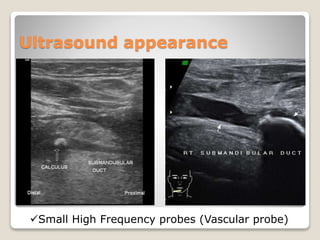
A 45-year-old female presented with sudden pain and swelling in the right cheek, diagnosed with sialolithiasis after imaging revealed a 1.7mm stone in the right parotid gland. The patient received IV pain relief and was discharged with medications and follow-up instructions. Clinical management included hydration, warm compresses, and analgesics, emphasizing the need for potential follow-up if symptoms persisted.