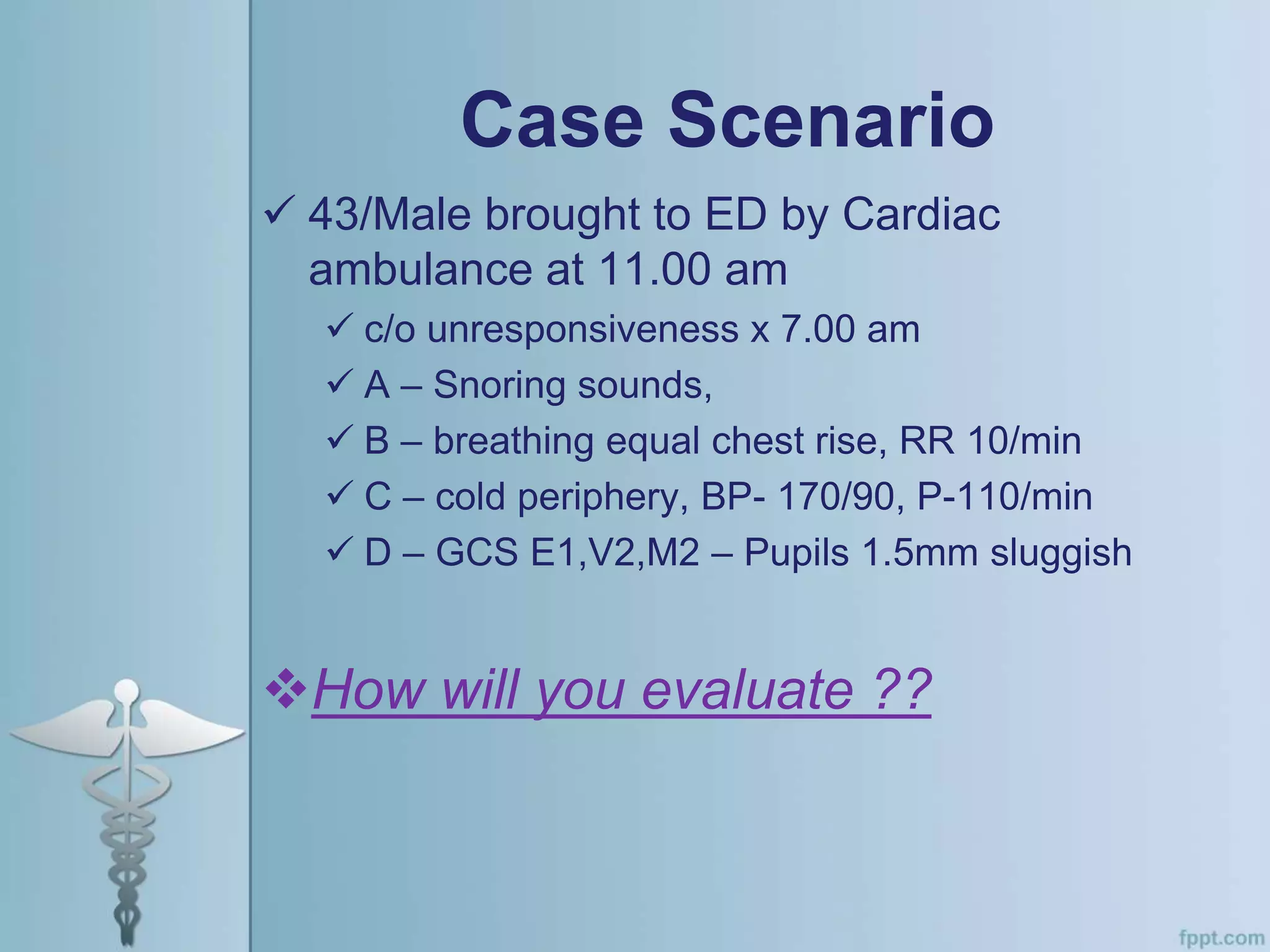
