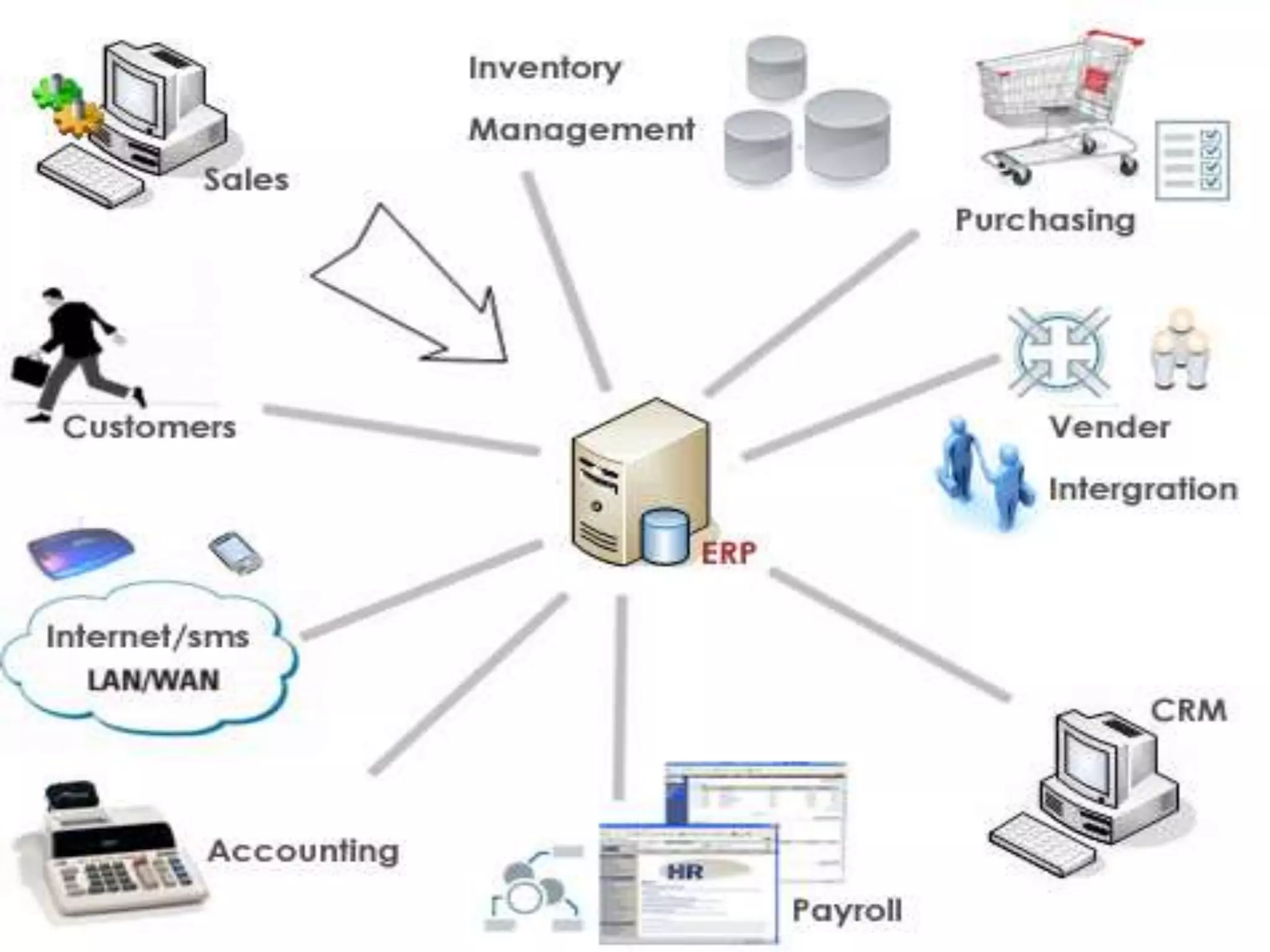
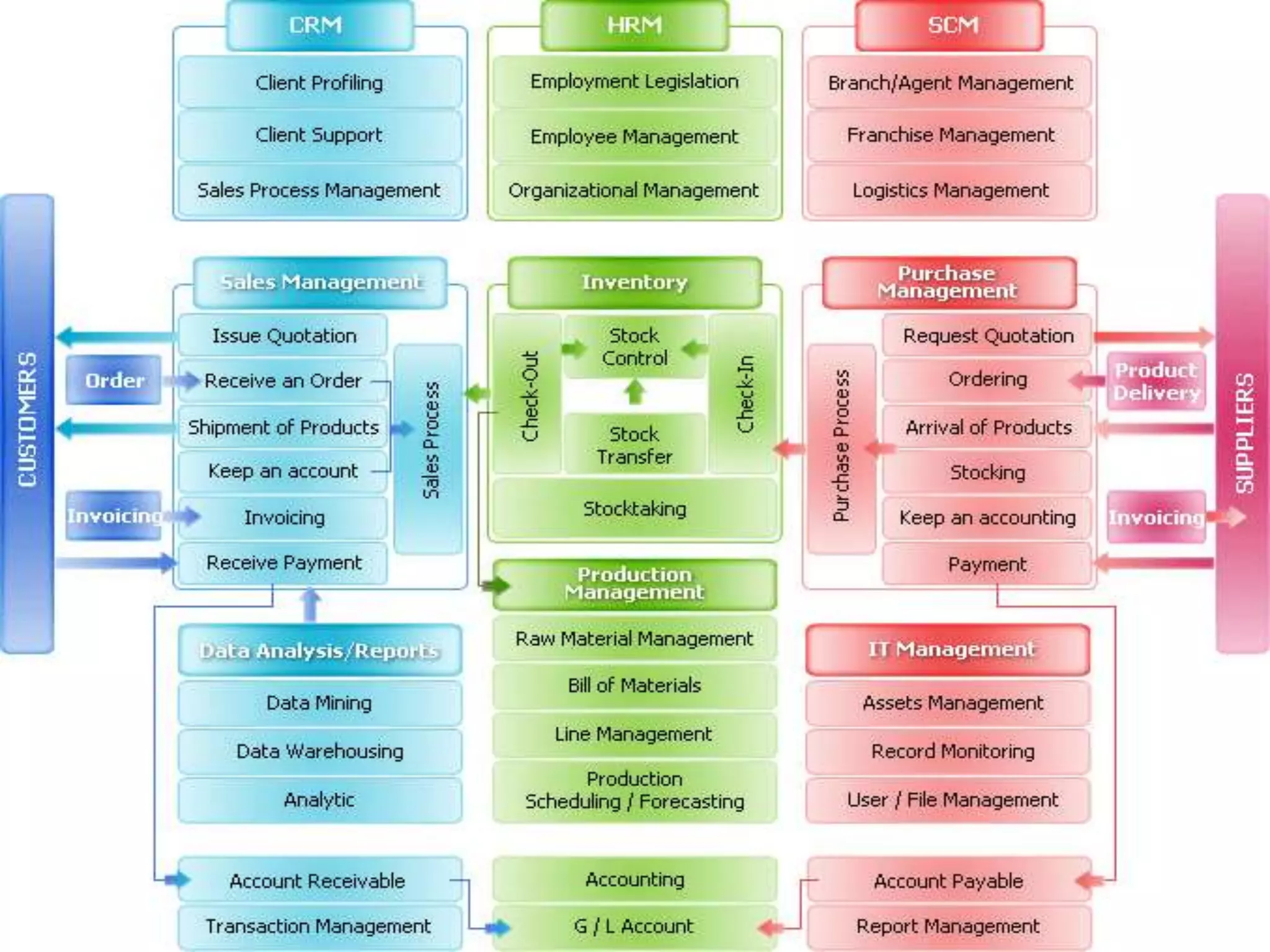
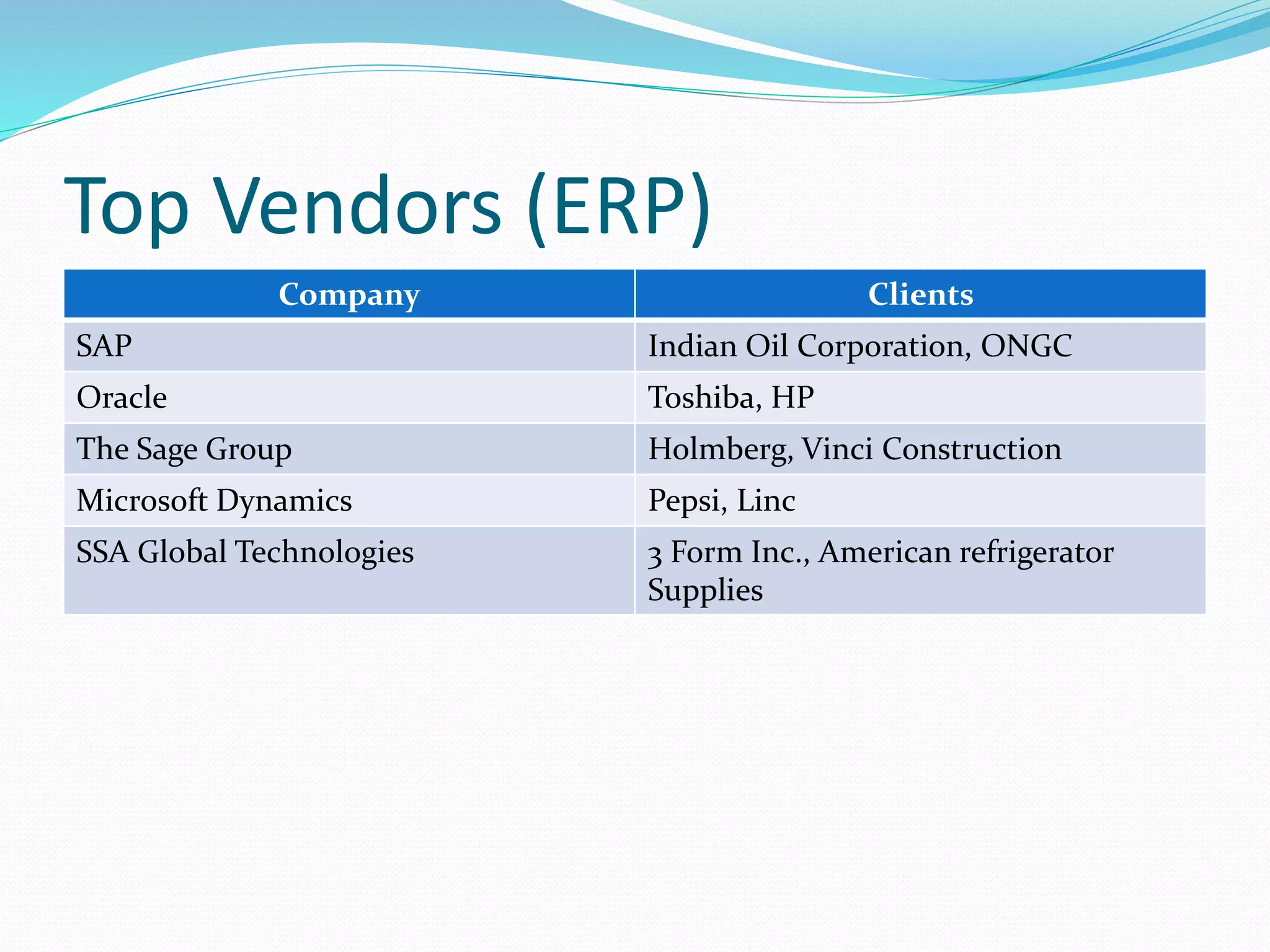
