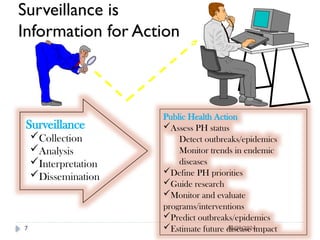
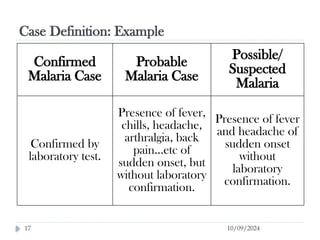
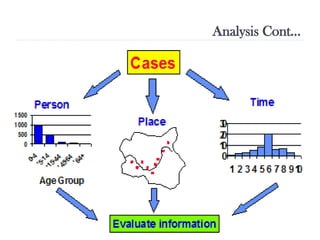
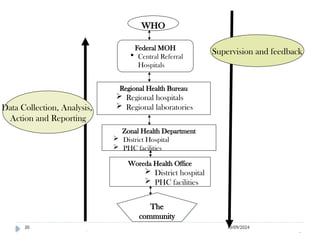
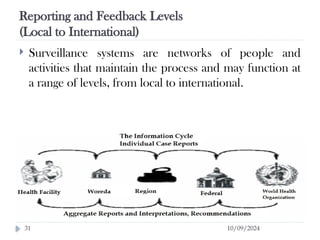
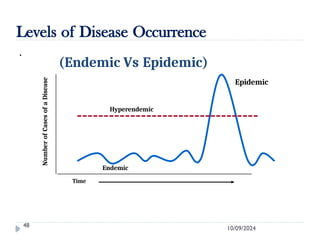
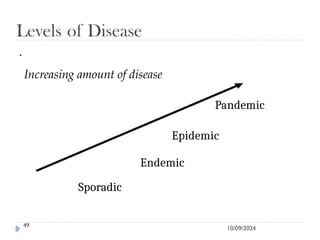
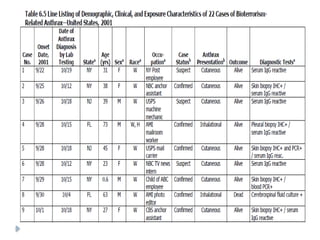
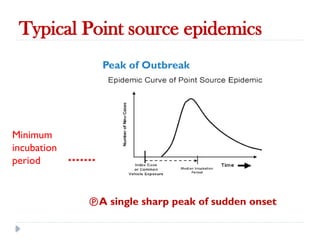
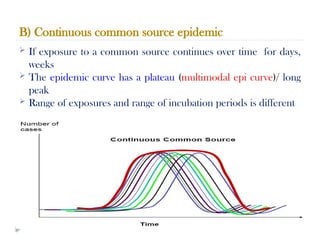
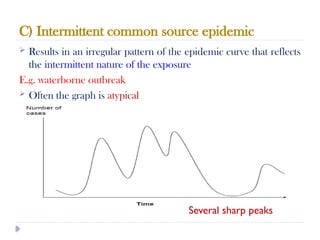
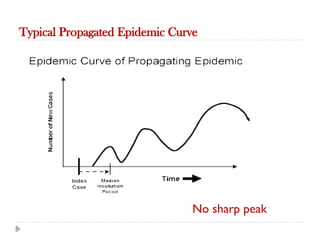
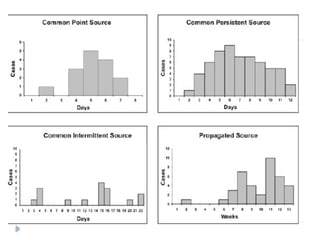
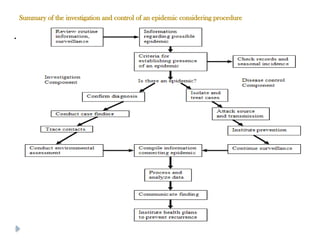
Public health surveillance is defined as the systematic collection, analysis, interpretation, and dissemination of health-related data that guides health interventions. It serves as an early warning system for epidemics, informing about disease patterns, monitoring trends, and evaluating public health programs. Various types include passive, active, and sentinel surveillance, each fulfilling specific functions in disease detection and monitoring.