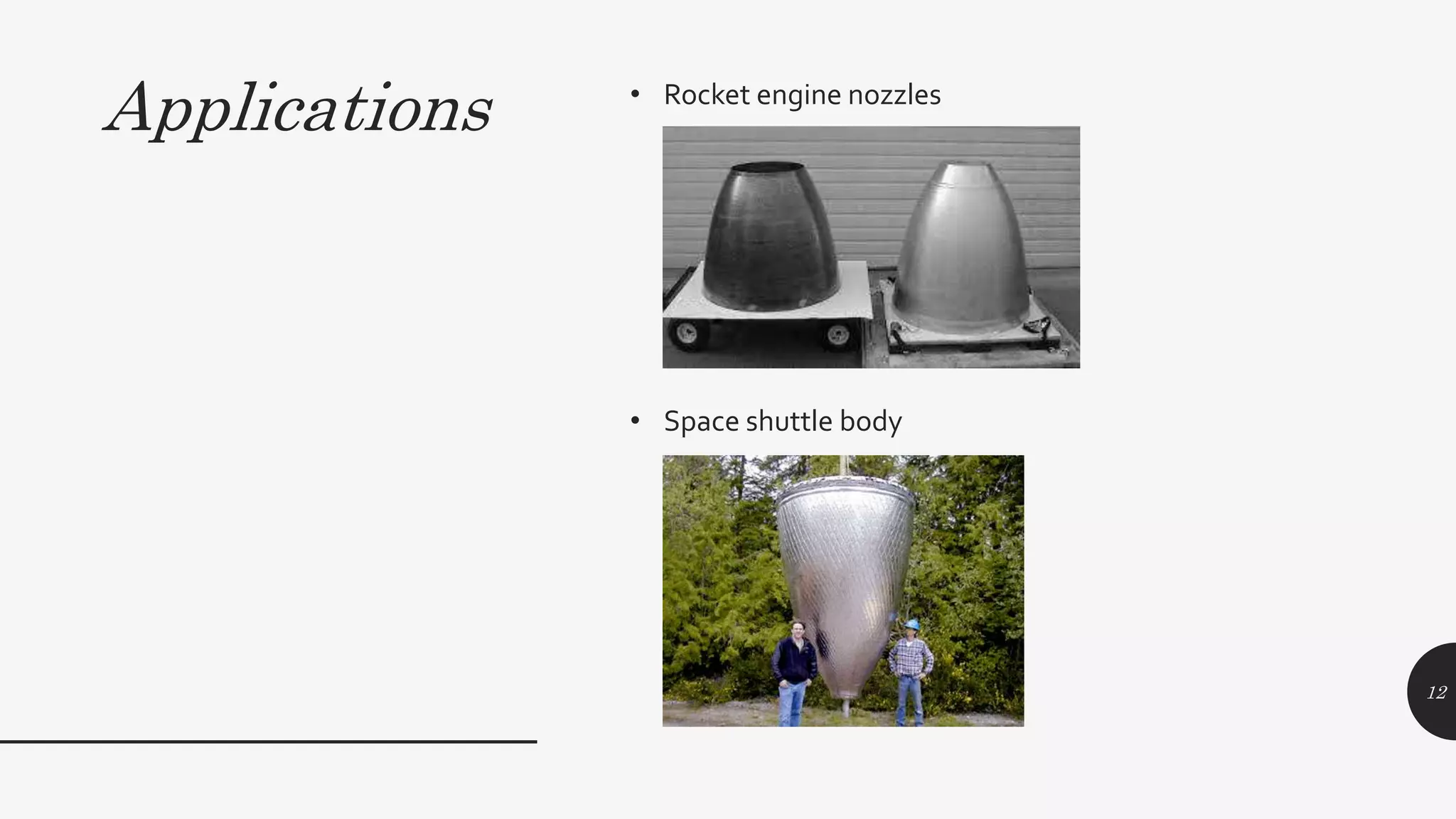
This document discusses explosive forming, a metal forming process that uses explosives. There are two main types - confined and unconfined. Unconfined uses a standoff distance between the explosive and workpiece, while confined places the explosive in direct contact with the workpiece. The process works by placing the metal workpiece on a die, then igniting the nearby explosive. The explosive's shockwave deforms the metal into the die's shape. Research showed deformation of an aluminum plate reached 39mm after 400 microseconds, with peak velocities of 280m/s near the center. Explosive forming can form large, complex parts but requires safety precautions due to using explosives.