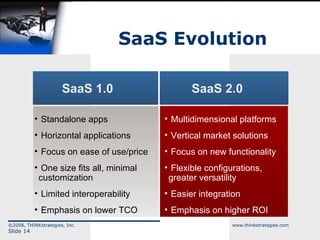
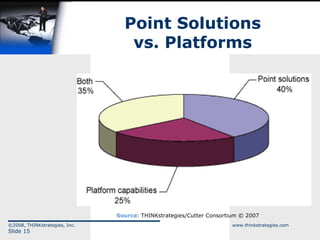
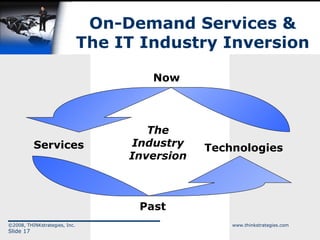
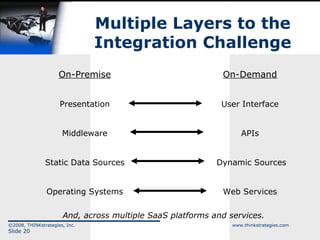
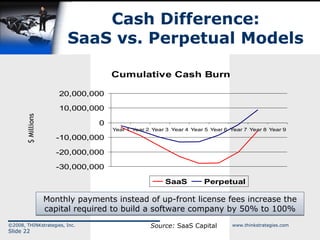
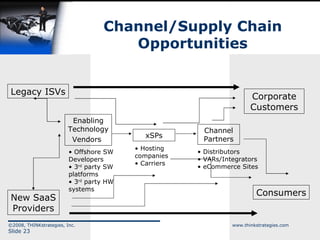
The document discusses the convergence of open source and Software as a Service (SaaS), highlighting the changing business environment and the shift from legacy on-premise applications to more flexible SaaS solutions. It emphasizes the economic pressures driving this transformation, the advantages of SaaS in terms of operational costs and ROI, and the evolution towards enterprise-wide adoption and new functionality. The conclusion underlines the increasing demand for greater functionality, flexibility, and a competitive landscape where SaaS providers must innovate and reduce costs.
![Software 2008: The Convergence of Open Source & SaaS Presented by, Jeff Kaplan Managing Director THINKstrategies [email_address] 781-431-2690](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kaplan-sw-2008-v041108-1228305475194009-8/75/THINKstrategies-Open-Source-Presentation-Software-2008-1-2048.jpg)




















![For More Information… www.SaaS-Showplace.com www.thinkstrategies.com [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kaplan-sw-2008-v041108-1228305475194009-8/85/THINKstrategies-Open-Source-Presentation-Software-2008-32-320.jpg)