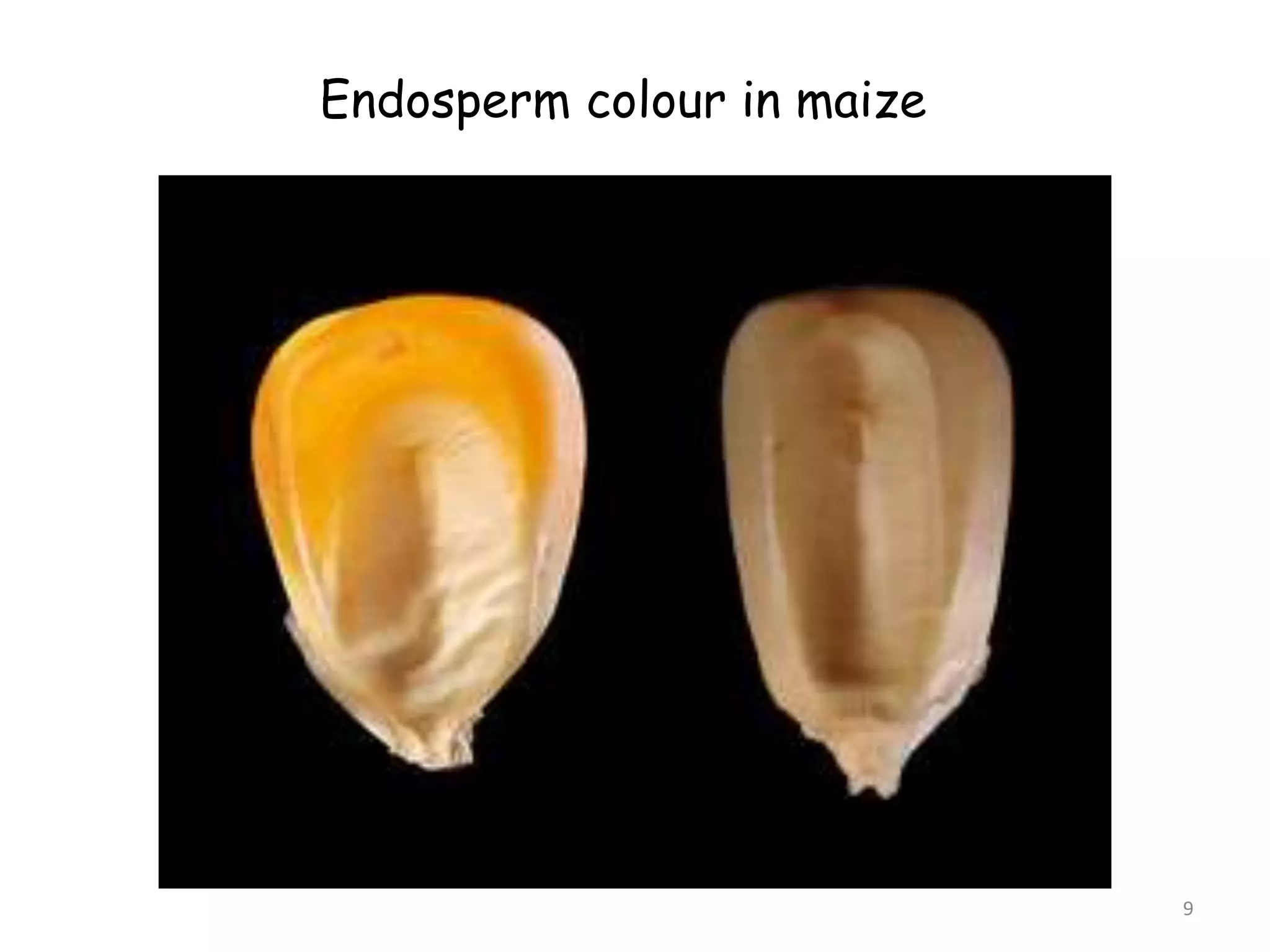
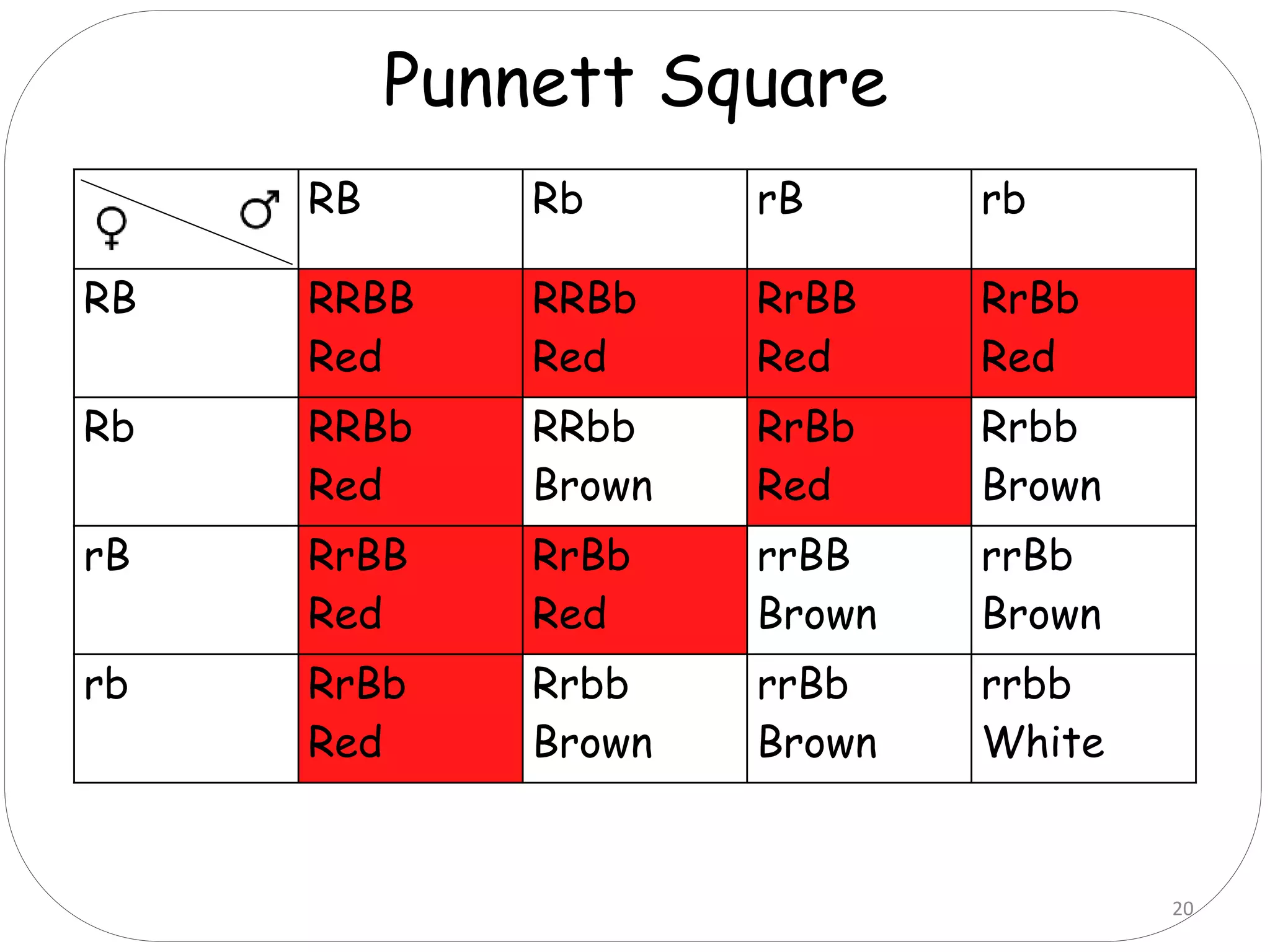
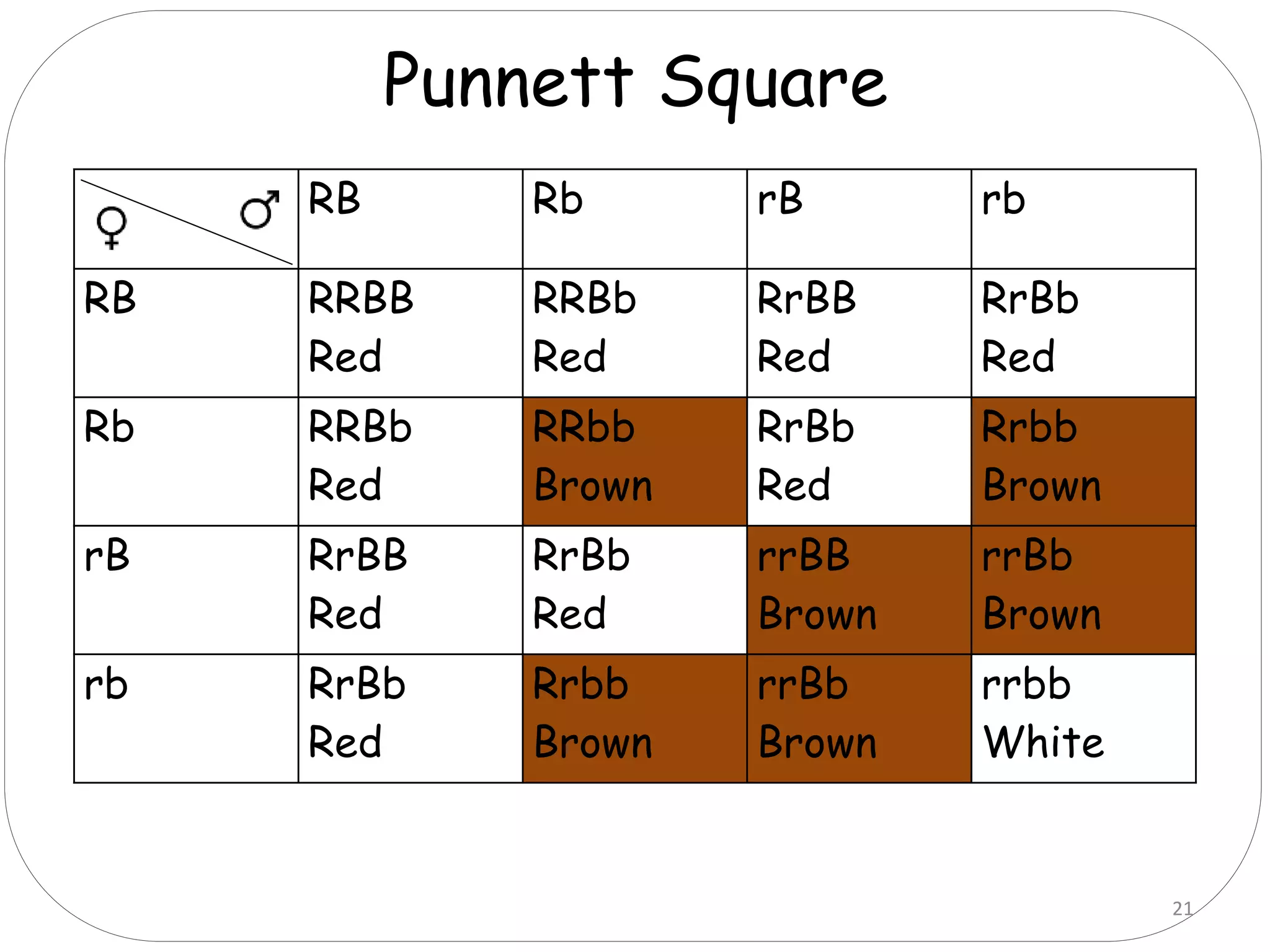
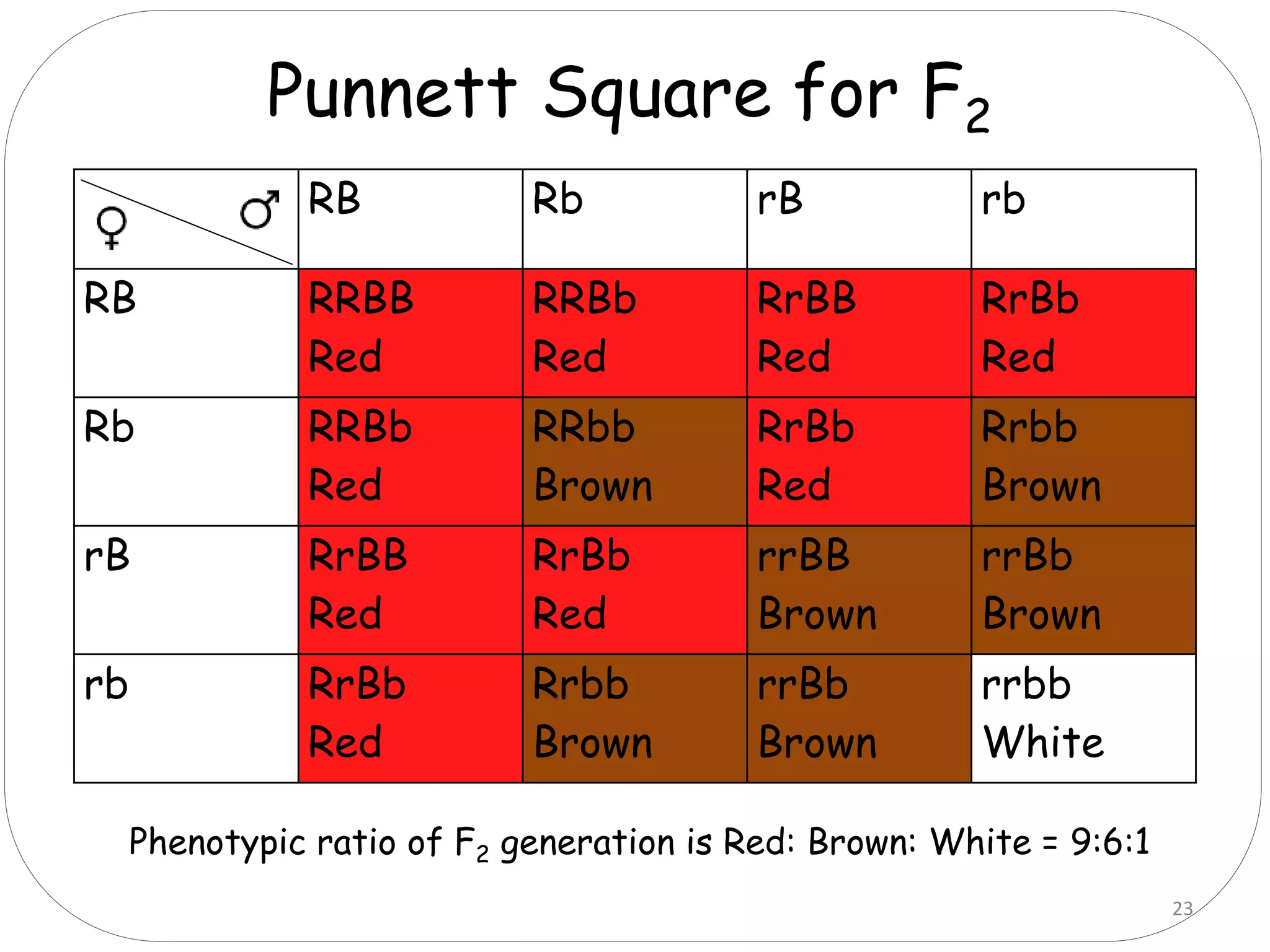
