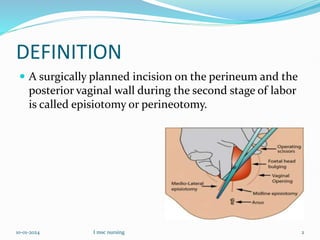
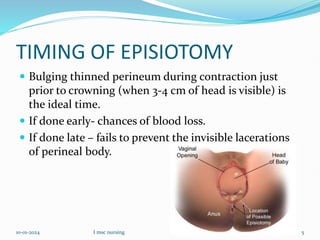
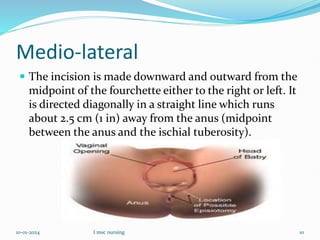
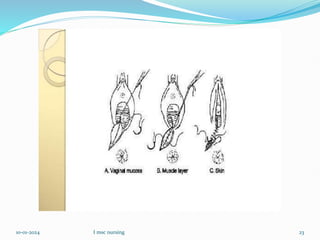
An episiotomy is a surgically planned incision made in the perineum and posterior vaginal wall during the second stage of labor. It is done to enlarge the vaginal opening to facilitate delivery, minimize tearing of the vagina and perineal tissues, and reduce stress on the fetal head. The ideal time for an episiotomy is when 3-4 cm of the baby's head is visible. A mediolateral incision is most common, starting at the midpoint of the vaginal opening and extending diagonally away from the anus. An episiotomy can benefit both mother and baby by allowing for an easier delivery and reducing maternal and fetal injuries.