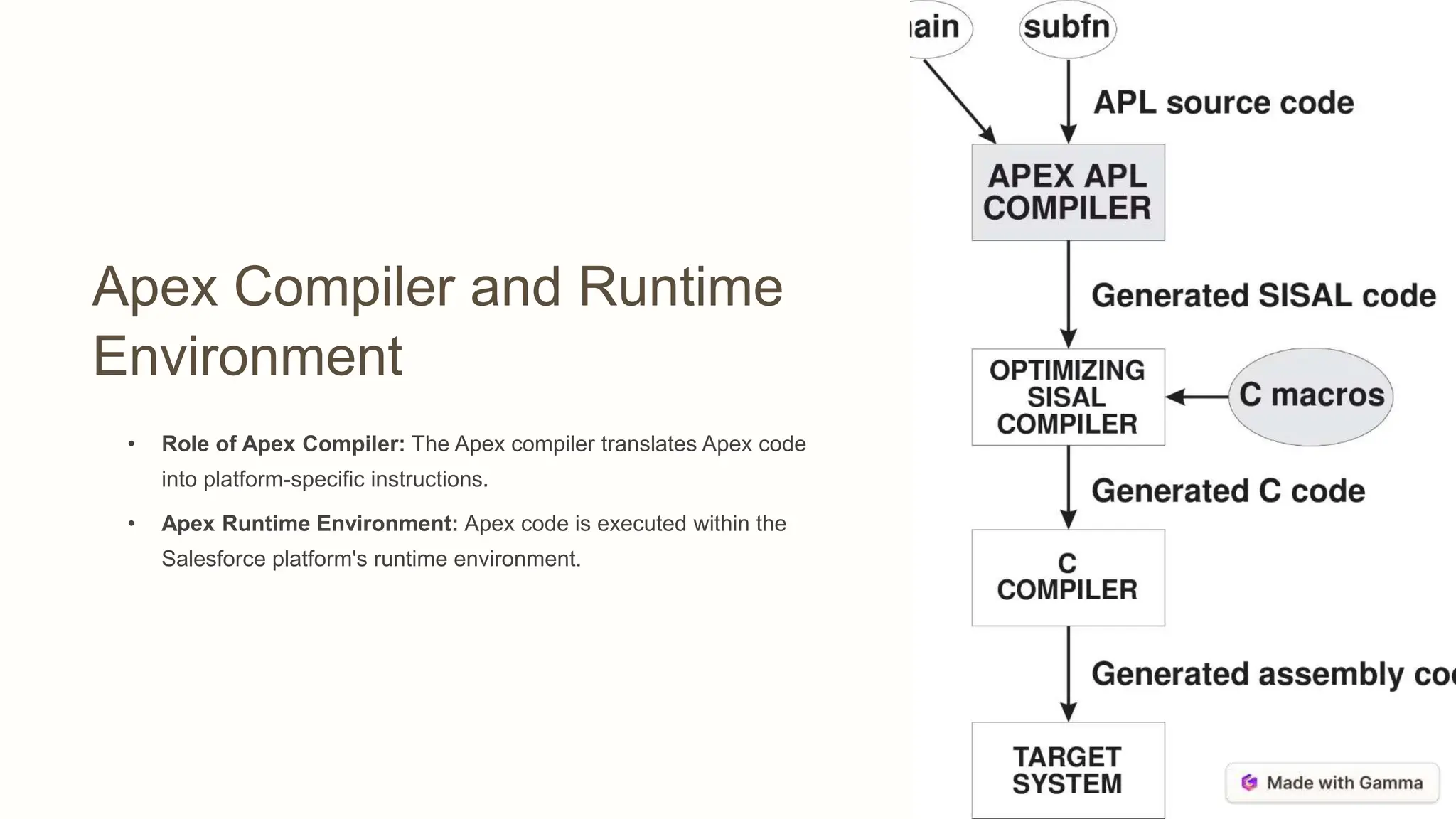
This document provides an overview of mastering Salesforce development by exploring key concepts like Apex programming, REST API, and asynchronous processing. It discusses fundamentals like data types, classes, and SObjects in Apex, and how Apex can be used to build custom REST endpoints and integrate with external APIs. The document also covers governor limits, batch, queueable, and scheduled Apex for asynchronous processing of large data volumes.