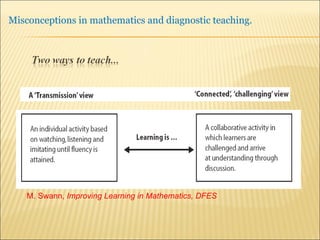
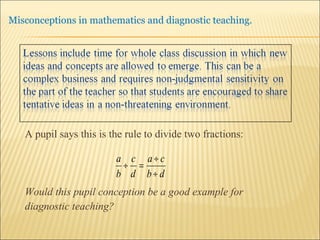
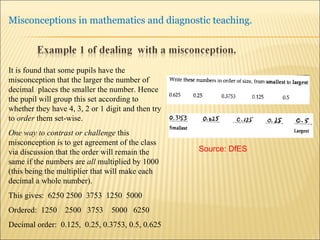
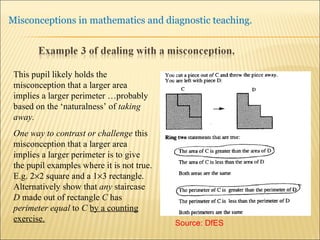
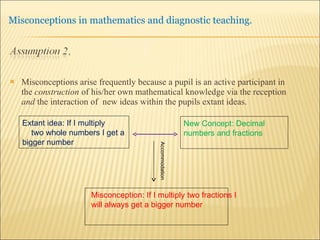
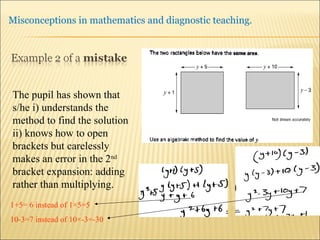
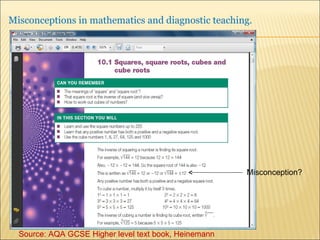
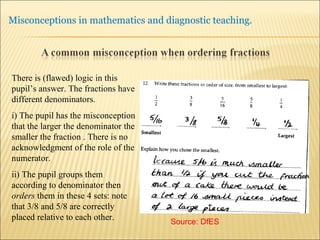
A pupil actively constructs their own mathematical knowledge by interacting new ideas with existing ideas, which can lead to misconceptions. Diagnostic teaching is important as it involves identifying misconceptions, challenging them through discussion to resolve conflicts, and replacing misconceptions with correct understanding. The teacher must understand the source of the misconception to effectively challenge it, and research shows this diagnostic approach promotes better learning compared to simply explaining again.




















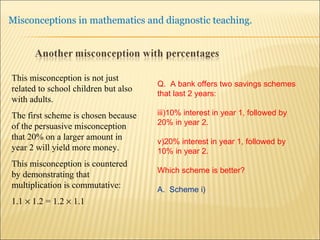



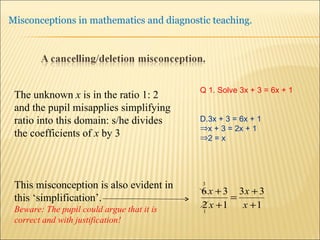

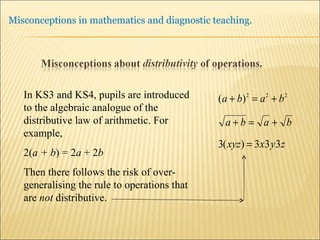


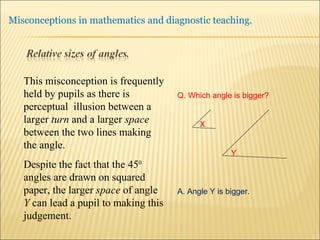


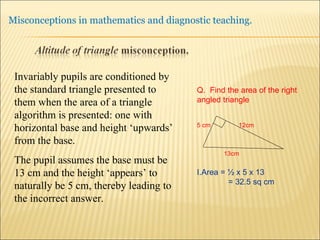
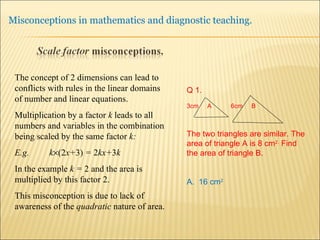


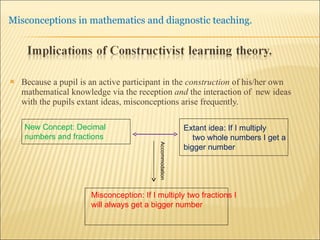
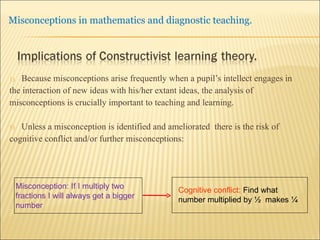
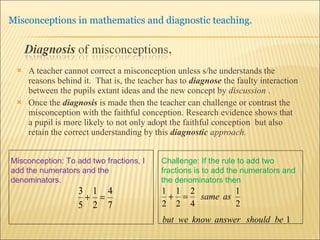
![Source : Swann, M : Gaining diagnostic teaching skills: helping students learn from mistakes and misconceptions , Shell Centre publications “ Traditionally, the teacher with the textbook explains and demonstrates, while the students imitate; if the student makes mistakes the teacher explains again. This procedure is not effective in preventing ... misconceptions or in removing [them]. Diagnostic teaching ..... depends on the student taking much more responsibility for their own understanding , being willing and able to articulate their own lines of thought and to discuss them in the classroom”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/misconppt-101211033818-phpapp01/85/Misconceptions-in-mathematics-44-320.jpg)