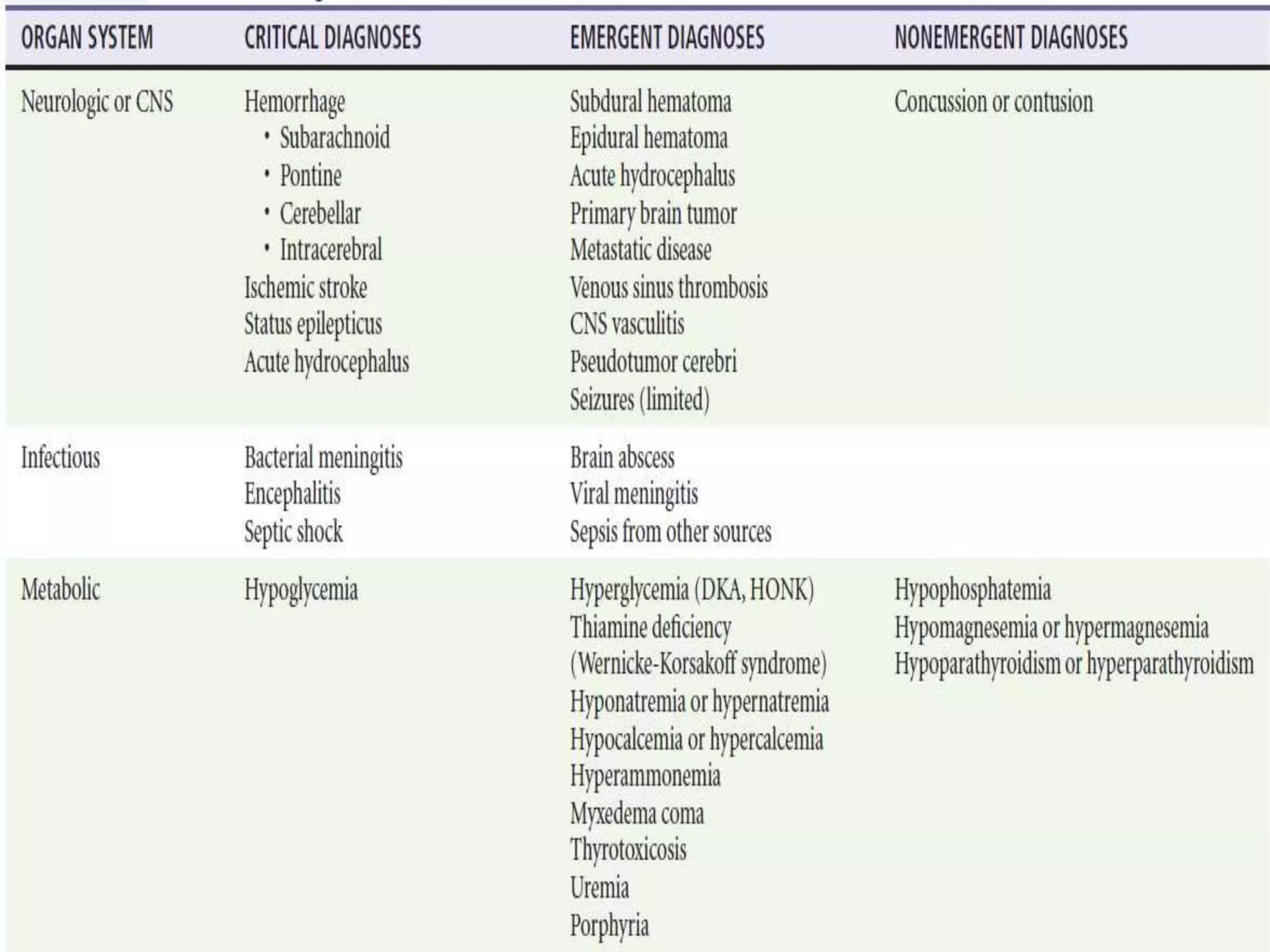
