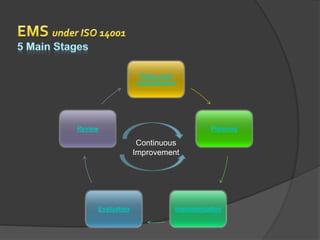
The document outlines an environmental management system (EMS) for a company. It discusses establishing an EMS policy, identifying environmental aspects and legal requirements, setting objectives and targets, implementing programs and procedures, monitoring performance, conducting management reviews, and continually improving the system. The goal is to systematically address regulatory compliance and environmental impacts in a cost-effective manner.









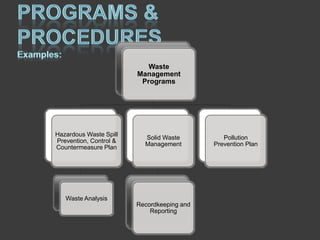
![WASTE MANAGEMENT
Example Applicable Legislation:
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
(RCRA)
Non-hazardous waste/Solid waste 40 CFR Part
239-259
Hazardous waste 40 CFR Part 260 [-279]
○ Details – Part 261
Ignitable Waste (I) Corrosive Waste (C) Reactive Waste (R)
Toxicity Characteristic Waste (E) Acute Hazardous Waste (H) Toxic
Waste (T) = Characteristic waste
Specific wastes such as, slop oil emulsion solids from the
petroleum refining industry [K049] = Listed waste
Pollution Prevention Act
Toxic Substances Control Act](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ems-13269877903421-phpapp02-120119094611-phpapp02/85/Environmental-Management-System-Development-14-320.jpg)
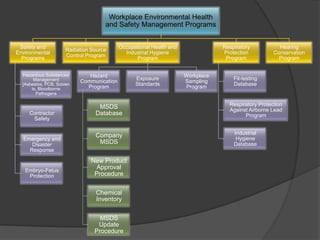

![Other Environmental
Program Management
Corporate Citizenship
EHS Management EMS Manual
Program
Tier II Reports
[Inventory of
Programs, Procedures Environmental Calendar
Substances for Compliance Reviews Policy
and work instructions and Training Schedule
Emergency
Responders]
Descriptions of Roles,
Toxic Release Inventory Responsibilities, Lists of Objectives and
Reports Authorities and Lines of Targets
Communications
Community Relations Equipment Calibration Environmental Aspects
and Communications Procedure and Impacts Inventory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ems-13269877903421-phpapp02-120119094611-phpapp02/85/Environmental-Management-System-Development-17-320.jpg)
![OTHER ENVIRONMENTAL
PROGRAM MANAGEMENT
Example Applicable Legislation:
Comprehensive Environmental
Response, Compensation, and Liability Act
(CERCLA) Hazardous Substances
[Superfund]
Superfund Amendments and
Reauthorization Act (SARA)
Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-
Know Act (EPCRA) [also known as SARA Title III]
○ Tier II Report [SARA 311/312] – Inventory of
Substances for Emergency Responders, 40 CFR
Part 370
○ Toxic Release Inventory Report – [SARA 313] Tier
III Report](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ems-13269877903421-phpapp02-120119094611-phpapp02/85/Environmental-Management-System-Development-18-320.jpg)


