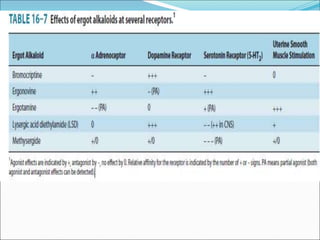
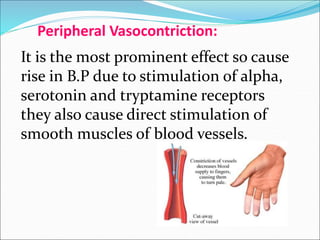
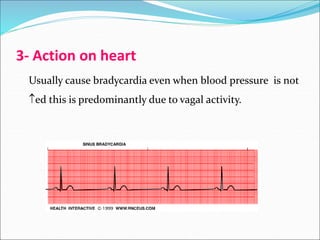
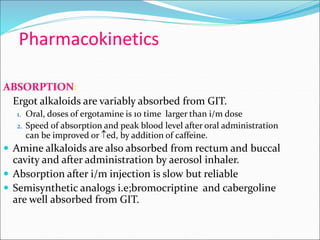
Ergot alkaloids are obtained from a fungus that infects grains like rye and act on receptors like alpha-adrenergic, dopamine, and serotonin receptors. They have various uses including treating migraines, postpartum hemorrhage, and hyperprolactinemia but can cause side effects like vasospasm, gangrene, and hypotension, so they are contraindicated in conditions like hypertension, pregnancy, and peripheral vascular disease. Bromocriptine, a semi-synthetic ergot alkaloid derivative, is useful for treating Parkinson's disease, suppressing lactation, and reducing prolactin levels in hyperpro