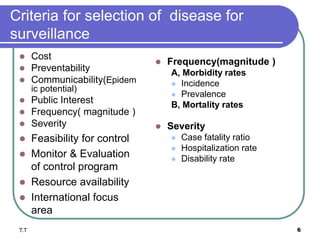
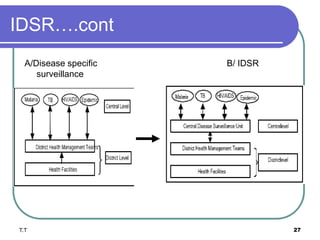
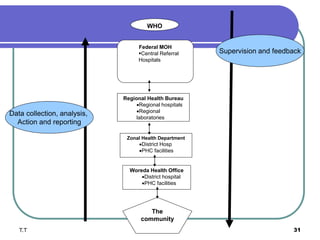
Public health surveillance involves the systematic collection, analysis, and dissemination of health data to monitor disease occurrence and trends. The main types of surveillance are passive, active, and sentinel. Surveillance data is used to determine disease magnitude, set priorities, monitor health events, and evaluate programs. Key features of a good surveillance system include timely notification and comprehensive response. Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response aims to strengthen national surveillance by coordinating activities and ensuring timely data sharing between programs.