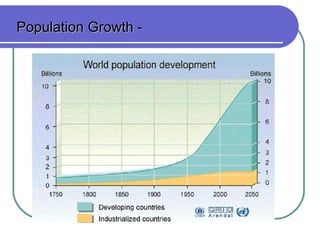
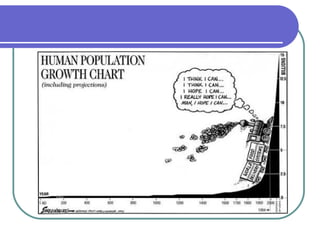
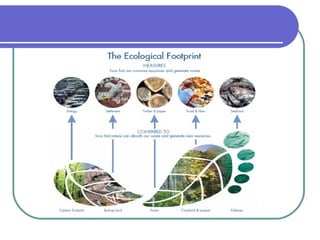
Environmental science is an interdisciplinary field that studies how Earth systems function and how human activity impacts the planet. It addresses growing environmental concerns like population growth, resource depletion, loss of biodiversity, and climate change. Understanding science, sustainability, and our role as stewards of the planet can help us develop solutions to environmental problems and leave a habitable world for future generations.