This document discusses several key environmental issues including poverty and the environment, deforestation, water crisis, environmental refugees, global warming, and bioterrorism. It notes that environmental degradation and resource depletion are restricting human development. Deforestation is caused by land clearance for agriculture, overgrazing, uncontrolled logging, and other factors. The water crisis stems from increasing uses for drinking, sanitation, industry, and irrigation compounded by climate change. Environmental refugees, who are the largest class of displaced persons, flee issues like landlessness, deforestation, and drought. Global warming is exacerbated by the greenhouse effect and leads to problems like rising sea levels and disrupted ecosystems. Bioterrorism involves the covert use of disease



![Causes to restrict human development
• Environmental degradation
• Resource deplection
• Population growth
• Inequitable distribution of income
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doc-20180905-wa0050-191016062402/85/Environmental-Issues-4-320.jpg)

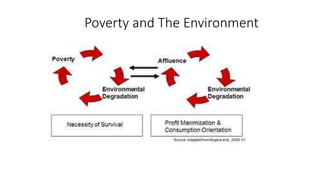
![Poverty
• “ poverty is an integral part of the goal of an
environmental strategy for the world. ”[2]
• Global citizenship and ‘spaceship earth’
Inter- linked responsibilities of
environmental protection & human
development.
• Word’s almost one-fifth population is below
the poverty line.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/doc-20180905-wa0050-191016062402/85/Environmental-Issues-6-320.jpg)