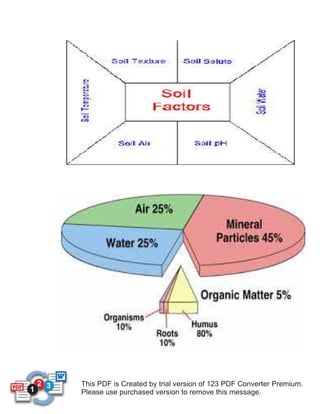
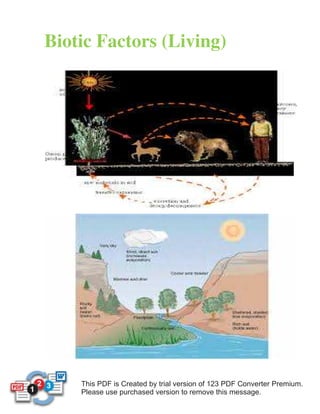
Environmental factors that affect ecosystems include edaphic or soil-related factors like soil type, pH, water, and mineral content. Climatic factors such as temperature, rainfall, light intensity, wind, and humidity also impact ecosystems. Biotic or living factors include food sources, competition, predation, parasitism, pollination, seed dispersal, and human activity. Fire can impact ecosystems by affecting plants, soils, water, air, and animals through regeneration, increased fertility, erosion, noxious gases, and particulate matter.