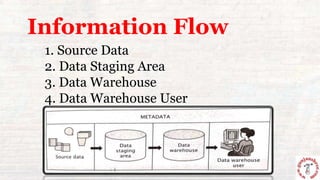
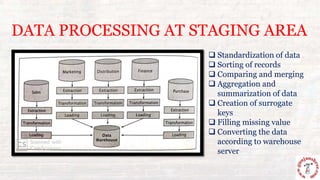
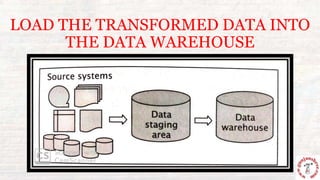
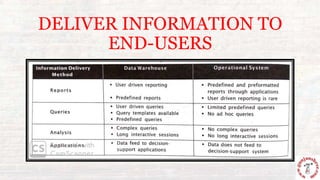
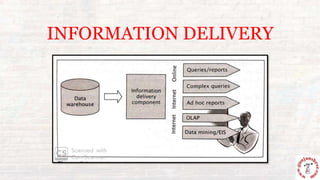
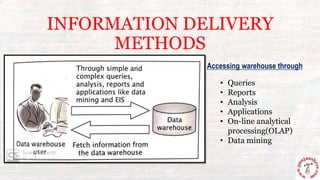
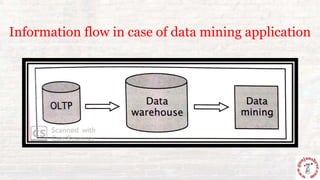
This document outlines the process of information flow from source systems into a data warehouse for end users. It involves extracting data from various source systems, transforming it, and loading it into the data warehouse. The key steps are extracting data from production, internal, external, and archived sources; transforming the data by standardizing, merging, aggregating etc; loading the transformed data into the data warehouse; and delivering the information to end users through queries, reports, applications and other methods. The overall process is called ETL (extract, transform, load).