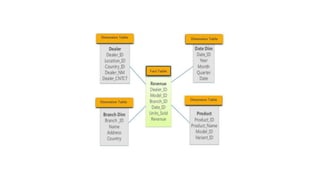
The document outlines the architecture of data warehouses, detailing four key elements: data sources, data transformation processes, data loading methods, and access mechanisms for analysis. It emphasizes the Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) cycle for maintaining data quality and usage of schemas like star and snowflake for organizing data. Best practices for data warehousing projects include alignment with corporate strategy, management of user expectations, and incremental system development.