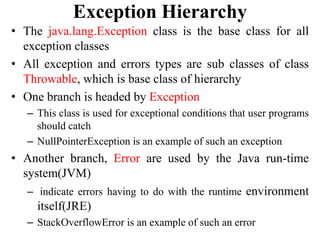
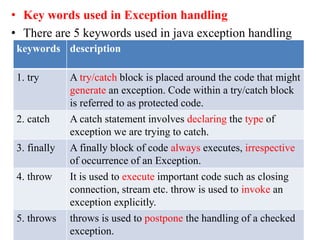
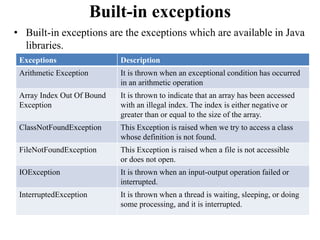
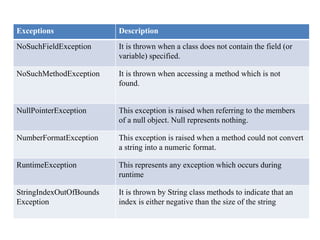
The document discusses exception handling and multithreading in Java. It begins by defining exceptions as unexpected events that occur during program execution and disrupt normal flow. There are three categories of exceptions: checked exceptions which occur at compile time; unchecked exceptions which occur at runtime; and errors which are problems beyond a program's control. The document then covers how to handle exceptions using try, catch, finally and throw keywords. It provides examples of built-in and user-defined exceptions. The document concludes by explaining Java's multithreading model, how to create and manage threads, set thread priorities and states, and techniques for inter-thread communication.







![public class JavaExceptionExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
//code that may raise exception
int data=100/0;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{System.out.println(e);
}
//rest code of the program
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}
}
• Output:
Exception in thread main java.lang.ArithmeticException:/ by zero
rest of the code...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-10-320.jpg)
![//ArrayindexoutofBounds Exception
public class ExcepTest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{ int a[] = new int[2];
try
{ System.out.println("Access element three :" +a[3]);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{ System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}
finally
{
a[0] = 6;
System.out.println("First element value: " + a[0]);
System.out.println("The finally statement is
executed");
} } }
Output
Exception thrown
:java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsE
ception:3
First element value: 6
The finally statement is executed
Note : here array size is 2 but we
are trying to access 3rdelement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-11-320.jpg)




![• There are two ways to obtain a Throwable object:
1. using a parameter in a catch clause
2. creating one with the new operator.
Example:
public class TestThrow1{
static void validate(int age){
if(age<18)
throw new ArithmeticException("not valid");
else
System.out.println("welcome to vote");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
validate(13);
System.out.println("rest of the code...");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-16-320.jpg)

![• Program to create user defined exception that test for odd numbers.
import java.util.Scanner;
class OddNumberException extends Exception
{
OddNumberException() //default constructor
{
super(“Odd number exception”);
}
OddNumberException(String msg) //parameterized constructor
{
super(msg);
}}
public class UserdefinedExceptionDemo{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num;
Scanner Sc = new Scanner(System.in); // create Scanner object to
read input](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-21-320.jpg)














![System.out.println(“Child thread is exiting”);
}}
public class ExtendThread
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
new NewThread(); // create a new thread
try
{
for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
System.out.println(“Main Thread: “ + i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(“Main thread interrupted.”);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-39-320.jpg)
![System.out.println(“Main thread is exiting.”);
}
}
Sample Output:
(output may vary based on processor speed and task load)
Child thread: Thread[Demo Thread,5,main]
Main Thread: 5
Child Thread: 5
Child Thread: 4
Main Thread: 4
Child Thread: 3
Child Thread: 2
Main Thread: 3
Child Thread: 1
Child thread is exiting.
Main Thread: 2
Main Thread: 1
Main thread is exiting.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-40-320.jpg)


