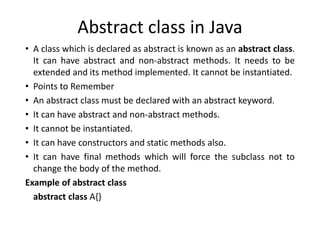
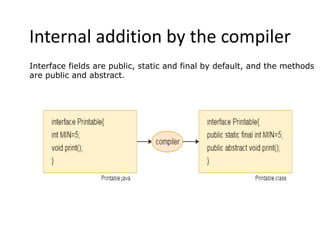
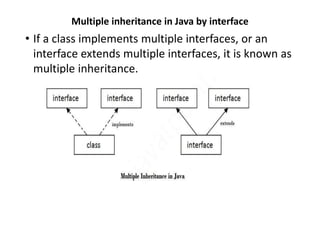
Abstract classes in Java can have both abstract and non-abstract methods. They cannot be instantiated and must be extended. Abstract methods do not have a method body. Interfaces in Java provide full abstraction and contain only abstract method declarations. Classes implement interfaces to inherit their methods. Both abstract classes and interfaces allow for abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java.



![Example of Abstract class that has an abstract method
abstract class Bike
{
abstract void run();
}
class Honda extends Bike
{
void run()
{
System.out.println("running safely
");
}
public static void main(String ar
gs[])
{
Bike obj = new Honda();
obj.run();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abstractclassesandinterfaces-231102170954-caa0ba11/85/ABSTRACT-CLASSES-AND-INTERFACES-ppt-5-320.jpg)
![Understanding the real scenario of Abstract class
abstract class Shape
{
abstract void draw();
}
class Rectangle extends Shape
{
void draw()
{
System.out.println("drawing rectang
le");
}
}
class Circle1 extends Shape
{
void draw()
{
System.out.println("drawing circle")
;
}
}
class TestAbstraction1
{
public static void
main(String args[])
{
Shape s=new Circl
e1();
s.draw();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abstractclassesandinterfaces-231102170954-caa0ba11/85/ABSTRACT-CLASSES-AND-INTERFACES-ppt-6-320.jpg)



![Example
interface printable{
void print();
}
class A6 implements printable{
public void print(){System.out.println("Hello");}
public static void main(String args[]){
A6 obj = new A6();
obj.print();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abstractclassesandinterfaces-231102170954-caa0ba11/85/ABSTRACT-CLASSES-AND-INTERFACES-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![//Interface declaration: by first user
interface Drawable
{
void draw();
}
//Implementation: by second user
class Rectangle implements Drawab
le
{
public void draw()
{
System.out.println("drawing r
ectangle");
}
}
class Circle implements Drawable
{
public void draw()
{
System.out.println("drawing c
ircle");
}
}
//Using interface: by third user
class TestInterface1
{
public static void main(String a
rgs[])
{
Drawable d=new Circle()
;
d.draw();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abstractclassesandinterfaces-231102170954-caa0ba11/85/ABSTRACT-CLASSES-AND-INTERFACES-ppt-12-320.jpg)
![Example
interface Printable
{
void print();
}
interface Showable
{
void show();
}
class A7 implements Printable,Showable
{
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public void show()
{
System.out.println("Welcome");
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
A7 obj = new A7();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abstractclassesandinterfaces-231102170954-caa0ba11/85/ABSTRACT-CLASSES-AND-INTERFACES-ppt-14-320.jpg)