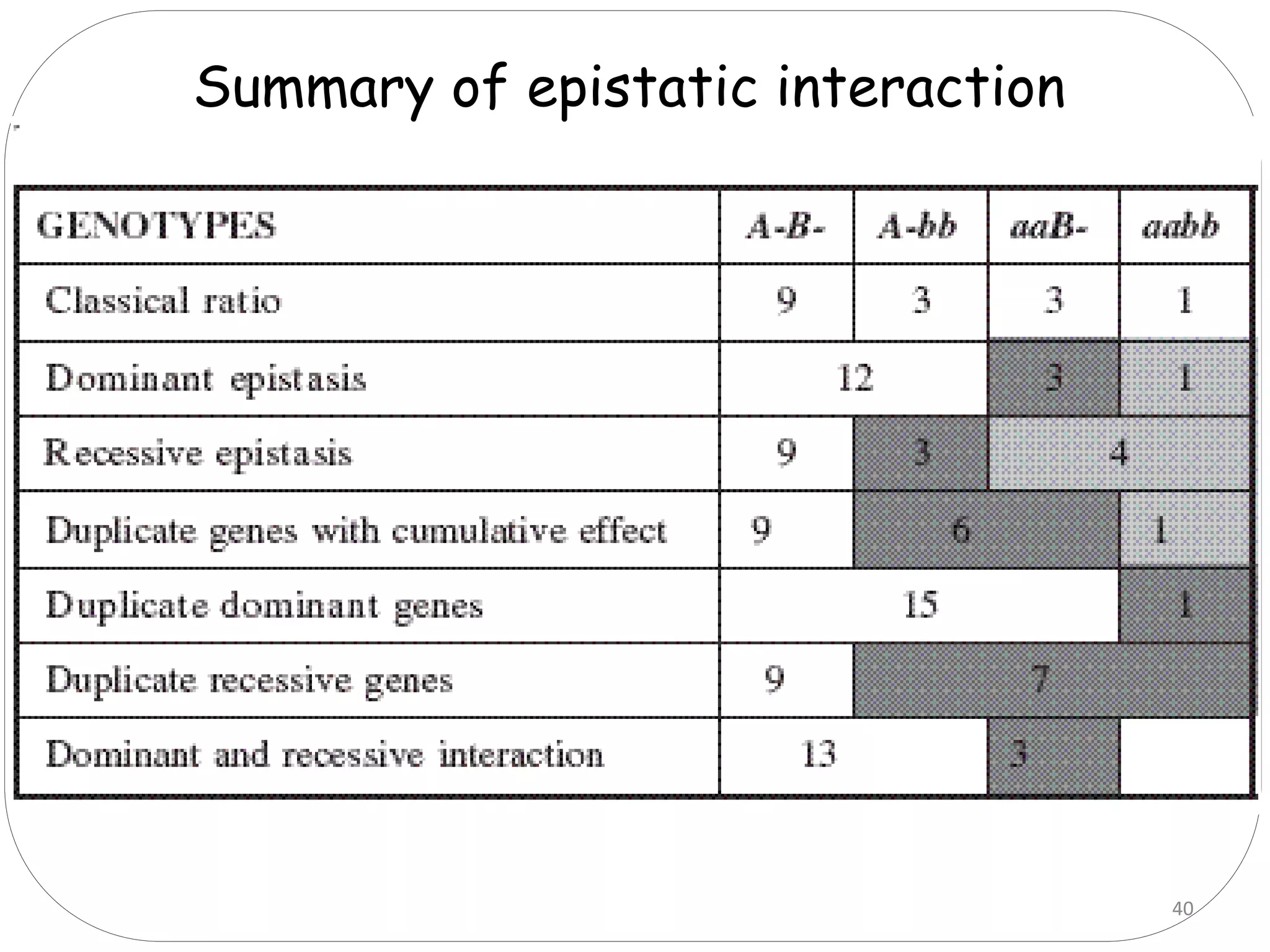
1. There are six main types of epistatic gene interactions: complementary, duplicate, suppressor, additive, dominant epistasis, and recessive epistasis.