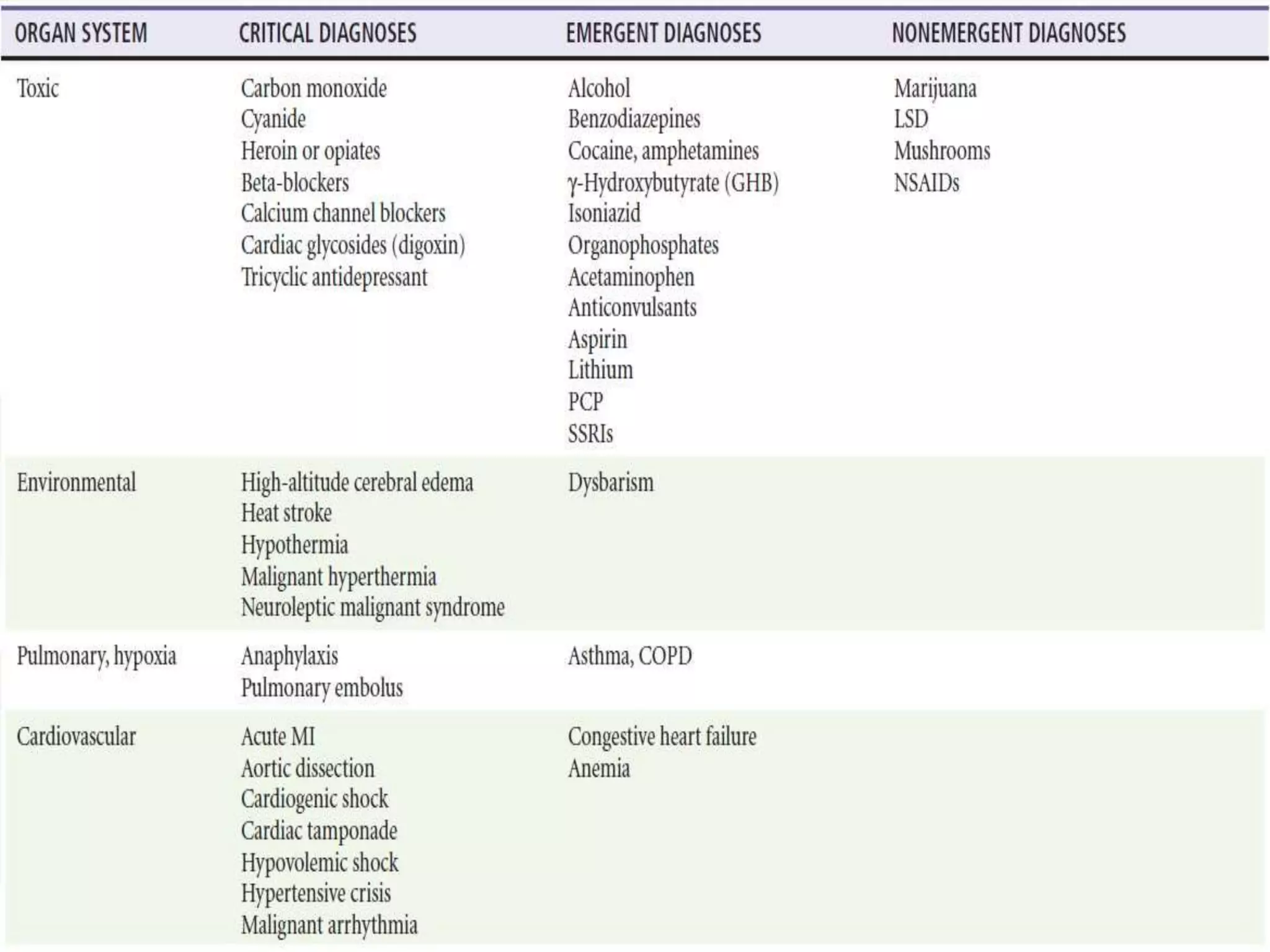
