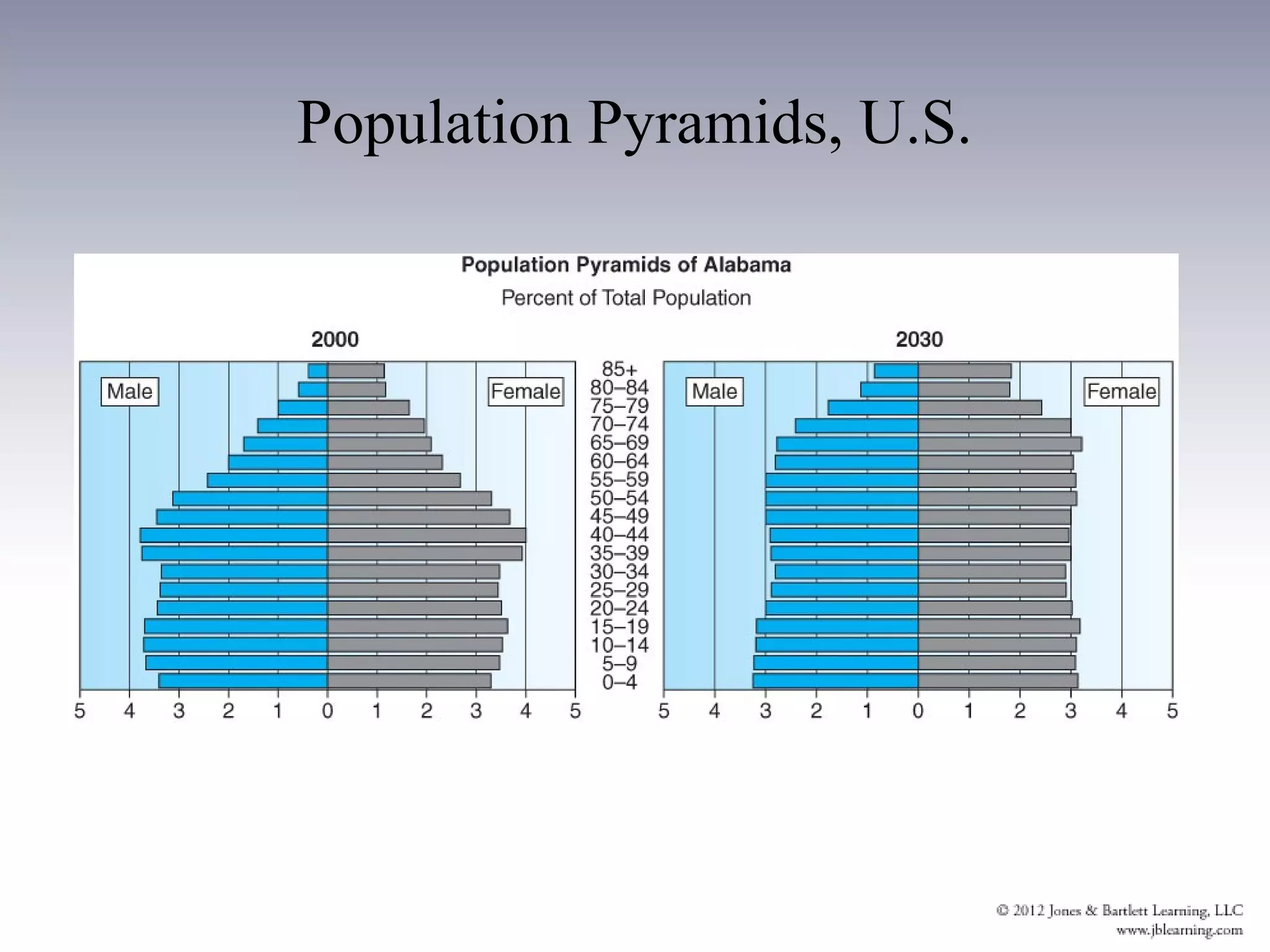
1. The elderly population is growing significantly due to increased life expectancy and the aging of the baby boom generation. Elders now represent 12.8% of the total US population.
