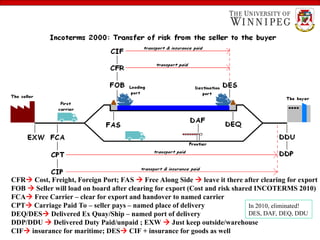
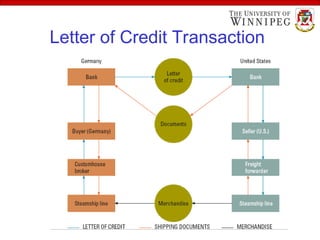
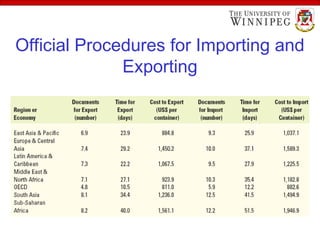
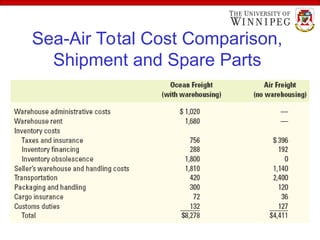
The document outlines the essential aspects of export and import practices, including reasons for exporting, sources of export financing, and necessary export documentation. It explains the roles of various institutions like the International Trade Administration and the Small Business Administration in providing support and counseling for exporters. Furthermore, it details payment procedures, shipping documents, and the use of foreign freight forwarders to facilitate international trade.