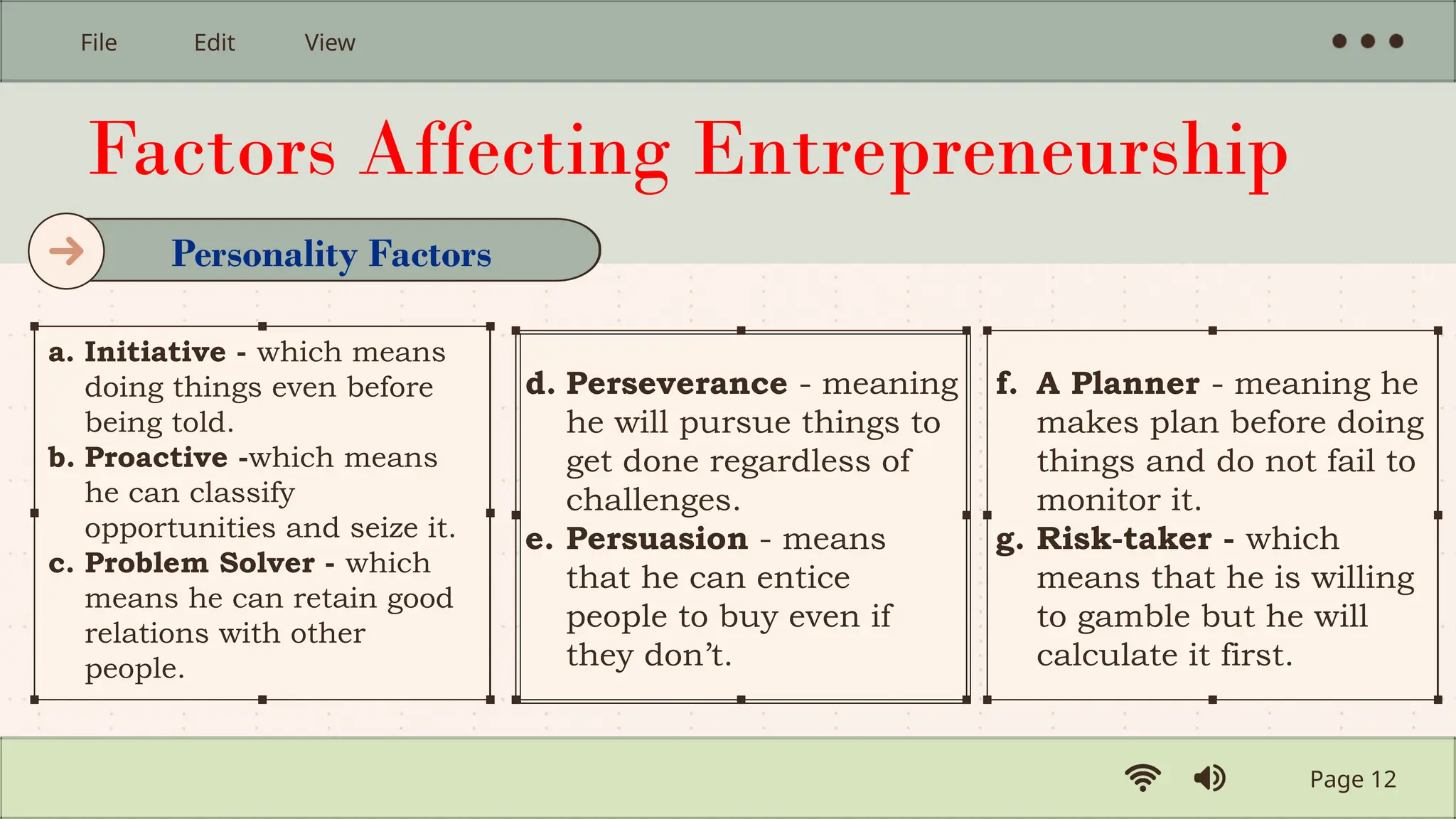
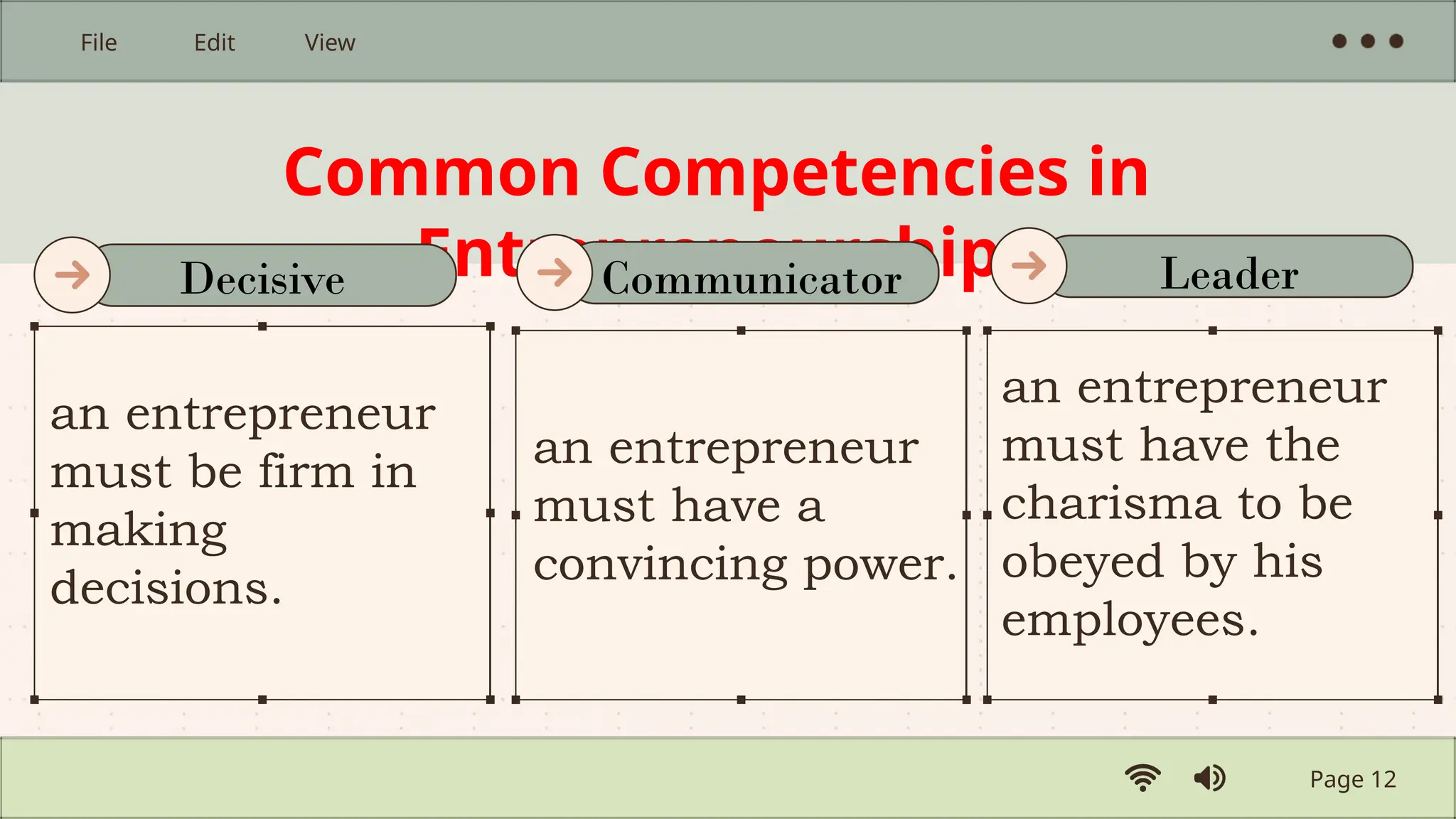
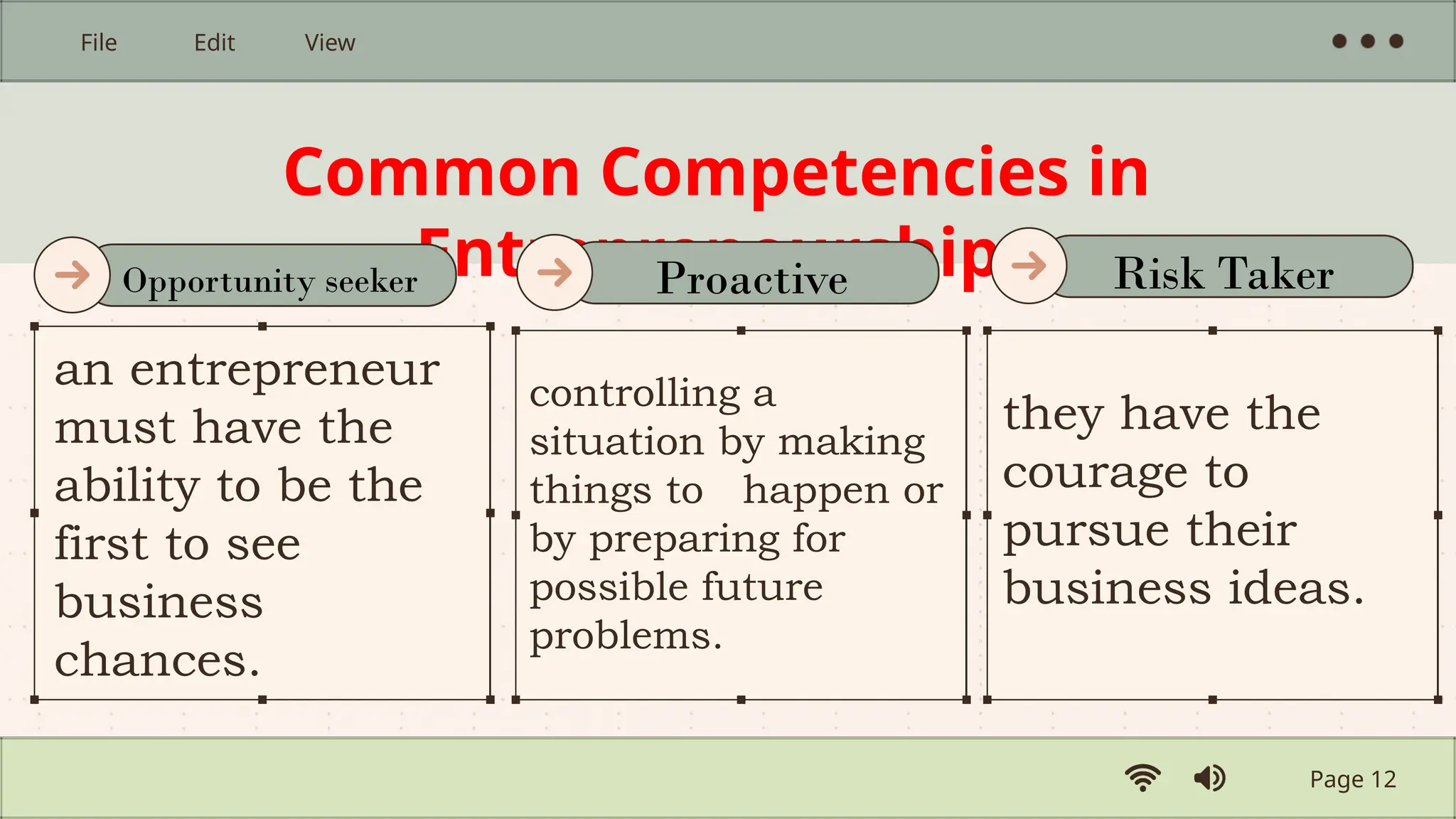
The document provides an introduction to entrepreneurship, defining key concepts and characteristics of successful entrepreneurs. It explores the role of entrepreneurs in creating and growing businesses, the differences between entrepreneurs and traditional businessmen, and the factors affecting entrepreneurship. Additionally, it outlines opportunities for individuals pursuing careers in entrepreneurship, emphasizing the importance of innovation and risk-taking.