![for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
System.out.println(“Child Thread: “ + i);
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(“Child interrupted.”);
}
System.out.println(“Child thread is exiting.”);
}
}
public class ThreadDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
new NewThread(); // create a new thread](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-43-320.jpg)
![try
{
for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--)
{
System.out.println(“Main Thread: “ + i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(“Main thread
interrupted.”);
}
System.out.println(“Main thread is exiting.”);
}
}
Sample Output:
(output may vary based on processor
speed and task load)
Child thread: Thread[Demo
Thread,5,main]
Main Thread: 5
Child Thread: 5
Child Thread: 4
Main Thread: 4
Child Thread: 3
Child Thread: 2
Main Thread: 3
Child Thread: 1
Child thread is exiting.
Main Thread: 2
Main Thread: 1
Main thread is exiting.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-44-320.jpg)


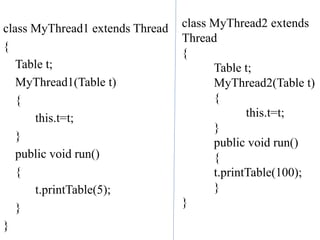
![public class TestSynchronization2{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Table obj = new Table();
//only one object
MyThread1 t1=new MyThread1(obj);
MyThread2 t2=new MyThread2(obj);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
Output:
5
10
15
20
25
100
200
300
400
500](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-49-320.jpg)

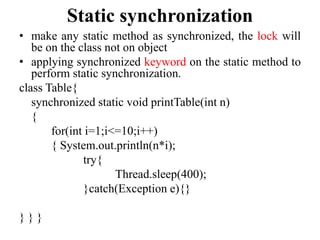

![public class TestSynchronization4
{
public static void main(String t[])
{
MyThread1 t1=new MyThread1();
MyThread2 t2=new MyThread2();
MyThread3 t3=new MyThread3();
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
Output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
100
200
300
400 500 600 700 800 900](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-54-320.jpg)




![synchronized void deposit(int amount)
{
System.out.println("going to deposit...");
this.amount+=amount;
System.out.println("deposit completed... ");
notify();
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String args[])
{
final Customer c=new Customer();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-59-320.jpg)


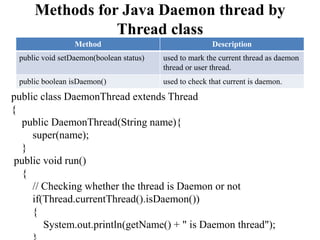
![else
{
System.out.println(getName() + " is User thread");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
DaemonThread t1 = new DaemonThread("t1");
DaemonThread t2 = new DaemonThread("t2");
DaemonThread t3 = new DaemonThread("t3");
// Setting user thread t1 to Daemon
t1.setDaemon(true);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-63-320.jpg)



![public class ThreadGroup_example implements Runnable{
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadGroup_example runnable = new
ThreadGroup_example();
ThreadGroup tg1 = new ThreadGroup(“Parent ThreadGroup”);
Thread t1 = new Thread(tg1, runnable,”one”);
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(tg1, runnable,”two”);
t2.start();
Thread t3 = new Thread(tg1, runnable,”three”);
t3.start();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-67-320.jpg)
![System.out.println(“Thread Group Name: “+tg1.getName());
tg1.list();
}
}
Sample Output:
one
two
three
Thread Group Name: Parent ThreadGroup
java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=Parent ThreadGroup,maxpri=10]
Thread [one,5,Parent ThreadGroup]
Thread [two,5,Parent ThreadGroup]
Thread [three,5,Parent ThreadGroup](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-68-320.jpg)

![catch (InterruptedException ex)
{
System.out.println(“Exception encounterted”);
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadGroup_example
{
public static void main(String arg[])
{
// creating the thread group
ThreadGroup gfg = new ThreadGroup(“parent thread group”);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiii2021r-230807172100-d9b849ee/85/UNIT-III-2021R-pptx-70-320.jpg)

