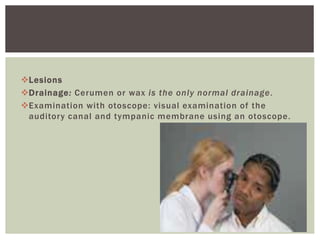
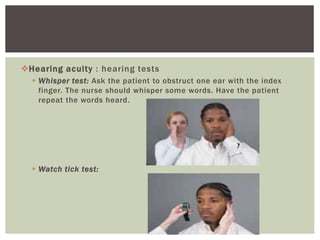
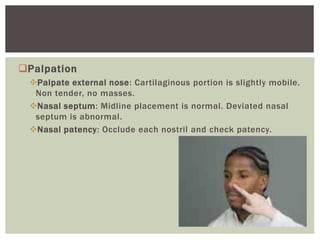
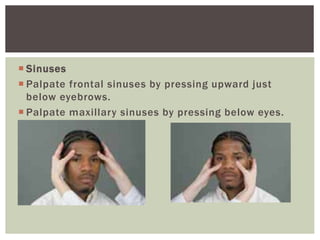
The document provides assessment guidelines for the ears, nose, and throat. It describes how to inspect the ears for color, shape, size, position, and lesions, and how to examine the ear canals and eardrums. Hearing tests like the whisper, watch tick, Weber, and Rinne tests are outlined. The nose is inspected for symmetry, drainage and nasal structure. Sinuses are palpated. The throat is inspected for the oropharynx, tonsils, uvula, and gag reflex while palpating lymph nodes.