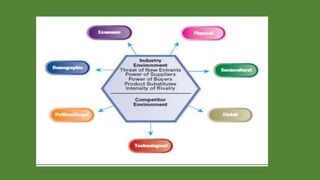
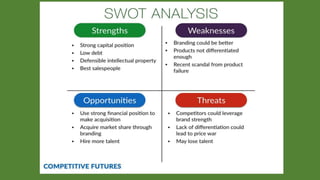
The document discusses environmental scanning and analysis for strategic management. It defines the internal and external environment and describes several approaches to environmental scanning. The external environment includes political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors. The internal environment comprises the organization's resources and capabilities. A SWOT analysis identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to help formulate strategies. Conducting environmental analysis is important for strategy formulation and performance.