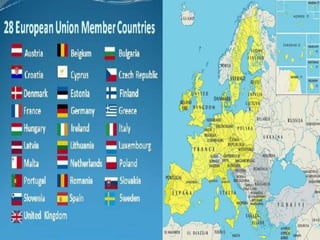
This document provides information about the European Union (EU). It begins with a brief definition of the EU as a political and economic community of 27 member states located primarily in Europe. It was established in 1993 by the Treaty of Maastricht. The EU combined generates an estimated 30% share of the world's nominal gross domestic product. The founding members were France, West Germany, Italy, Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg. The initial goals of the EU were to improve Europe's economy by regulating trade and forming a single market. Current issues facing the EU include enlargement, the Euro currency, multilingualism, transparency, and security. The document also discusses Brexit, the UK's decision to leave the EU, and some