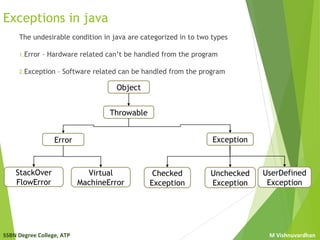
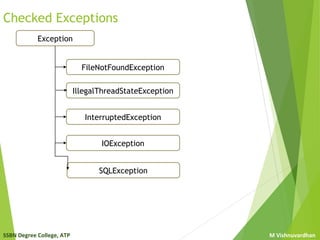
The document discusses exception handling in Java. It describes different types of errors like compile-time errors and run-time errors. It explains checked and unchecked exceptions in Java. Checked exceptions must be handled, while unchecked exceptions may or may not be handled. Finally, it covers how to create user-defined exceptions in Java by extending the Exception class and throwing exceptions using the throw keyword.








![SSBN Degree College, ATP M Vishnuvardhan
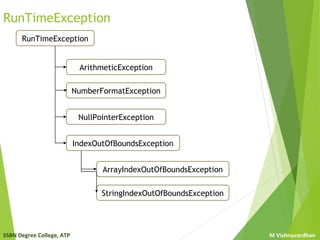
Runtime Exceptions
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:
Occurs when an array is referred beyond the boundaries
e.g: int a[]={10,20,30,40,50};
System.out.println(a[20]); //referring the array beyond boundaries
ArrayStoreException:
Occurs when an attempt is made to store wrong type of object
is stored in array of objects.
Eg: String s[]=new String [5];
s[0]=new Integer(75); // storing integer object in String array
StringIndexOutOfBoundsException:
Occurs when a String is referred beyond the string boundaries.
e.g. String s=“Java Program”;
char ch =s.charAt(23); // referring String beyond the
boundaries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-181106053250/85/Exception-handling-12-320.jpg)





![SSBN Degree College, ATP M Vishnuvardhan
throws keyword
throws:- It is generally used to postpone the exception handling.
Generally used at the method declaration to list the exception
which occur in the method. Any one who uses the method must
and should handle the exception listed
E.g.: public void test () throws IOException
{
======
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
test()
----
}
catch(IOException e)
{
---
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/exceptionhandling-181106053250/85/Exception-handling-18-320.jpg)
