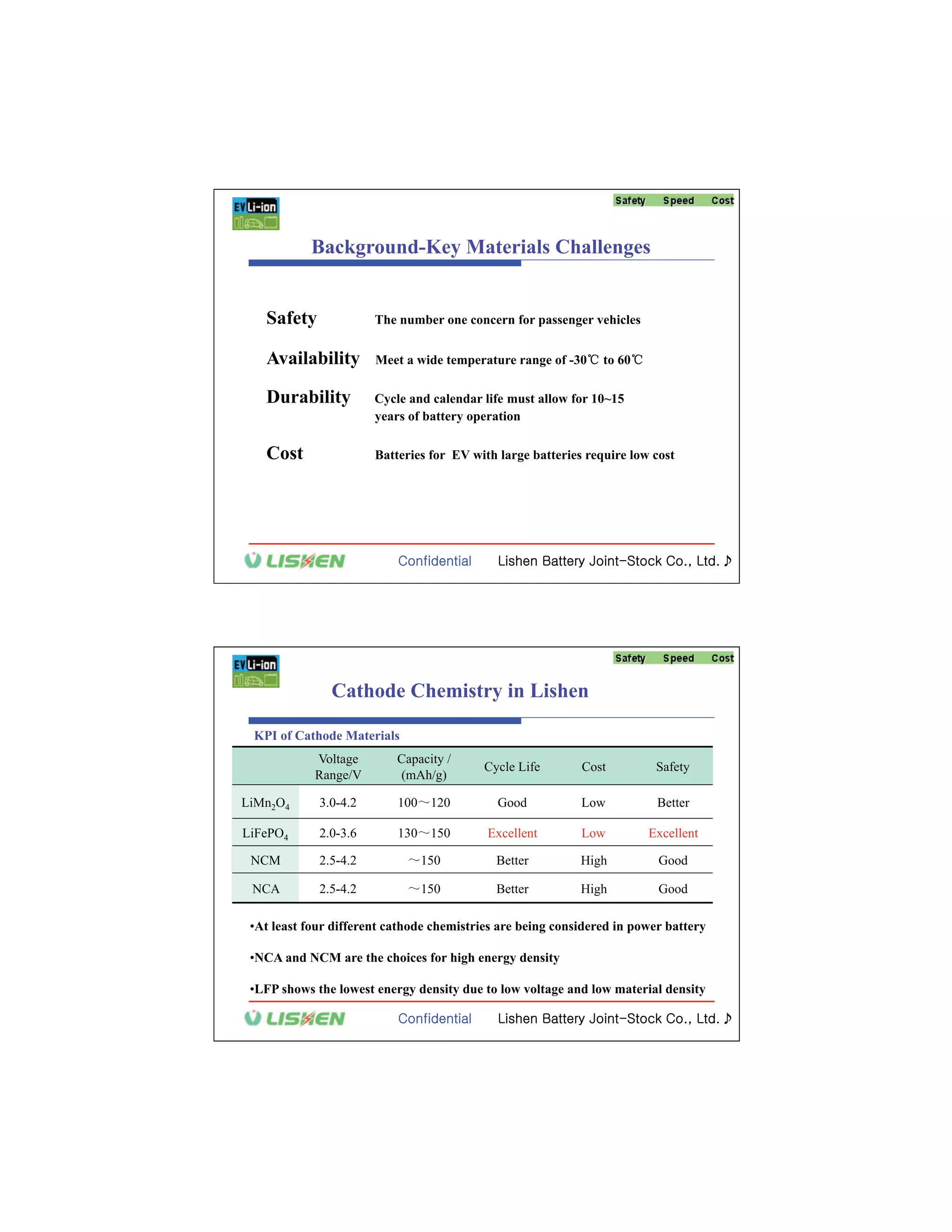
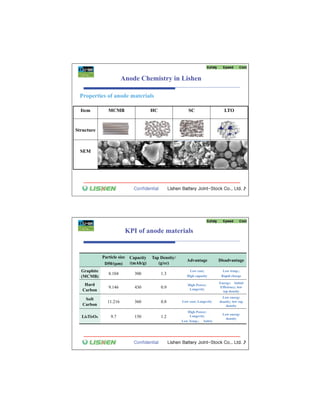
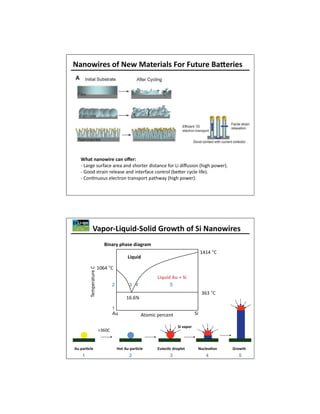
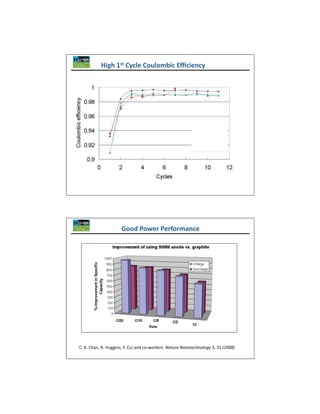
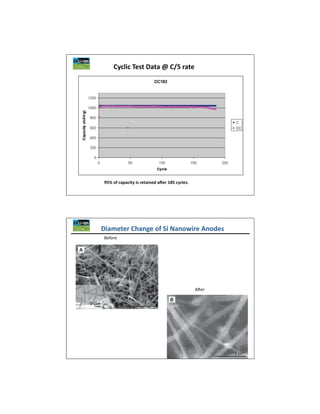
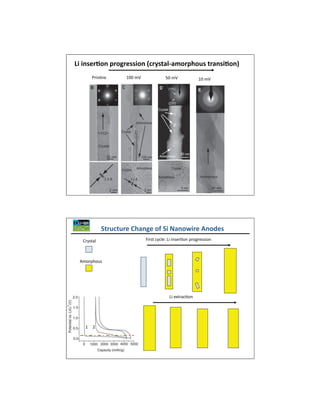
The document discusses key materials challenges for electric vehicle batteries, including safety, availability over a wide temperature range, durability for 10-15 years of operation, and cost. It examines several cathode chemistries and their properties, finding that LiFePO4 provides the best safety properties while NCA and NCM offer higher energy density. The document also analyzes anode materials, concluding that while hard carbon has the highest capacity, Li4Ti5O5 may be best for next generation vehicles due to its high rate charging ability especially at low temperatures. Overall, the document determines that LiFePO4 is currently one of the best cathode platforms for electric vehicles, but continued research is needed to improve performance and lower costs.