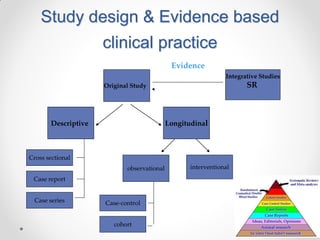
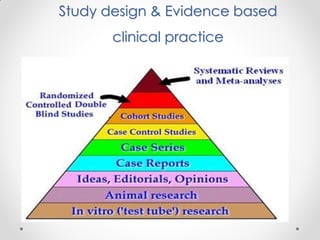
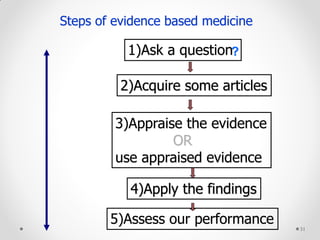
The document discusses evidence-based medicine and its importance. It provides an overview of the 5 steps of evidence-based medicine: 1) Ask a question, 2) Acquire evidence, 3) Appraise the evidence, 4) Apply the findings, 5) Assess performance. Key points include defining patient-oriented versus disease-oriented evidence, the types of study designs and evidence, and how evidence-based medicine has its roots in the scientific methods advocated by early physicians like Ibn Sina.