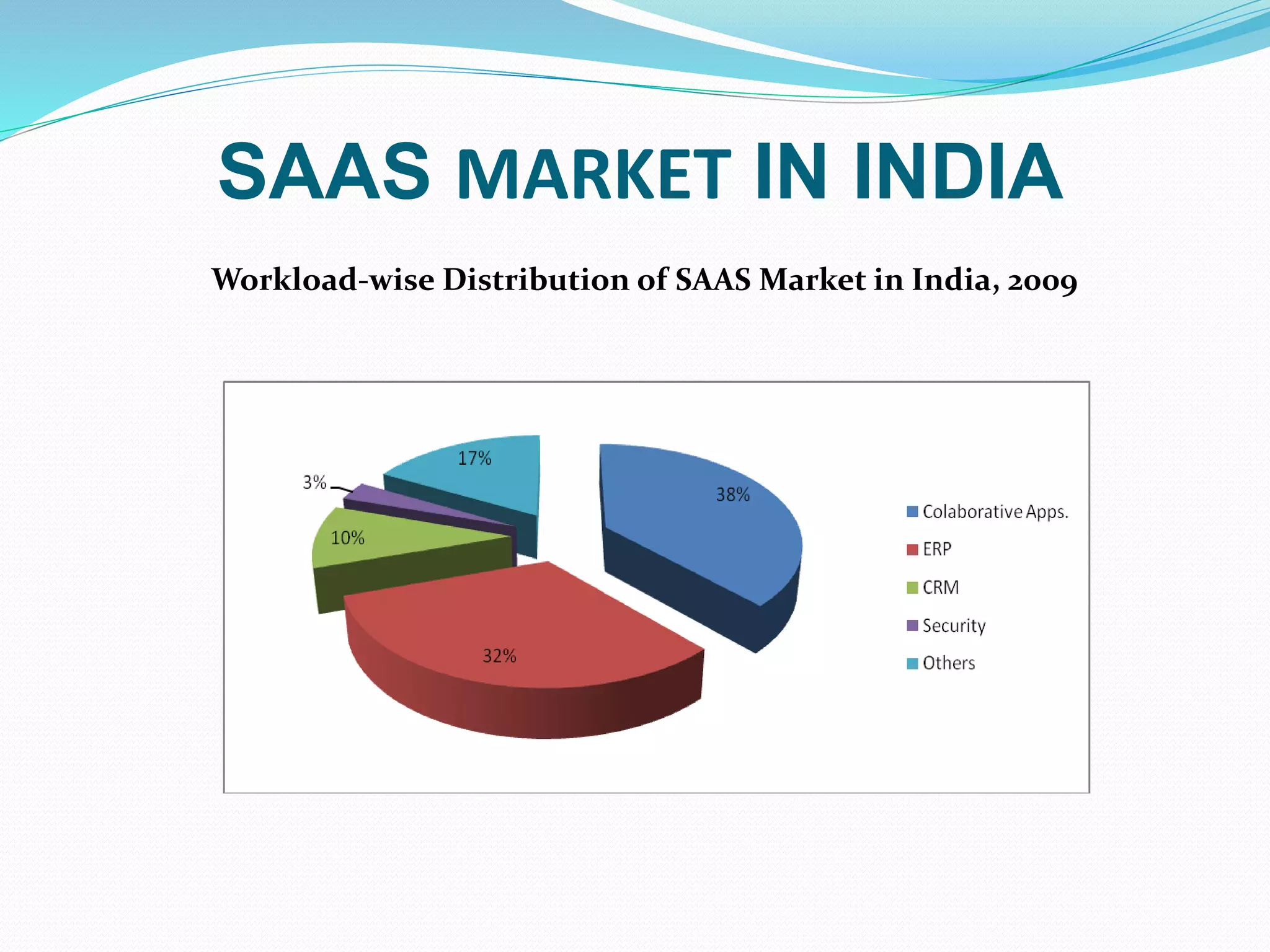
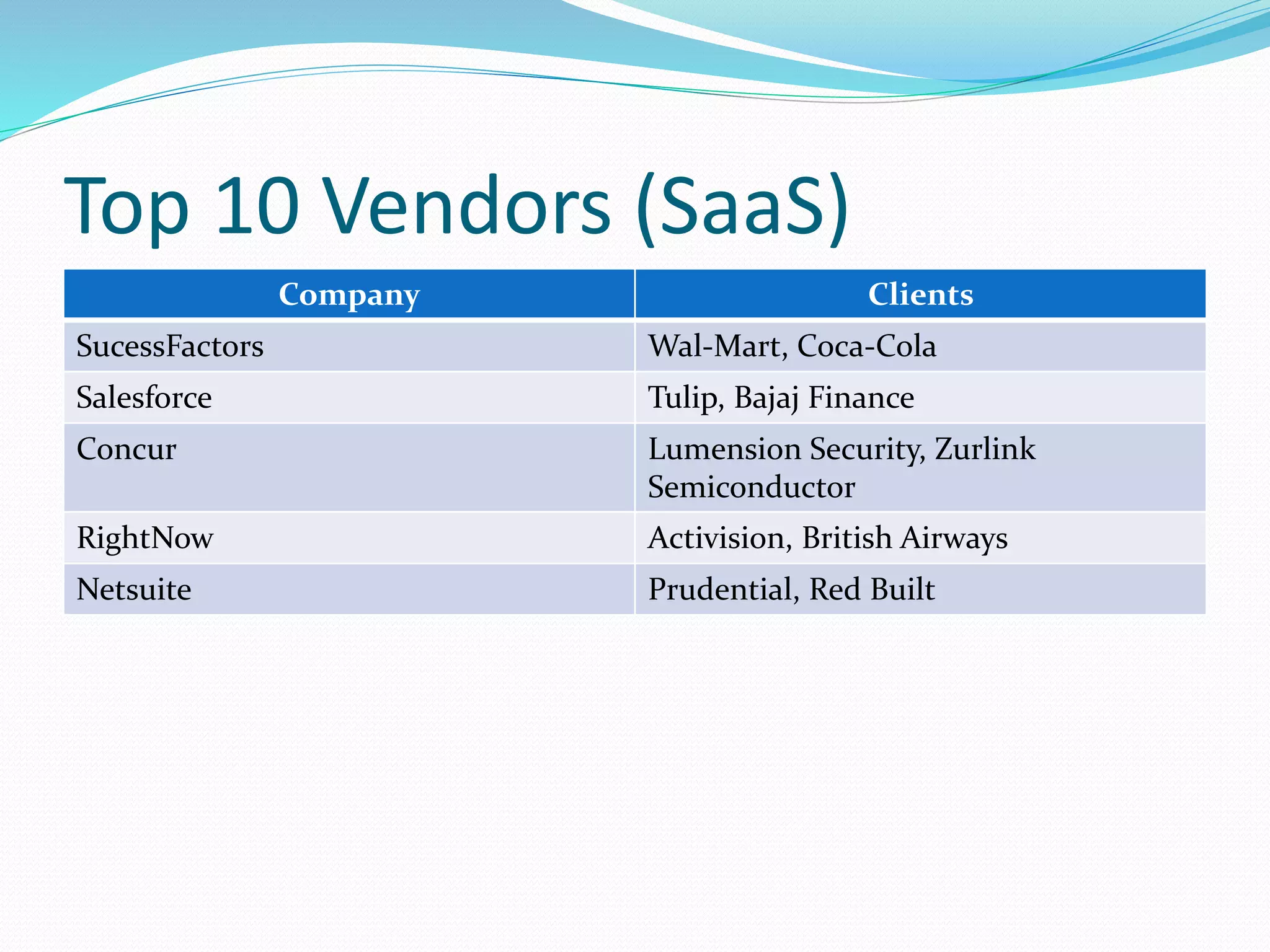
