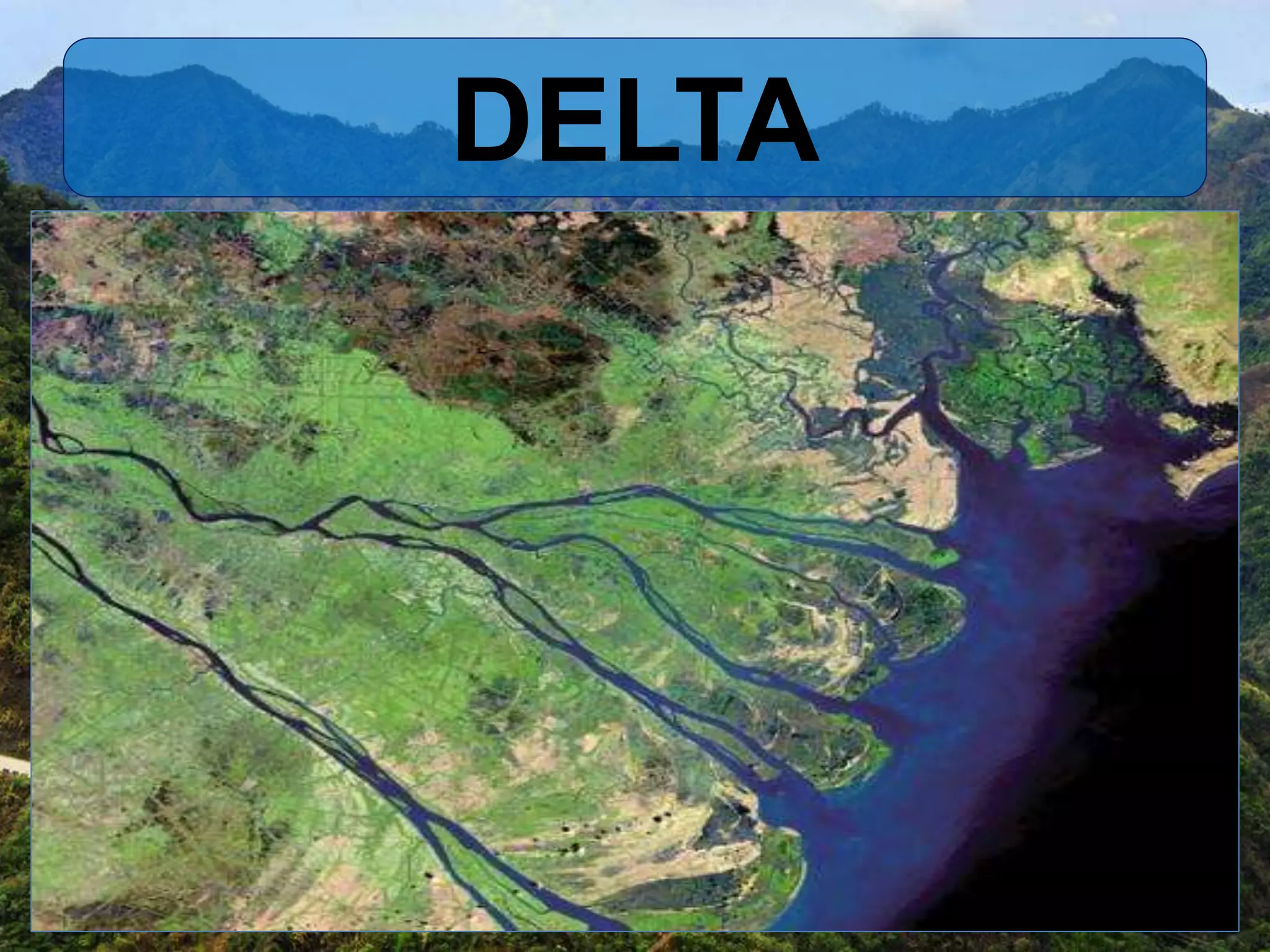
This document defines and provides examples of different types of landforms formed by various geological processes. It discusses aeolian forms like dunes, loess, and mushroom rocks shaped by wind; erosional landforms such as mesas, buttes, and canyons formed by erosion; mountainous landforms including volcanoes, hills, and valleys; glacial landforms resulting from glacier activity; fluvial landforms near rivers like deltas, meanders and coastal landforms such as sea cliffs, peninsulas and plains.