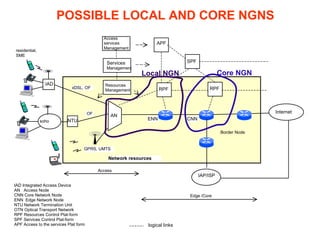
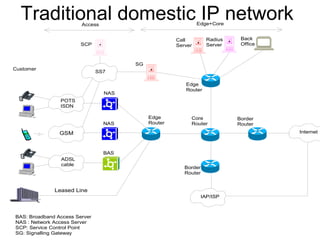
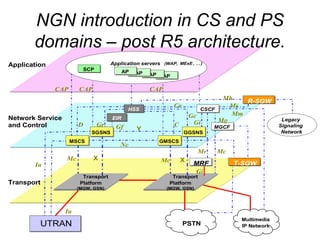
The document discusses the evolution of networks towards Next Generation Networks (NGNs) and describes some of the key components of NGN architectures including IP services, control plane architectures, VoIP, mobility support, QoS, IPv6 migration, and potential local and core network topologies. Reference network architectures are presented for traditional IP networks and the introduction of NGN services in circuit-switched and packet-switched domains.