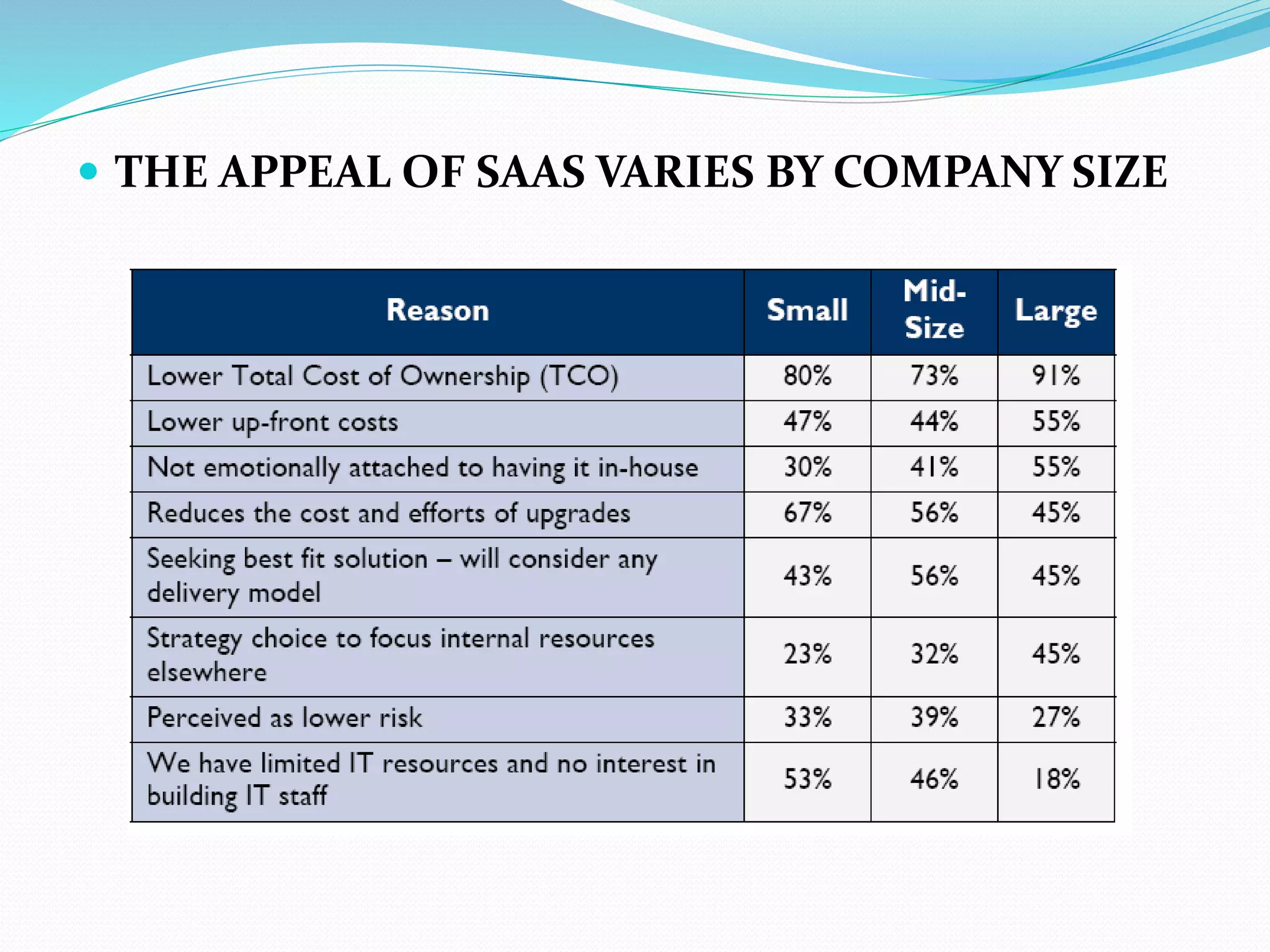
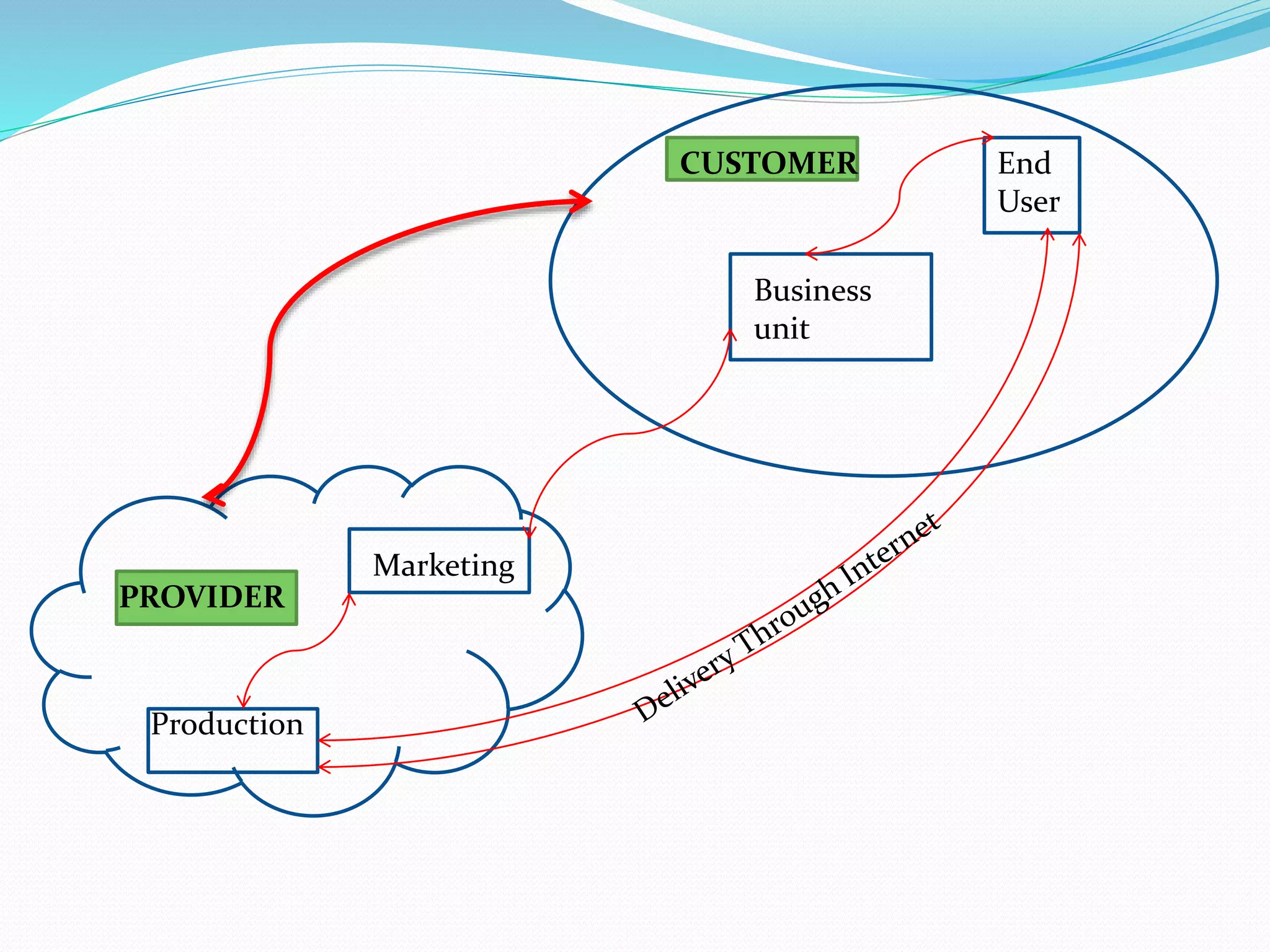
The document discusses Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and the impact of Software as a Service (SaaS) on the ERP industry. It defines ERP as software that integrates business processes across an organization. It notes that SaaS allows ERP software to be rented and hosted remotely. The advantages of SaaS ERP over on-premise ERP are reduced costs and faster implementation. However, SaaS ERP also faces challenges around customization and reliability of internet connections.