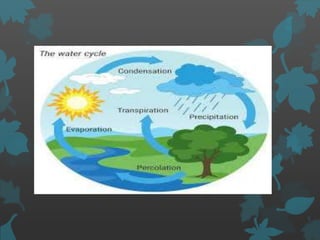
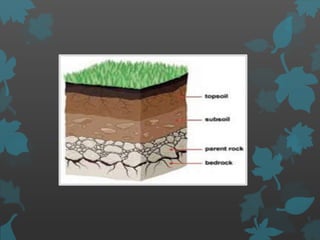
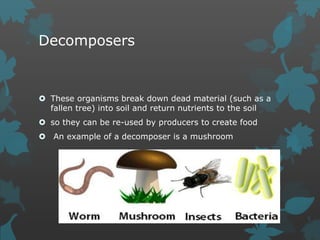
The document discusses various environmental factors that influence plant growth, including both biotic and abiotic factors. It describes abiotic factors like water, sunlight, temperature, soil composition and topography that affect plant survival and development. It also discusses important biotic factors such as producers, consumers, decomposers and their interactions through parasitism, mutualism, herbivory and allelopathy. Specific environmental conditions required for plant germination, growth and reproduction are also outlined.