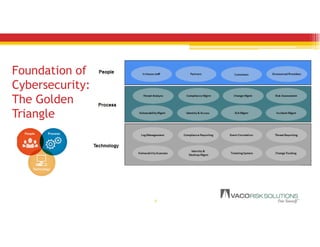
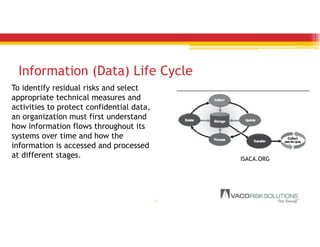
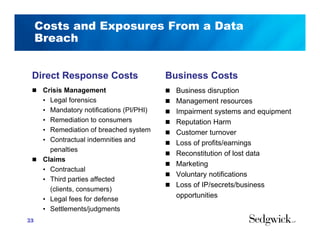
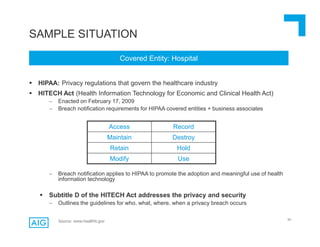
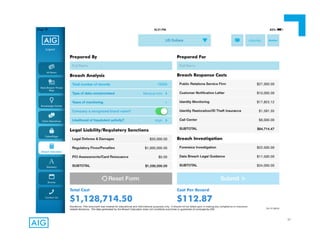
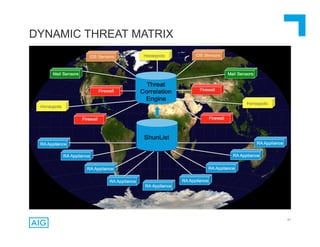
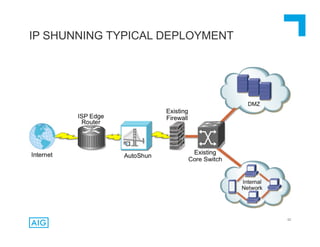
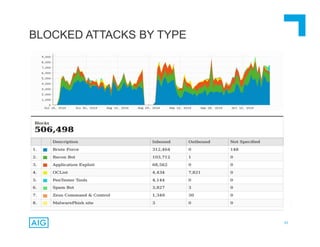
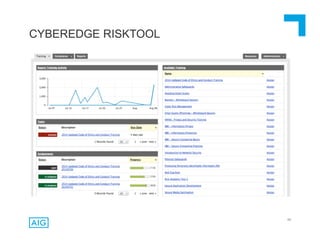
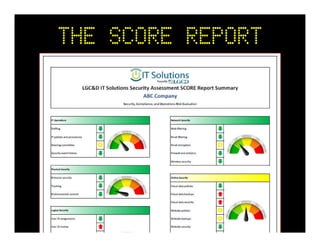
The document discusses emerging trends in information privacy and security, emphasizing the high costs of data breaches, including an average of $6.5 million per incident and various causes such as malicious attacks and human errors. It highlights the increasing importance of cybersecurity practices, integrated processes, and technology to protect sensitive data, along with legal and regulatory frameworks governing data protection. Additionally, it addresses the growing risks companies face due to interconnectivity, data privacy regulations, and the need for proactive risk management strategies.