2. Elders face challenges related to health, income, housing, transportation and accessing community services. While health has improved, most elders have multiple chronic conditions and disabilities that increase with age.
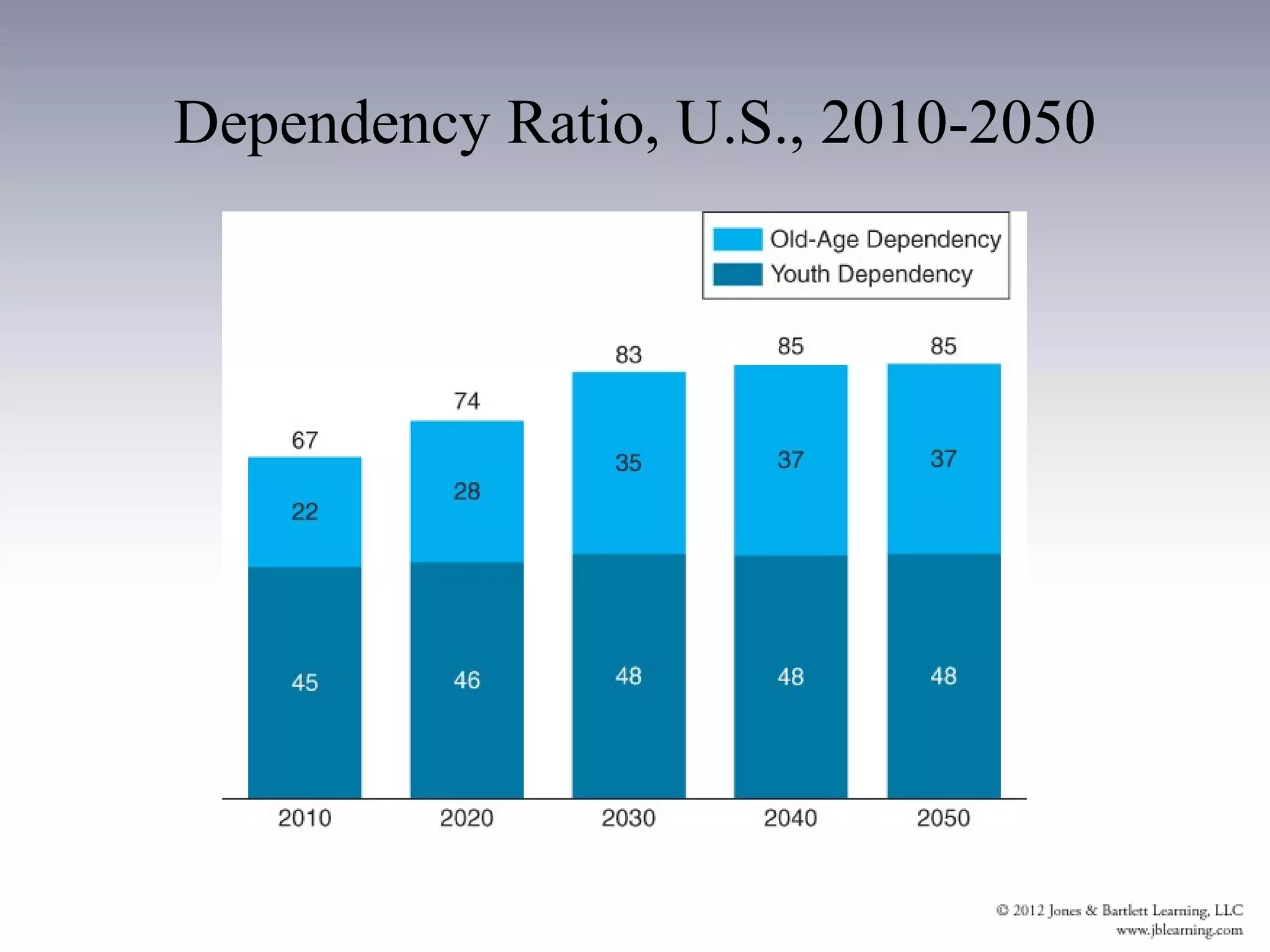
3. The aging of the population will strain health care services and increase the economic burden on working populations. It will also shift the geographic distribution and diversity of the elderly population in the US.