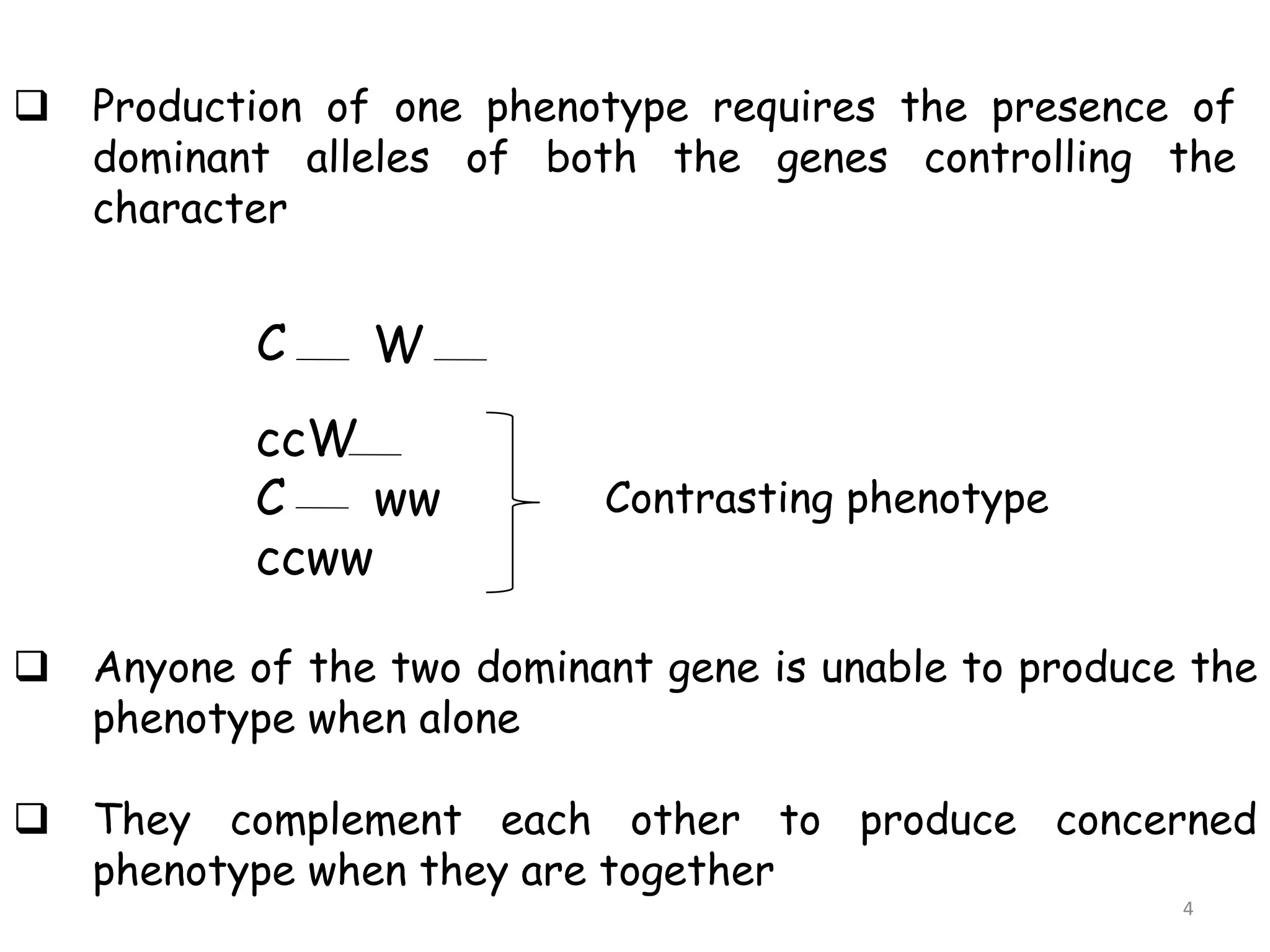
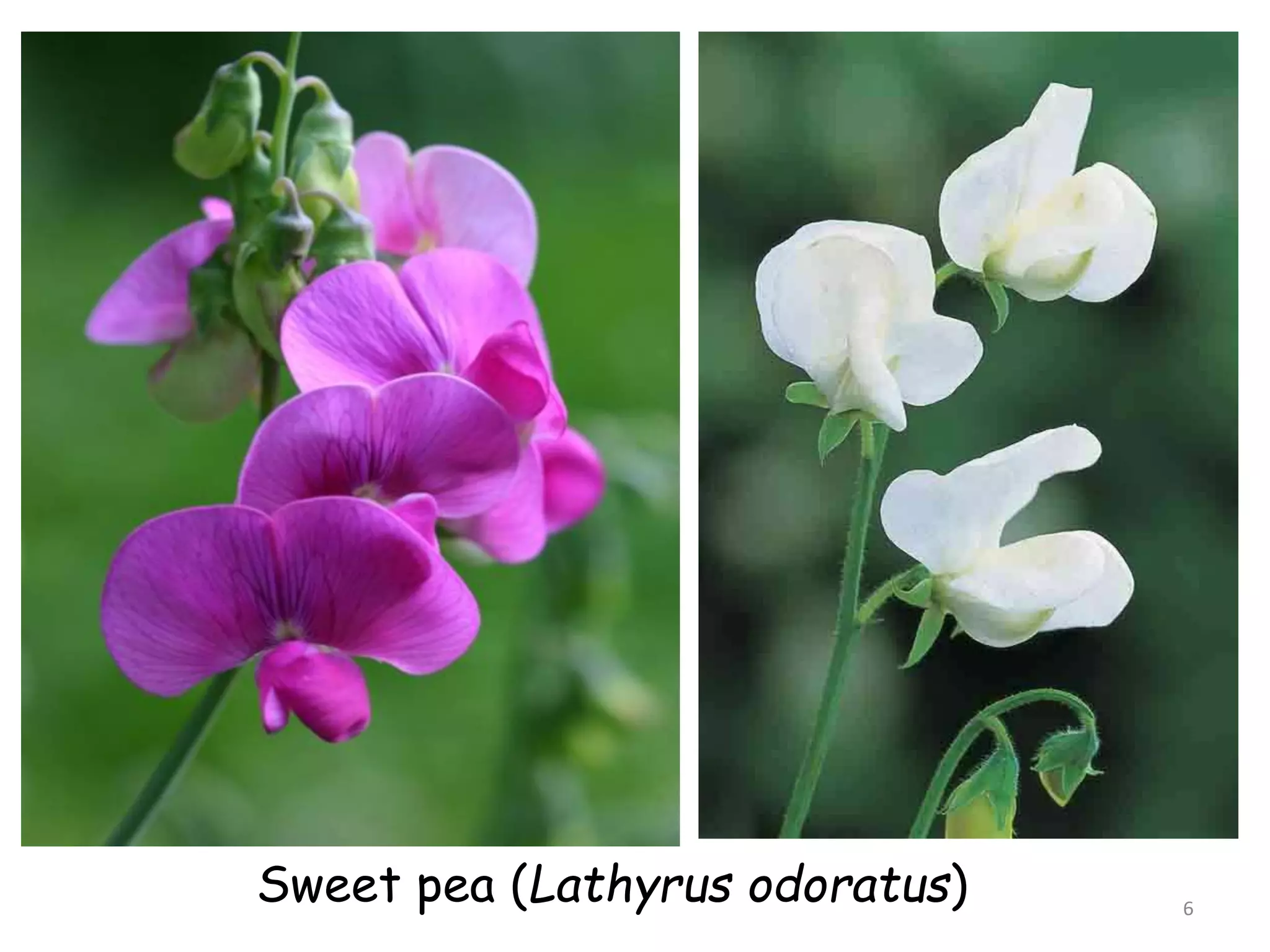
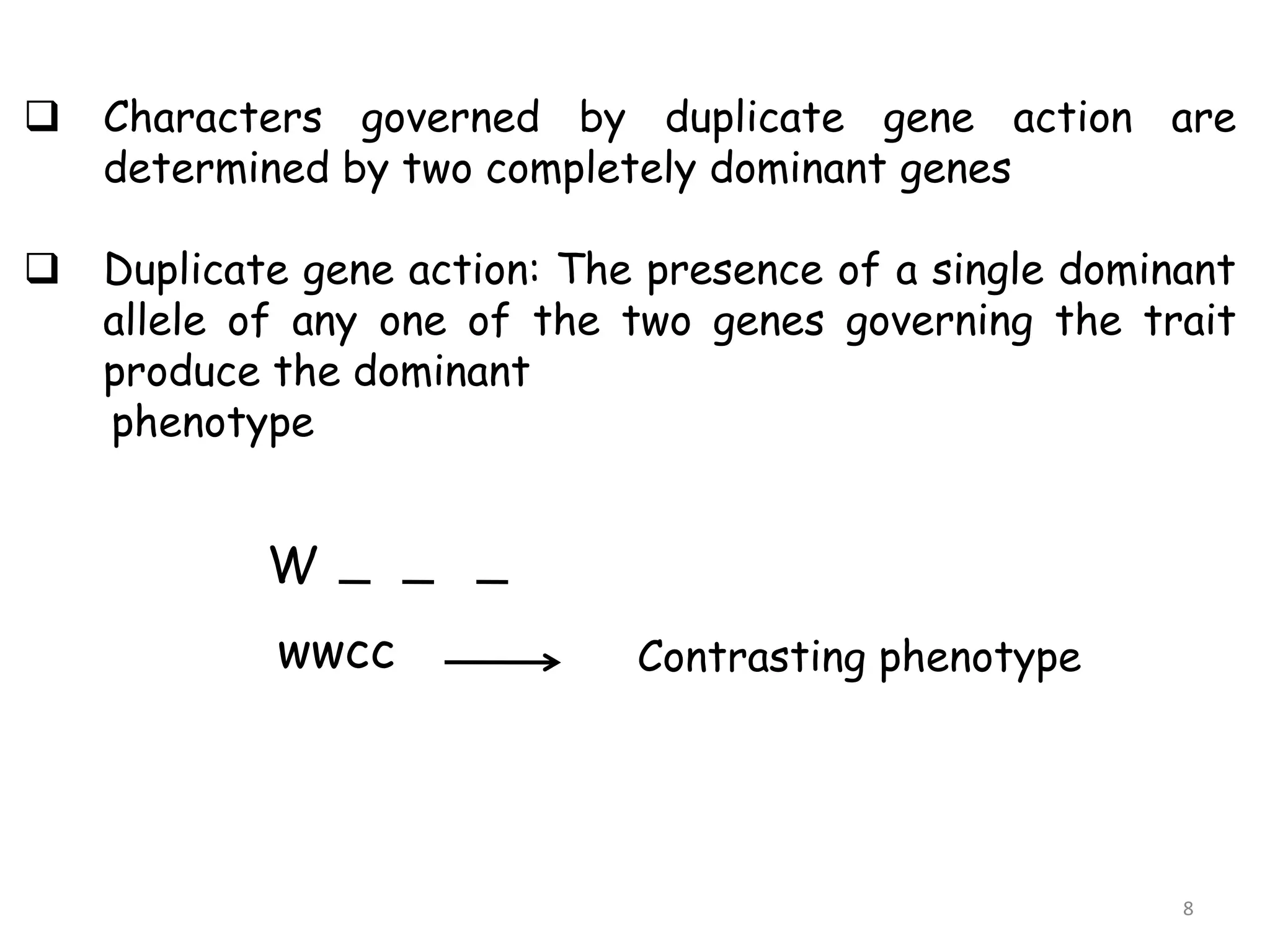
2. Complementary genes require the presence of dominant alleles of both genes to produce a phenotype, while duplicate genes produce the same phenotype when either gene is present.
