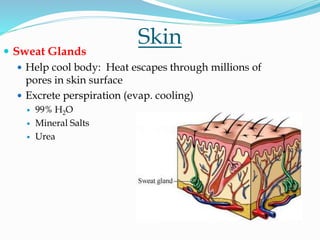
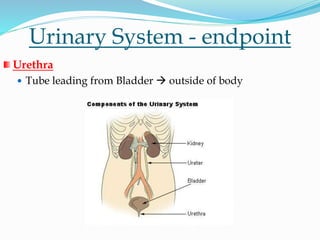
The document discusses the excretory organs and system in humans, highlighting the skin, lungs, and kidneys' roles in excreting waste such as carbon dioxide, water, and urea. While the kidneys are the primary organs responsible for waste removal through urine, other organs like the skin and lungs also assist in excretion. Failures in excretion can lead to serious health issues, including infections and kidney disease.