This document provides an overview of key concepts related to international trade, including:
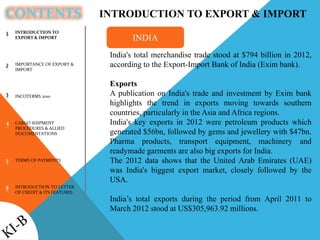
- Export and import definitions and India's trade statistics. India's top exports are petroleum products and gems/jewelry, while top imports are crude petroleum and gold.
- INCOTERMS 2010 - International commercial terms published by the ICC to clarify responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. Key terms covered include EXW, FCA, CPT, FOB, CIF, DAP, and DDP.
- Importance of international trade - Benefits include competitive advantage, economies of scale, access to new markets, insulation from domestic seasonal fluctuations, and improved returns on investment through diversification.