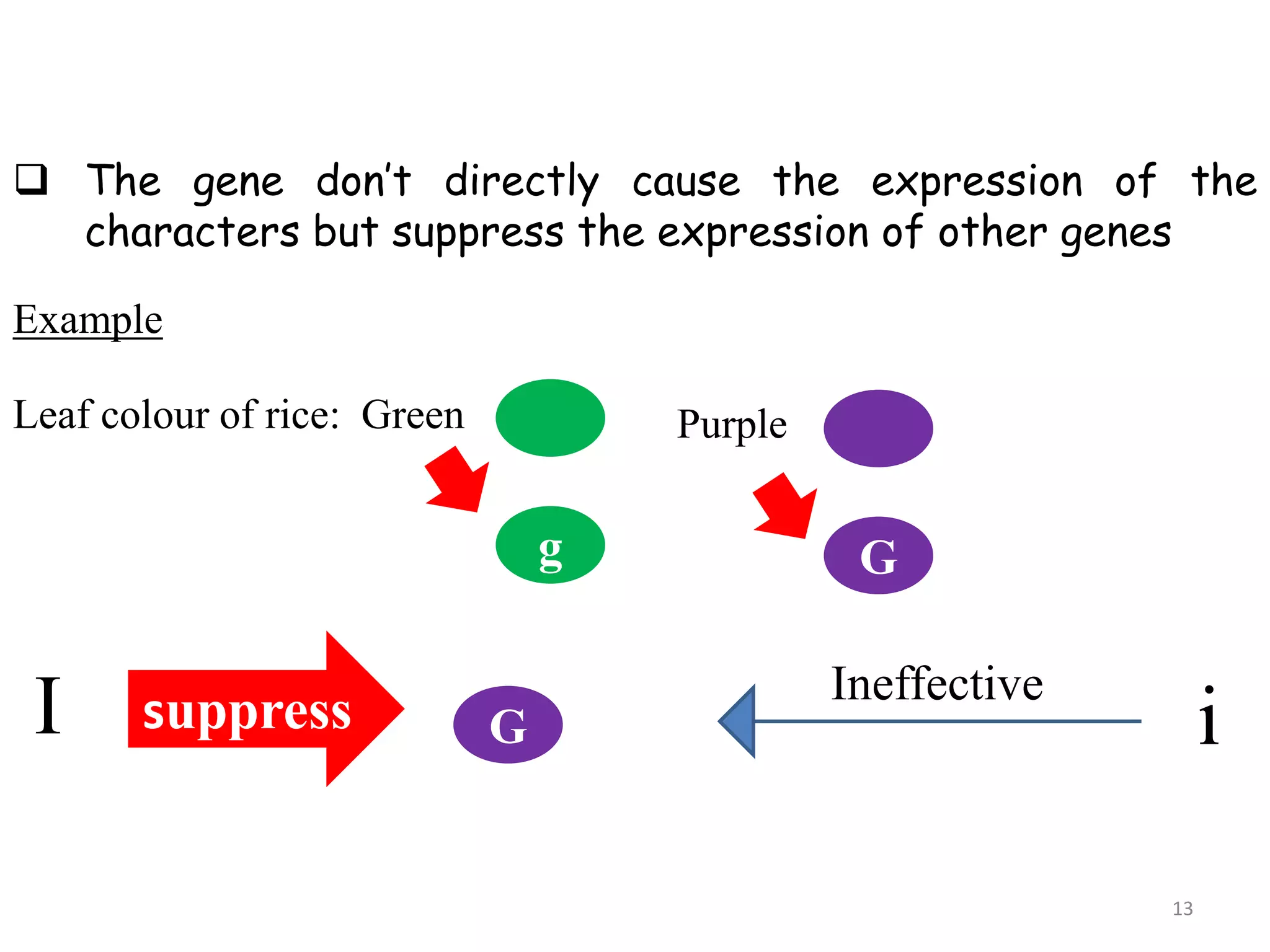
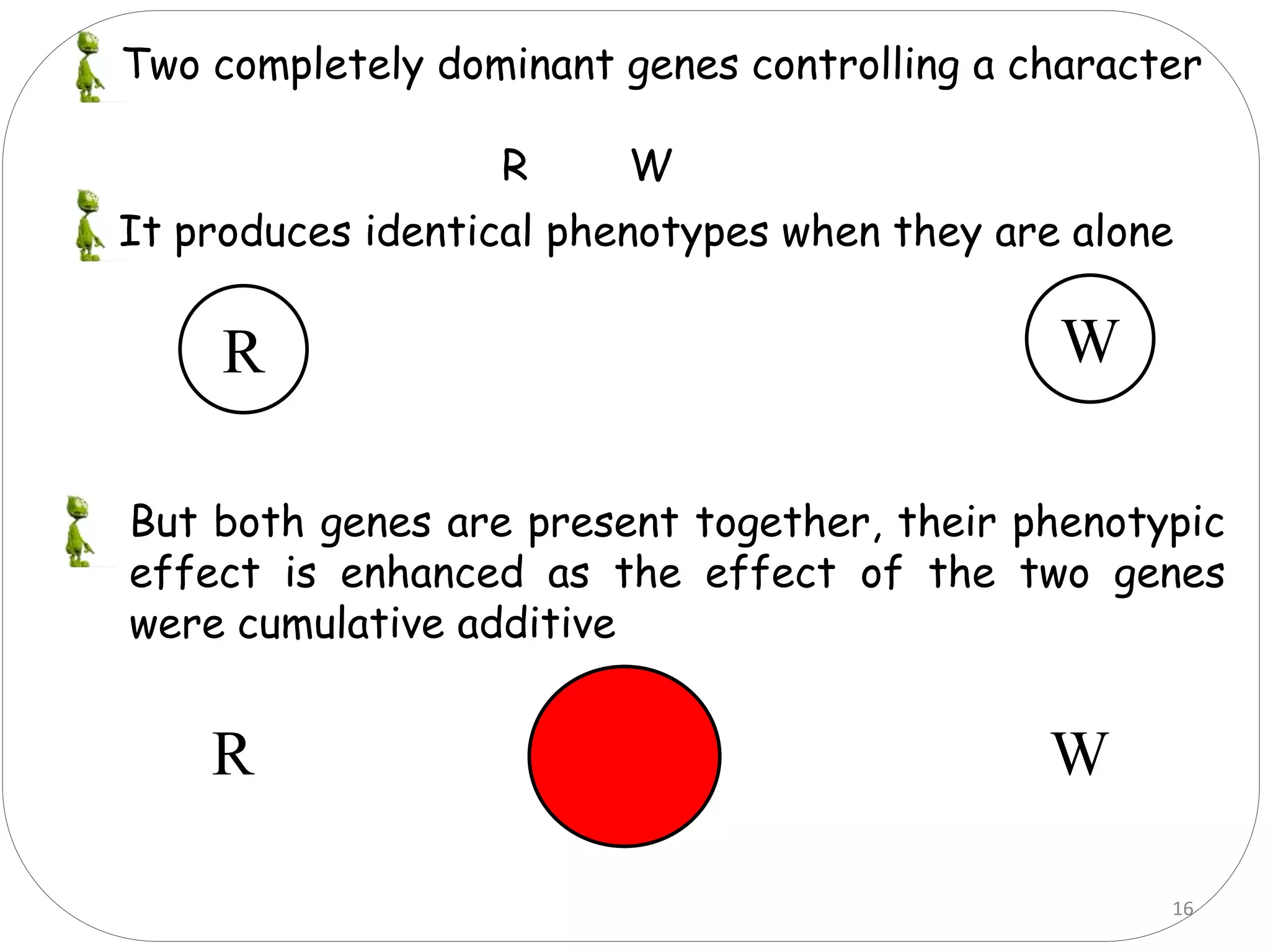
3. Suppressor genes do not directly cause phenotypes but suppress the expression of other genes. Additive genes have a cumulative effect when both are present.
