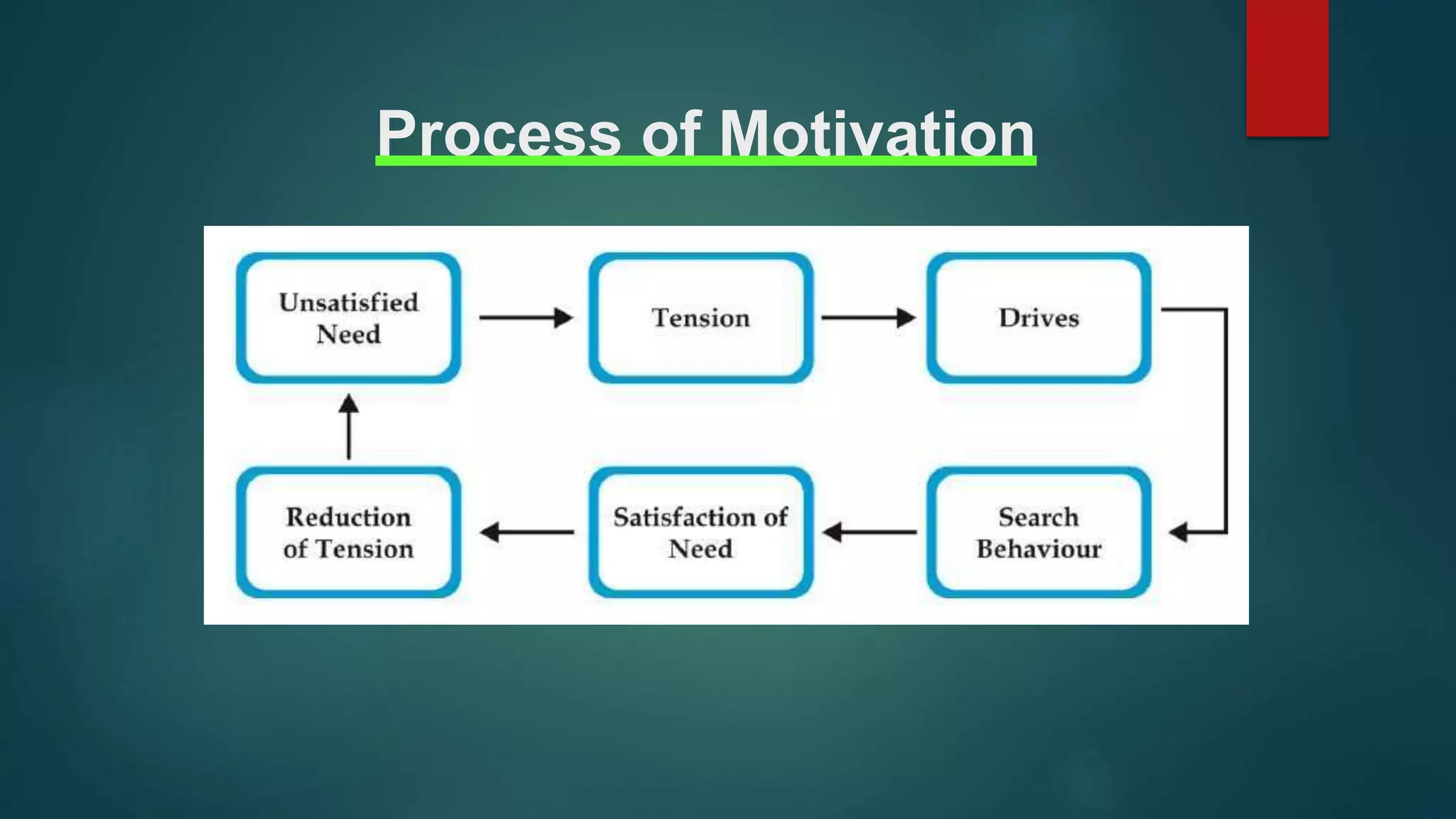
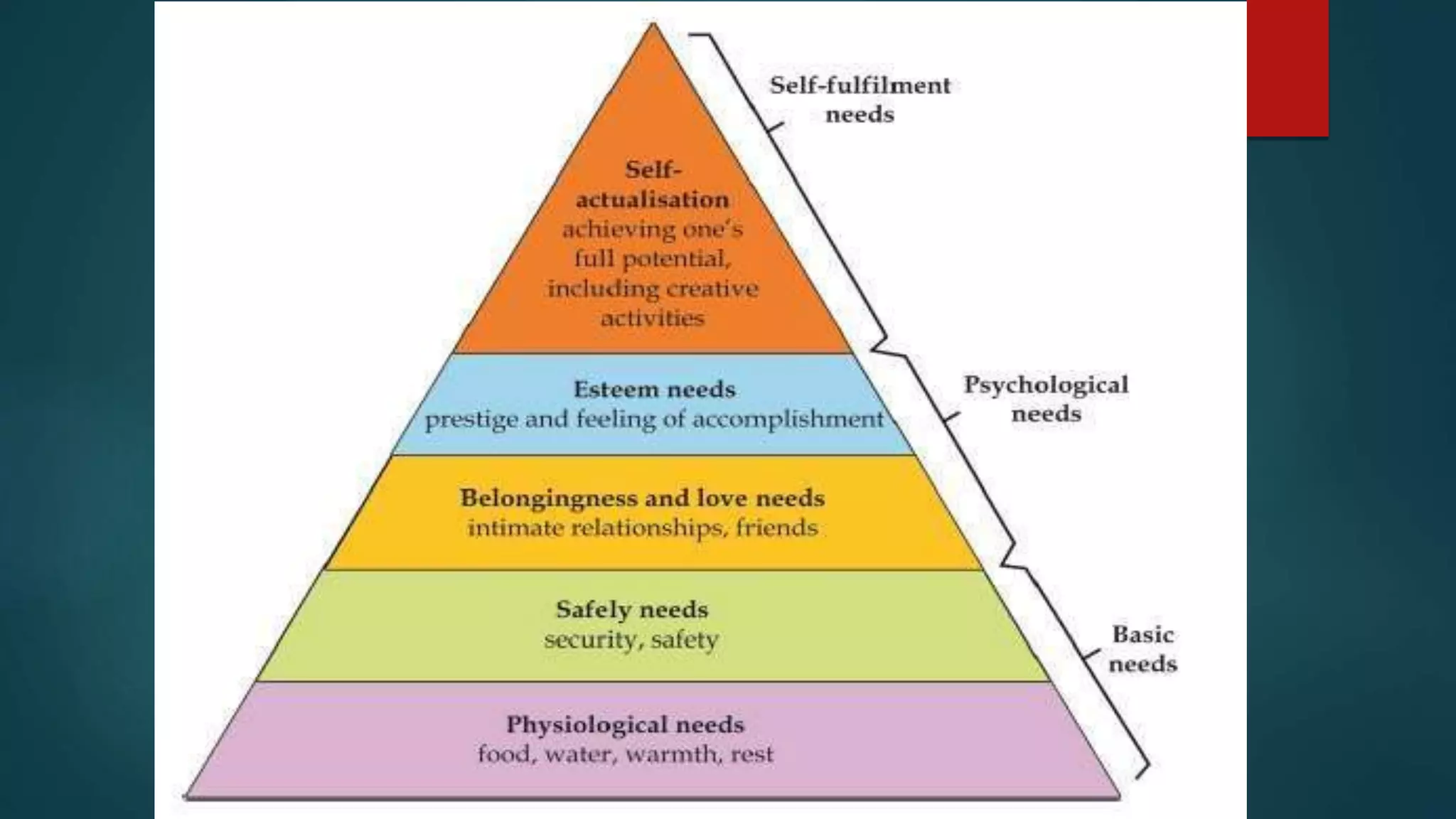
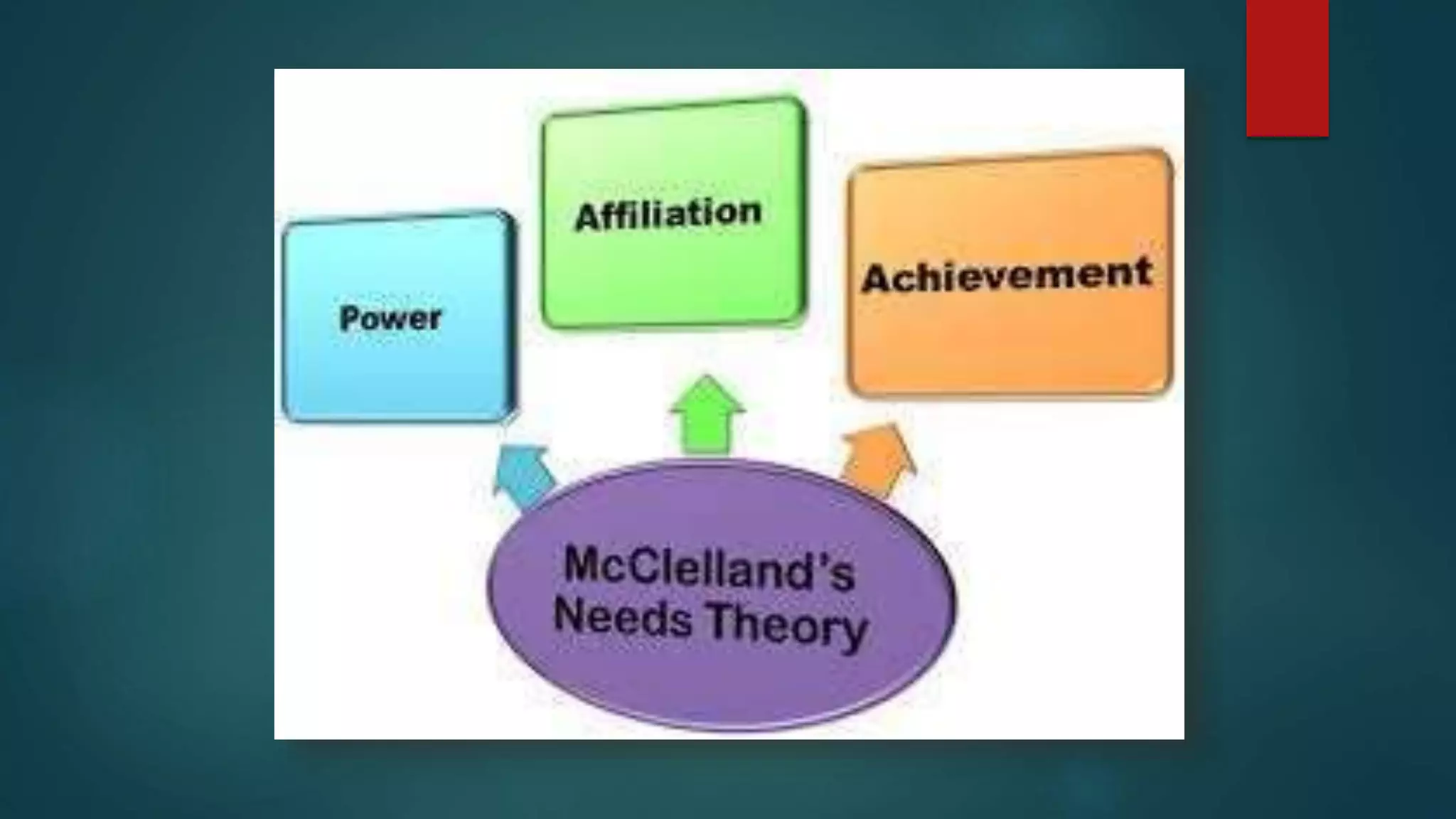
The document discusses several theories of motivation. It introduces Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, which proposes that people are motivated to fulfill a series of five needs in a hierarchical order: physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. It also discusses McClelland's theory of needs, which identifies three main motives that drive people: achievement, affiliation, and power. According to this theory, individuals are predisposed to behave in certain ways depending on their dominant motive. Recognizing these motives can help managers understand how to best motivate each person.