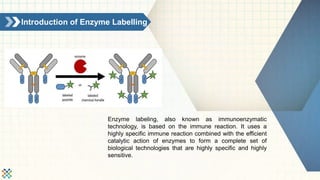
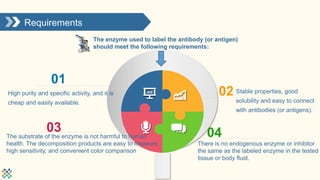
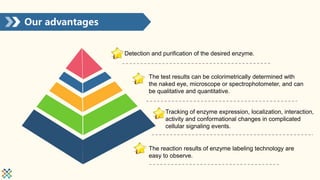
Enzyme labeling, or immunoenzymatic technology, utilizes specific immune reactions and enzyme catalytic actions for sensitive biological applications like enzyme immunoassays and immunohistochemical staining. Commonly used enzymes include horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (AP), each with unique characteristics and applications. Creative Enzymes Inc. offers various enzyme labeling services, developing techniques for a wide range of biomolecular probes to support research needs.