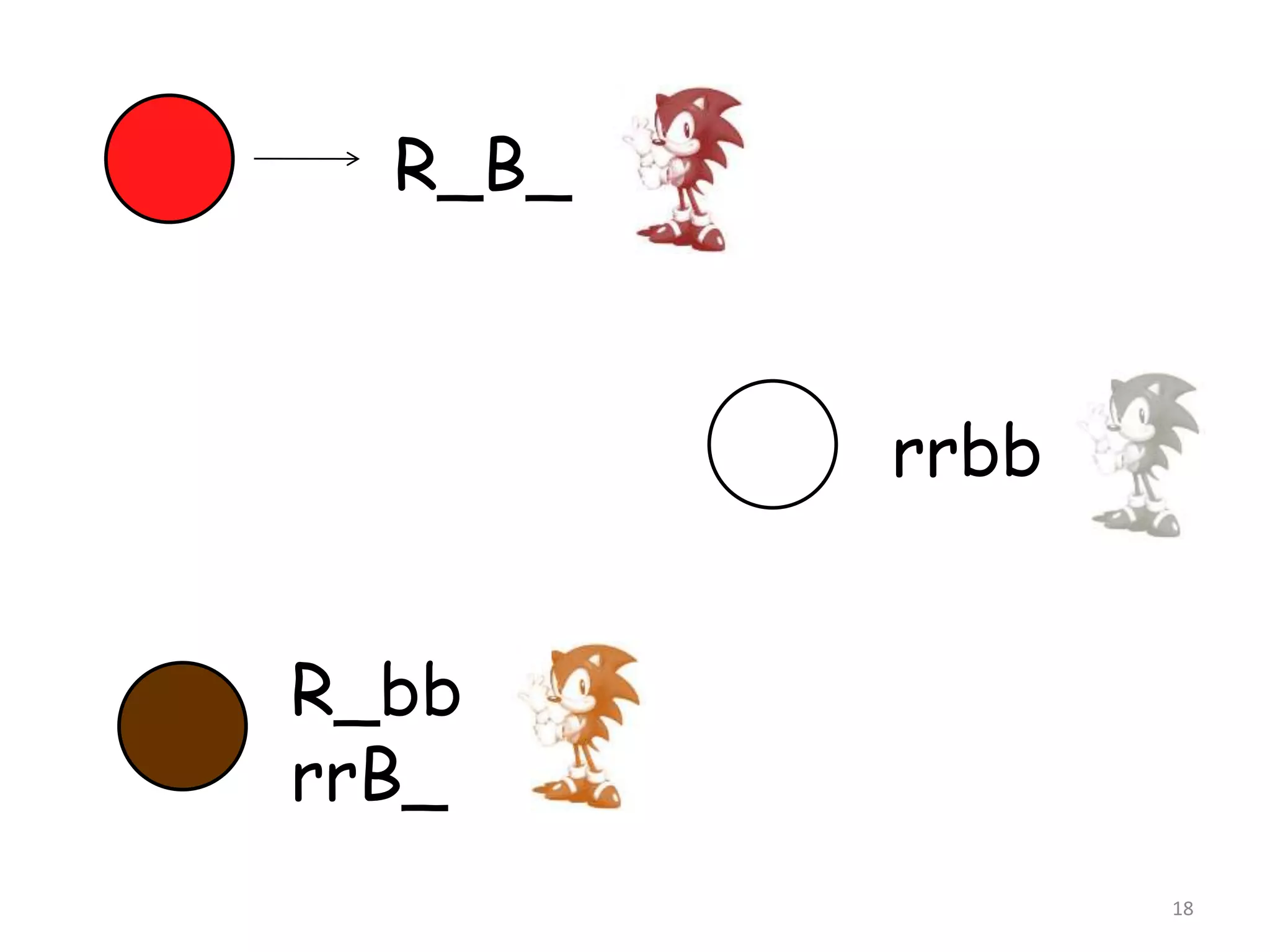
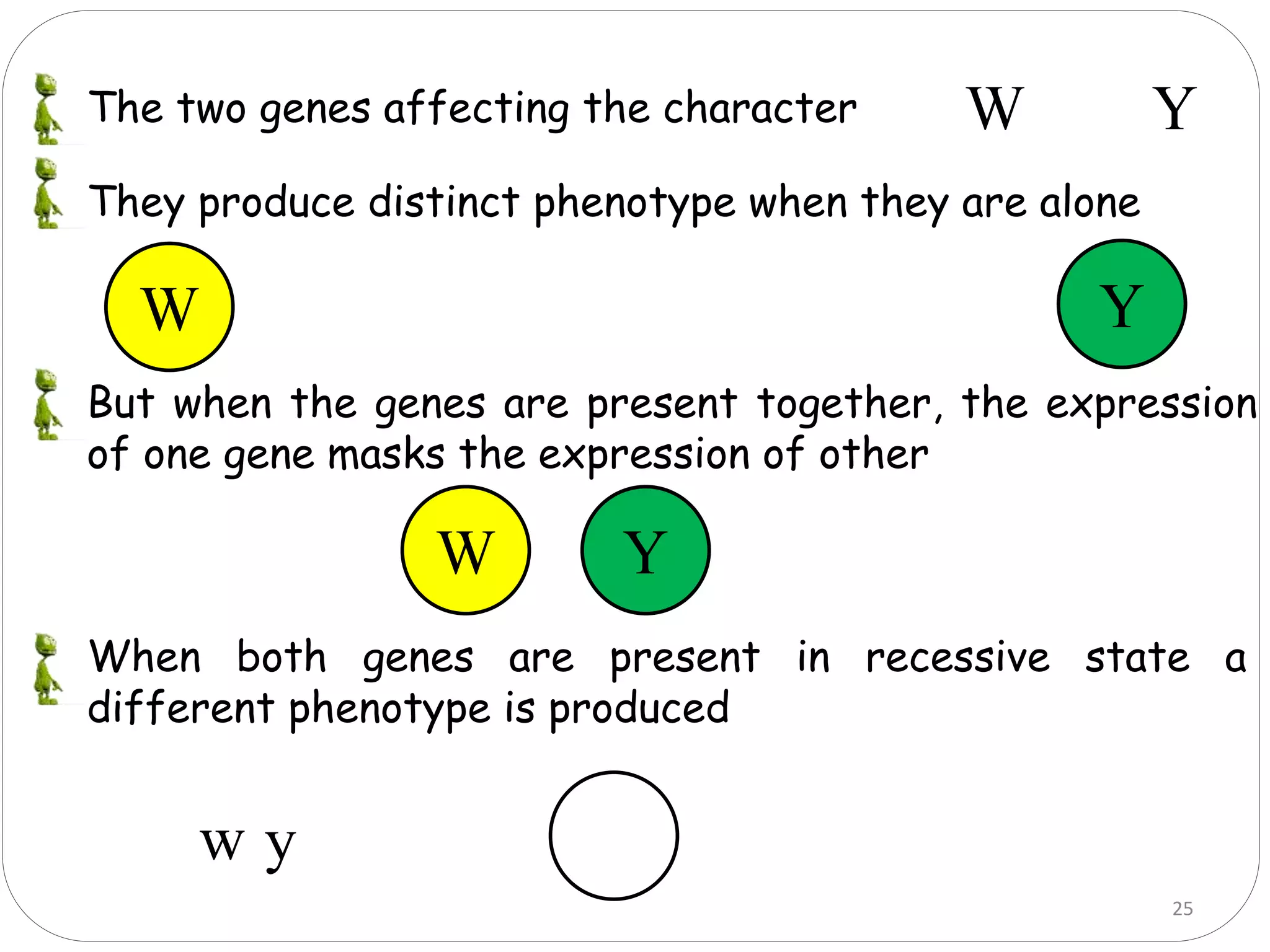
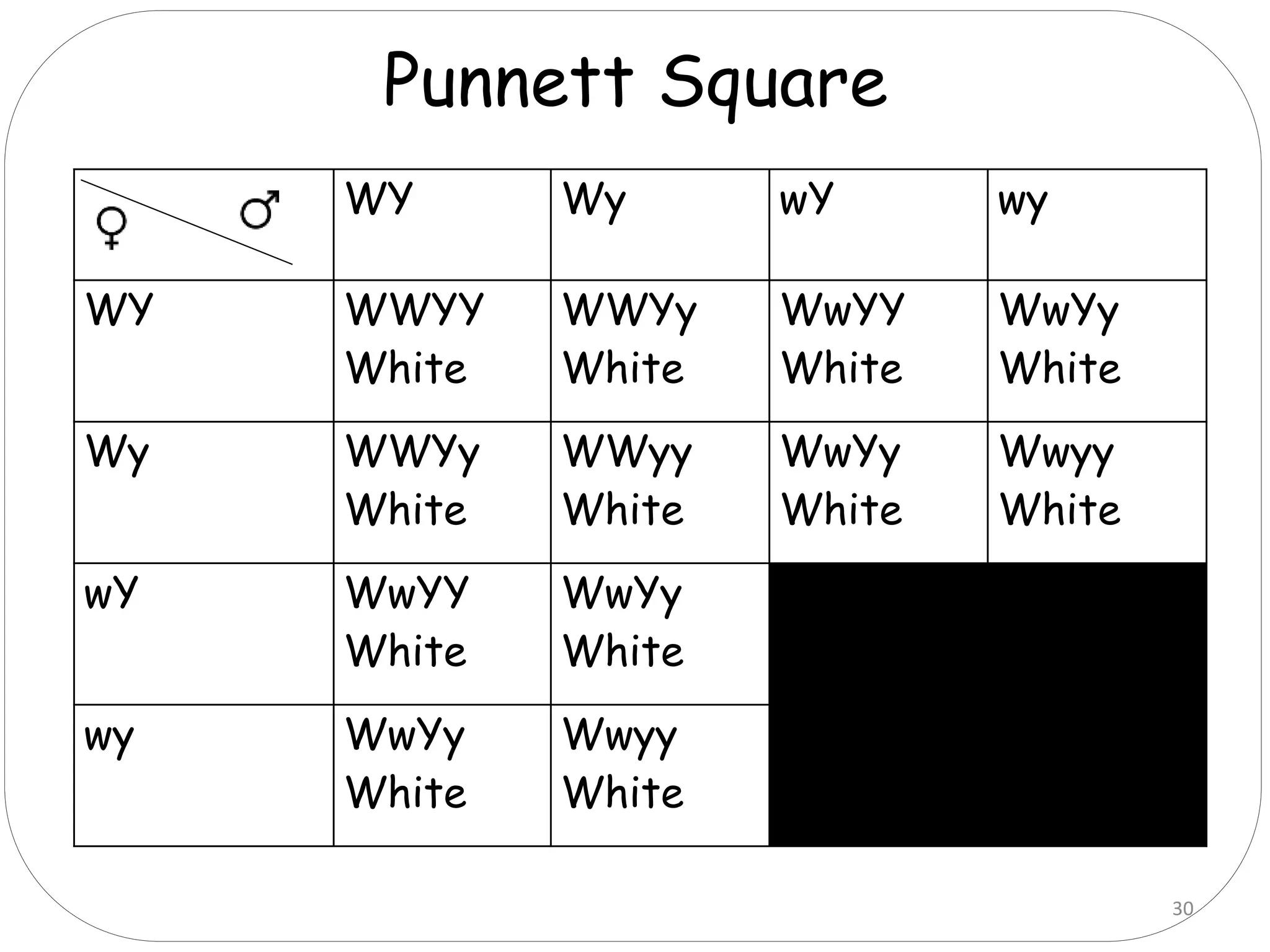
