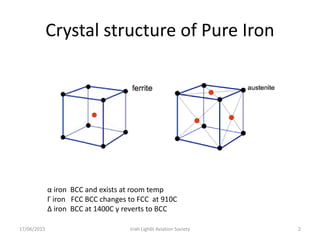
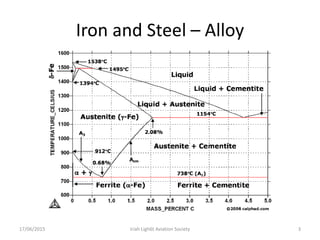
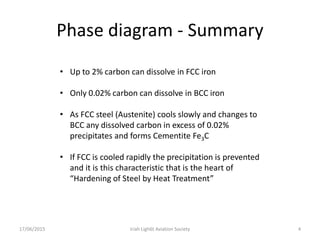
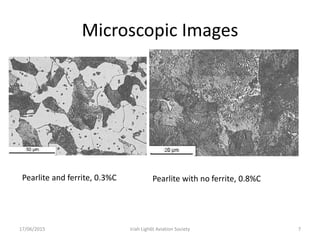
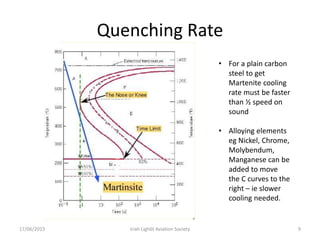
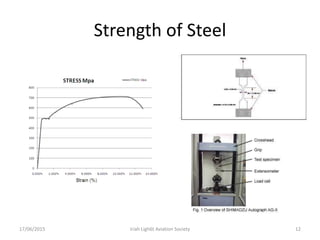
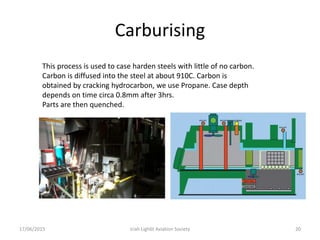
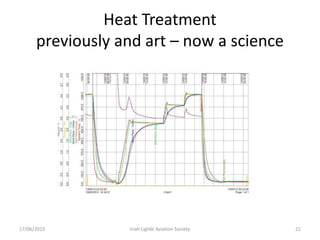
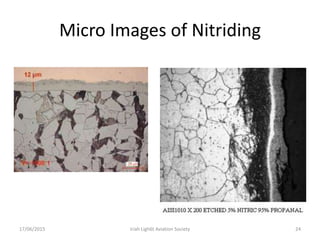
The document discusses various heat treatment processes and their effects on steel properties. It begins by explaining the crystal structures of pure iron and how they change with temperature. It then discusses how carbon content affects the cooling of steel from an austenite state. Rapid cooling forms martensite, while slower cooling forms pearlite or cementite. Various steel grades and their applications in heat treatment are also covered, along with processes like carburizing, nitriding, and precipitation hardening. Microscope images demonstrate the microstructural changes from these treatments.