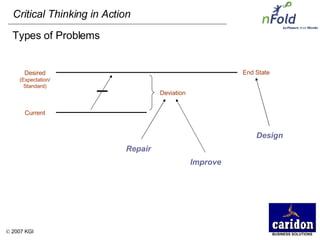
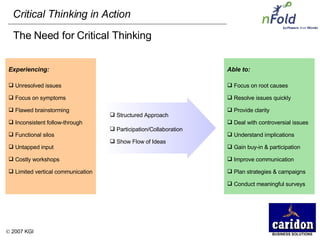
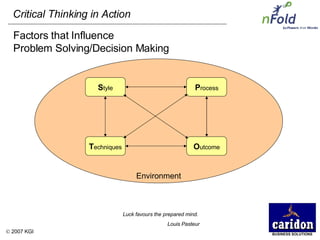
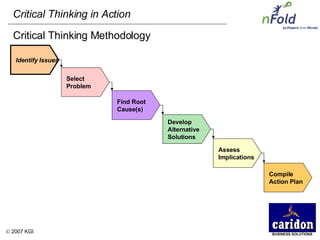
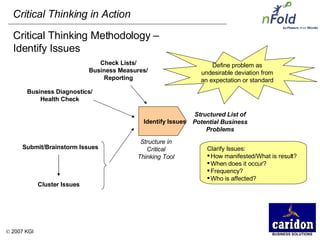
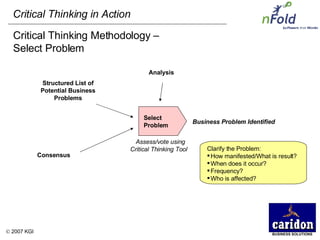
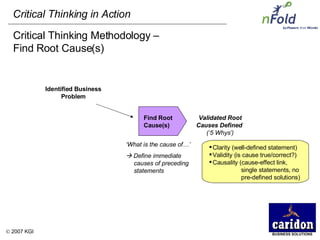
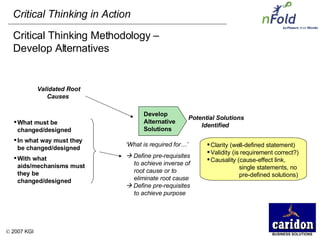
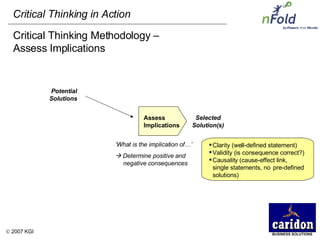
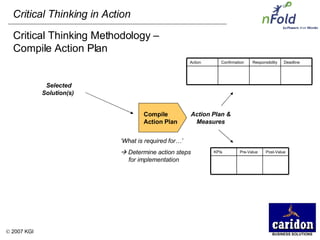
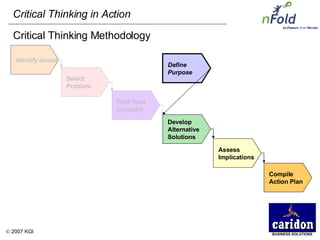
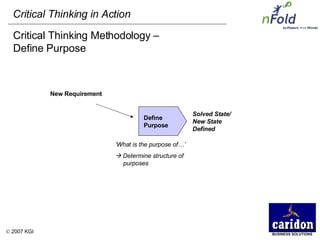
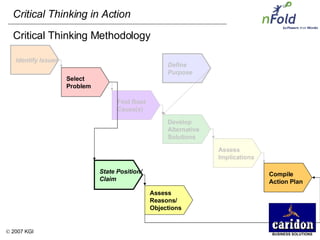
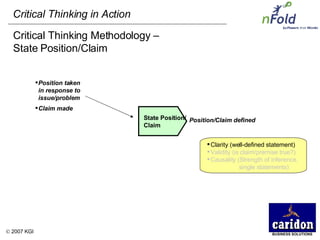
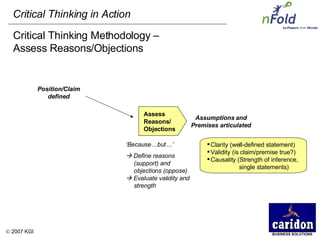
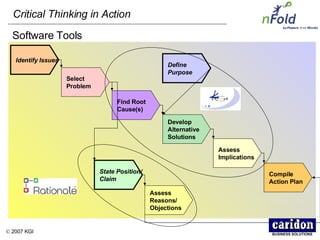
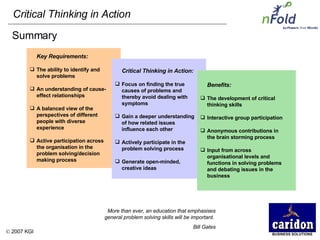
The document discusses the importance and benefits of critical thinking in problem solving. It outlines a methodology for critical thinking that involves identifying issues, selecting problems, finding root causes, developing alternative solutions, assessing implications, compiling action plans, and defining purposes. The methodology aims to focus on root causes rather than symptoms, understand how factors influence each other, and actively involve participation across an organization. Key benefits include developing critical thinking skills, interactive group participation, anonymous contributions to brainstorming, and input from various organizational levels in solving problems and debating issues.



![Escape Analysis Paralysis Critical Thinking in Action 2 day Seminar 28-29 May [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/escape-analysis-paralysis-27623/85/Escape-Analysis-Paralysis-22-320.jpg)