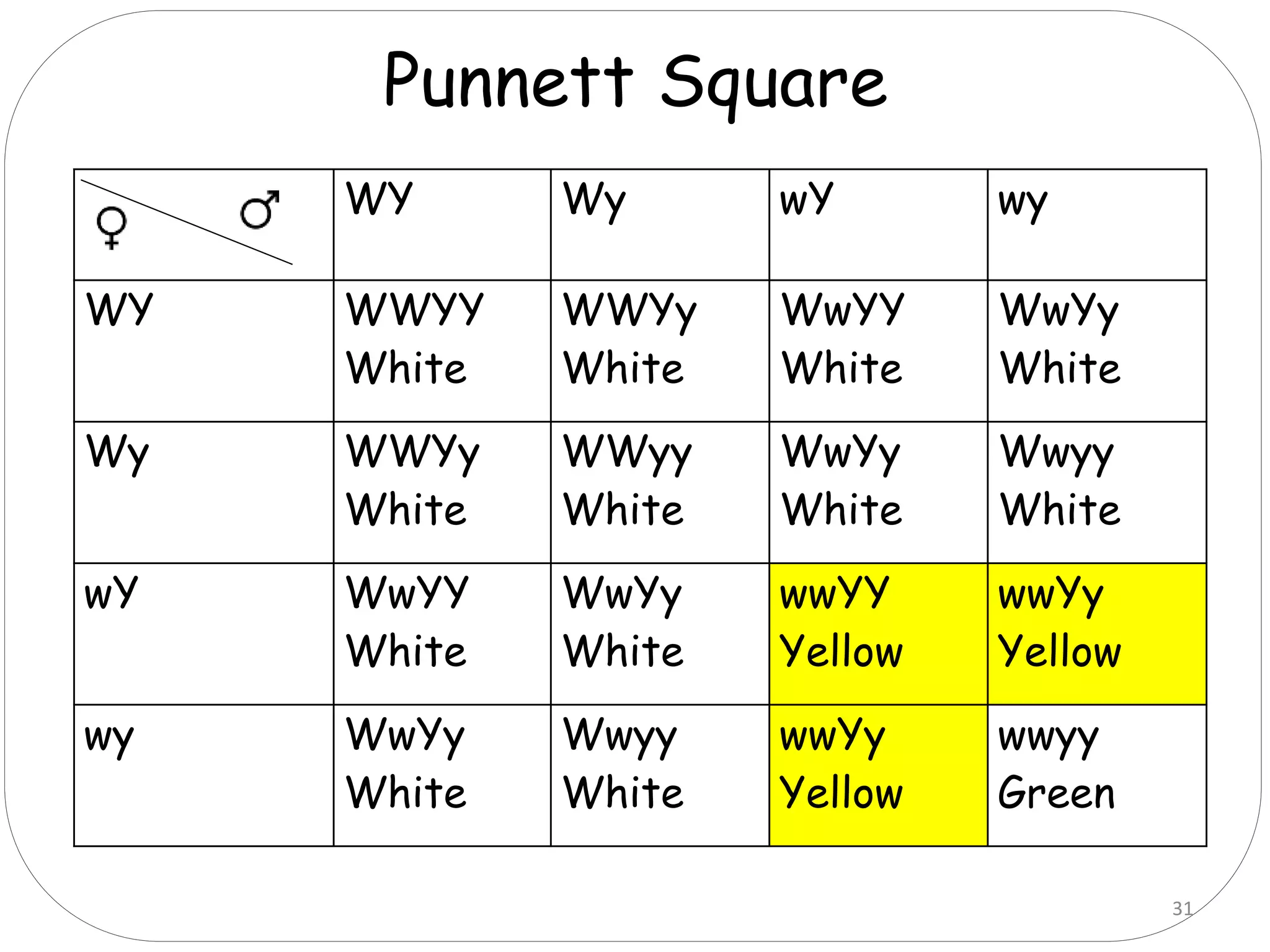
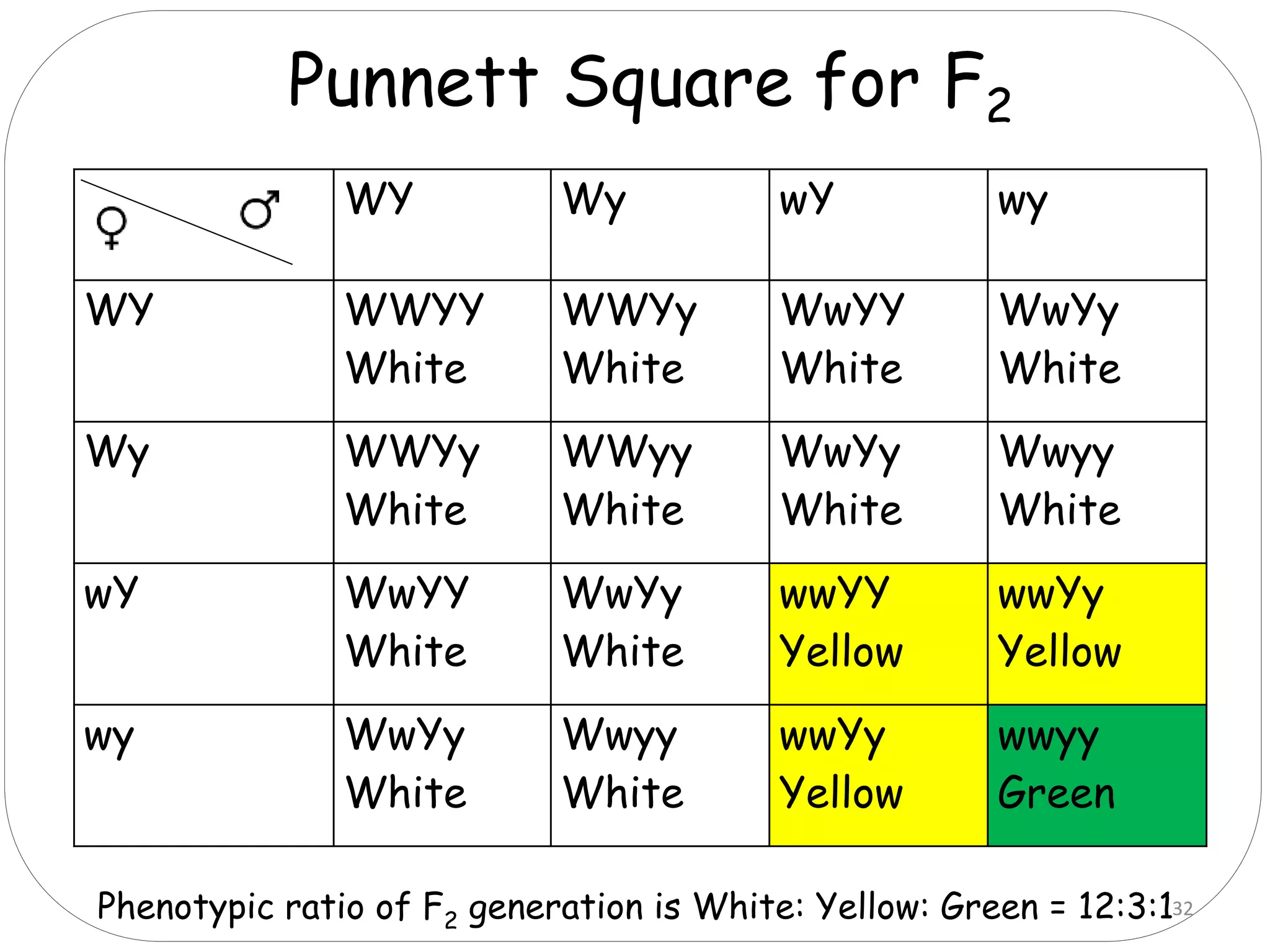
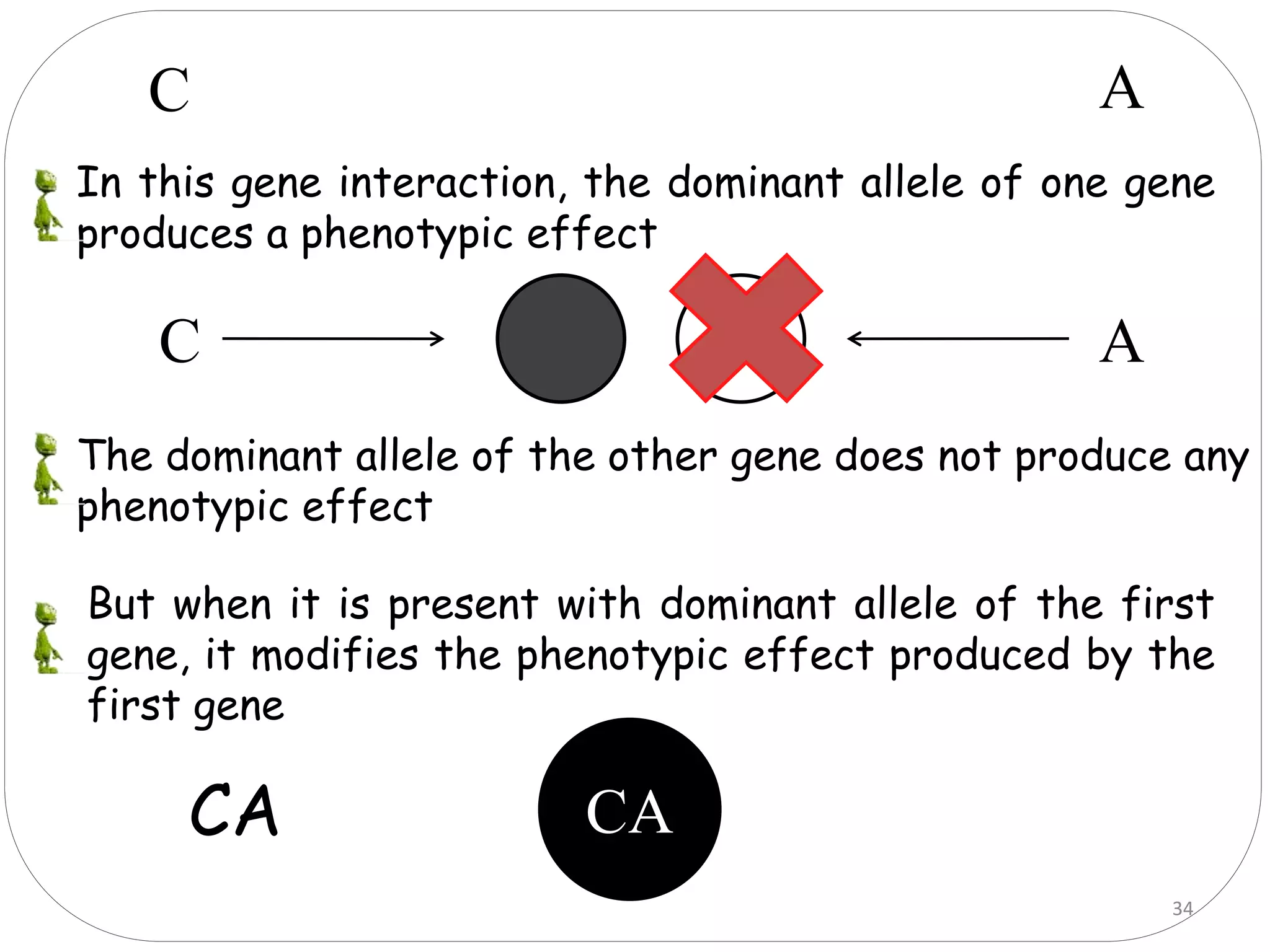
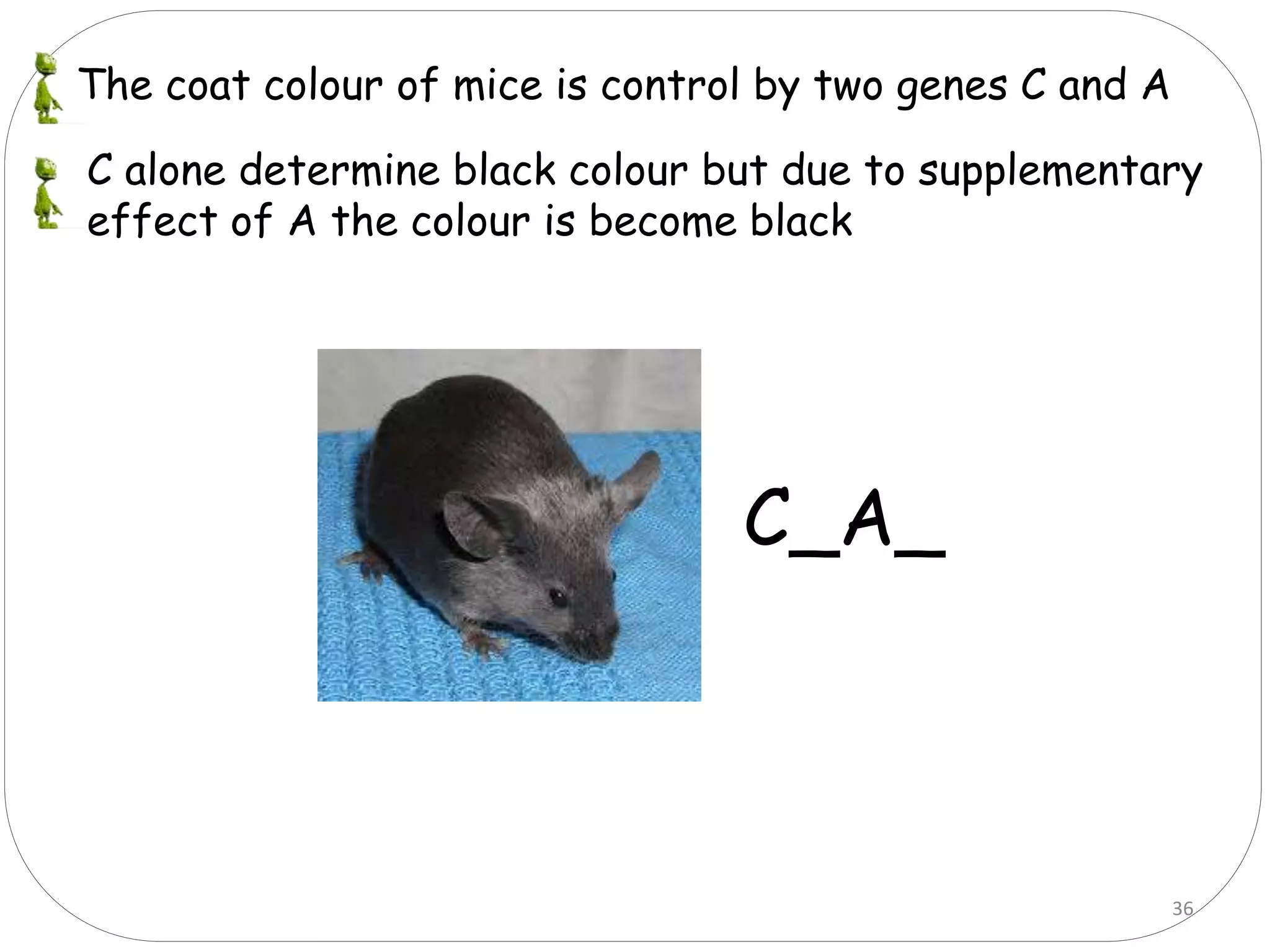
