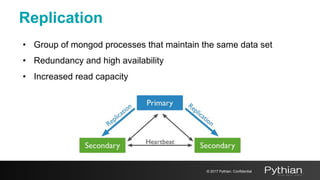
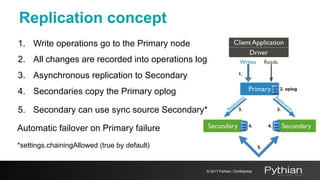
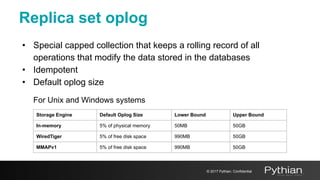
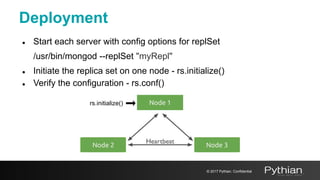
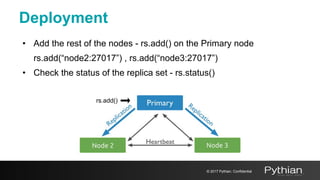
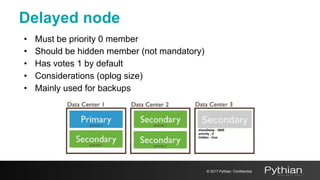
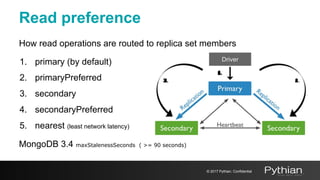
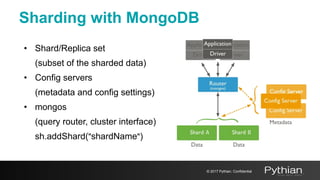
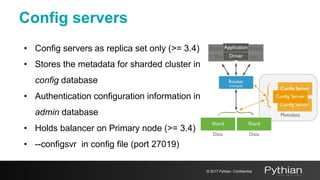
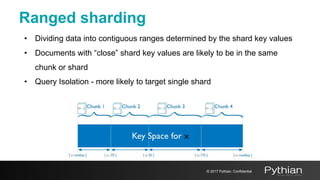
This document discusses replication and sharding in MongoDB, covering concepts like replica sets, cluster components, and the differences between vertical and horizontal scaling. Key topics include the configuration and operational details of replica sets, sharding methods, shard keys, their limitations, and considerations for deployment. It emphasizes the importance of choosing appropriate shard keys for even data distribution and outlines the model for scaling databases using MongoDB.