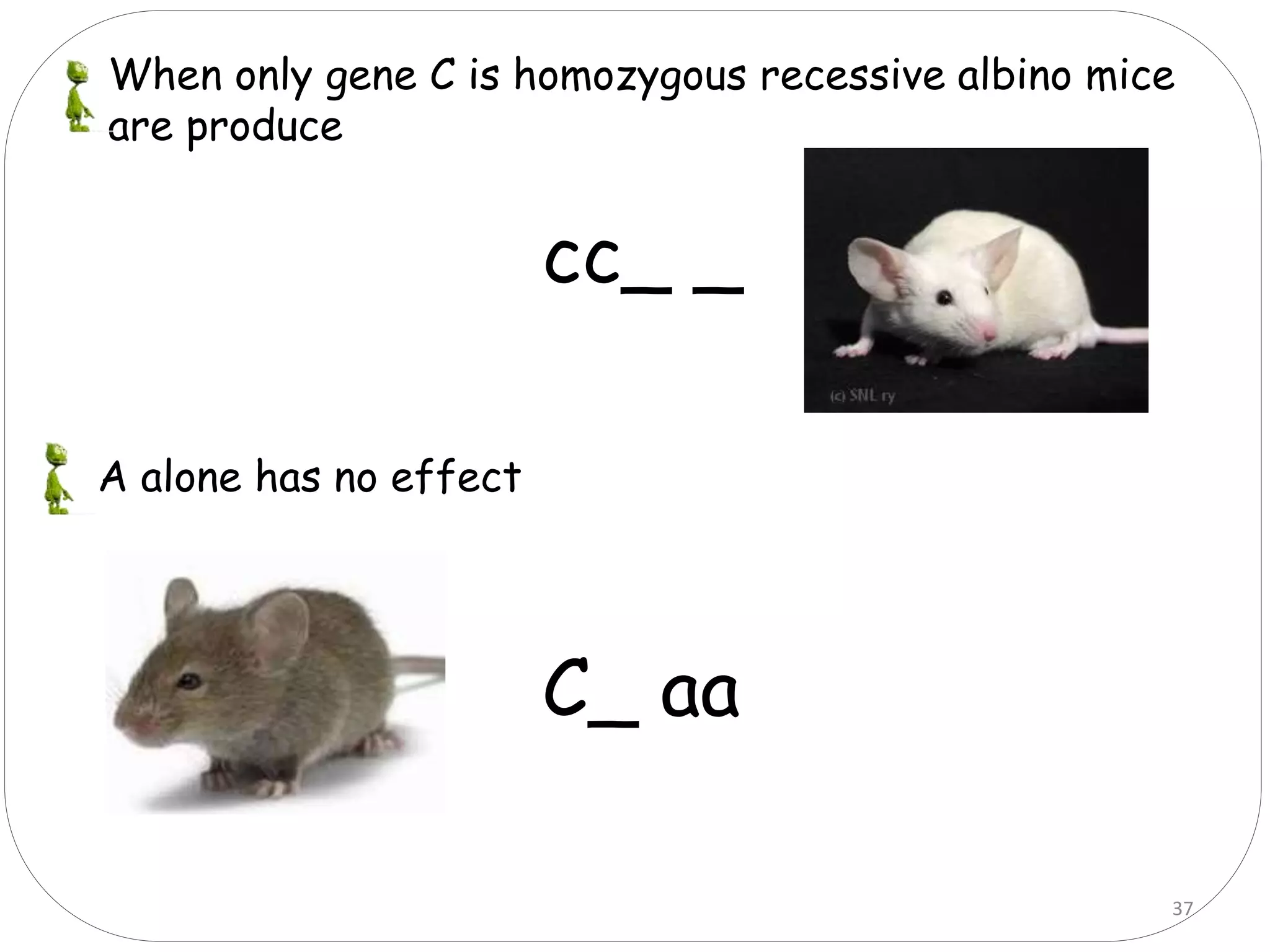
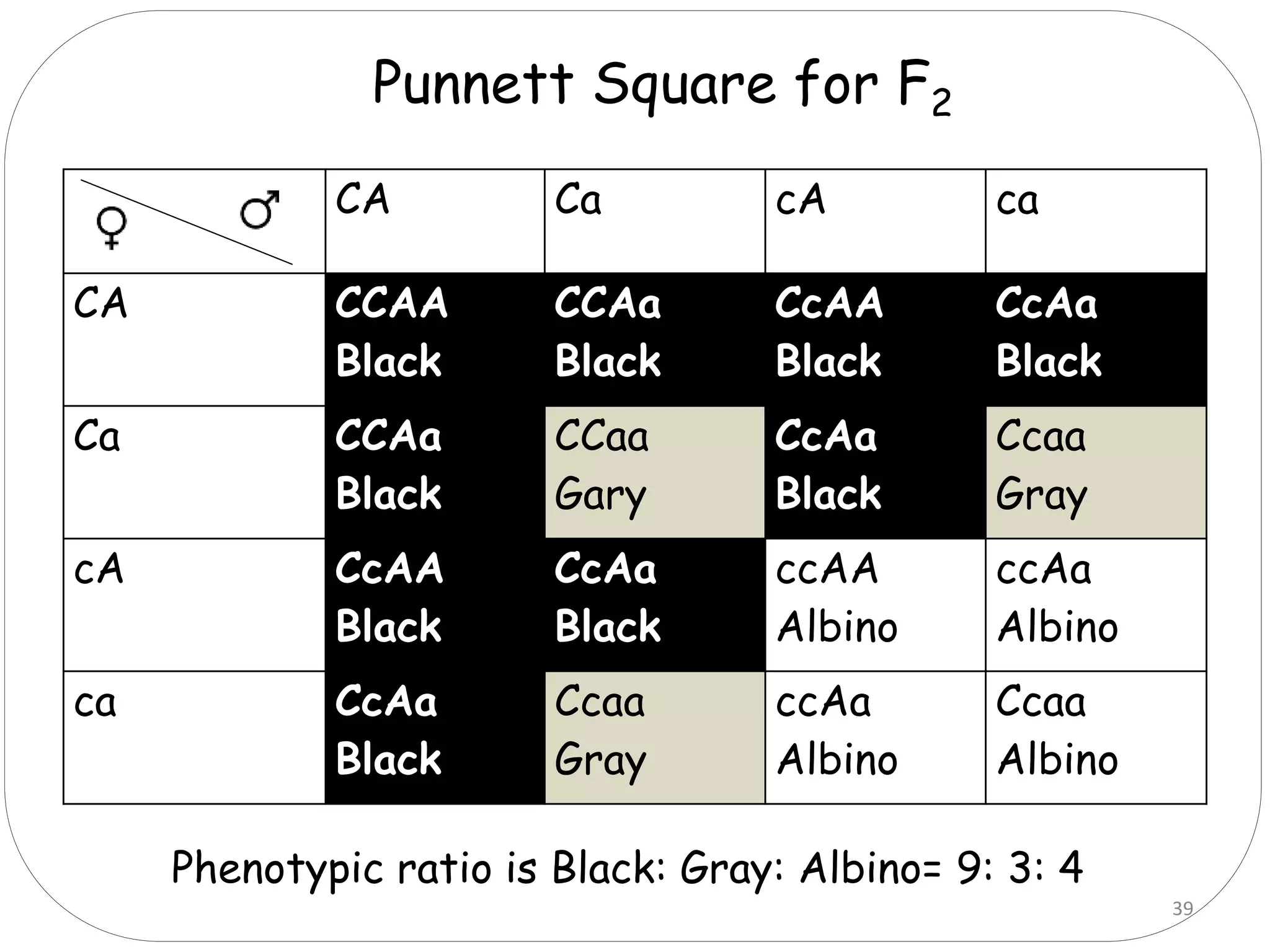
4. Dominant epistasis occurs when one dominant gene masks the expression of another. Recessive epistasis occurs when a recessive allele of one gene modifies the phenotype caused by the dominant allele of