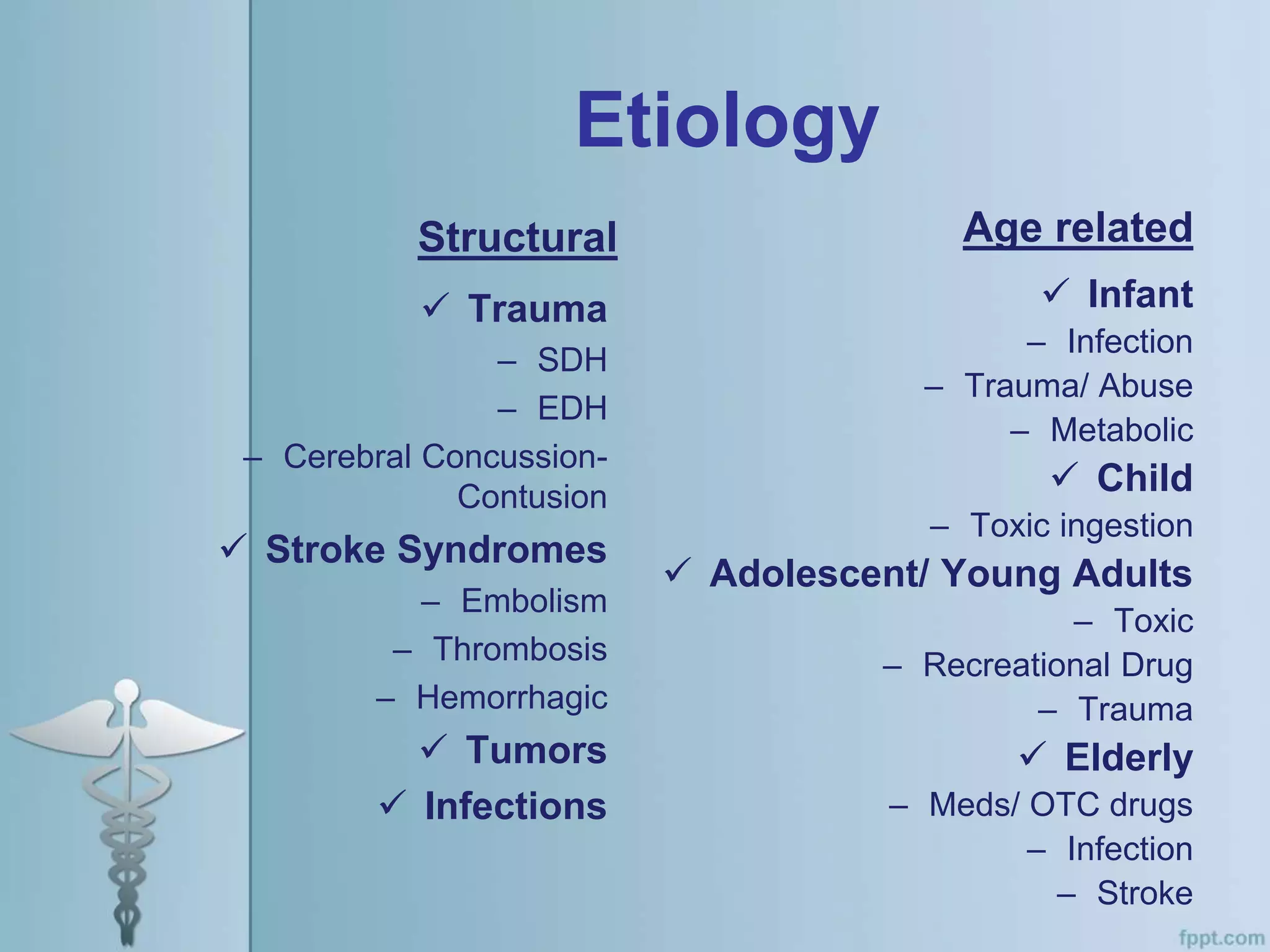
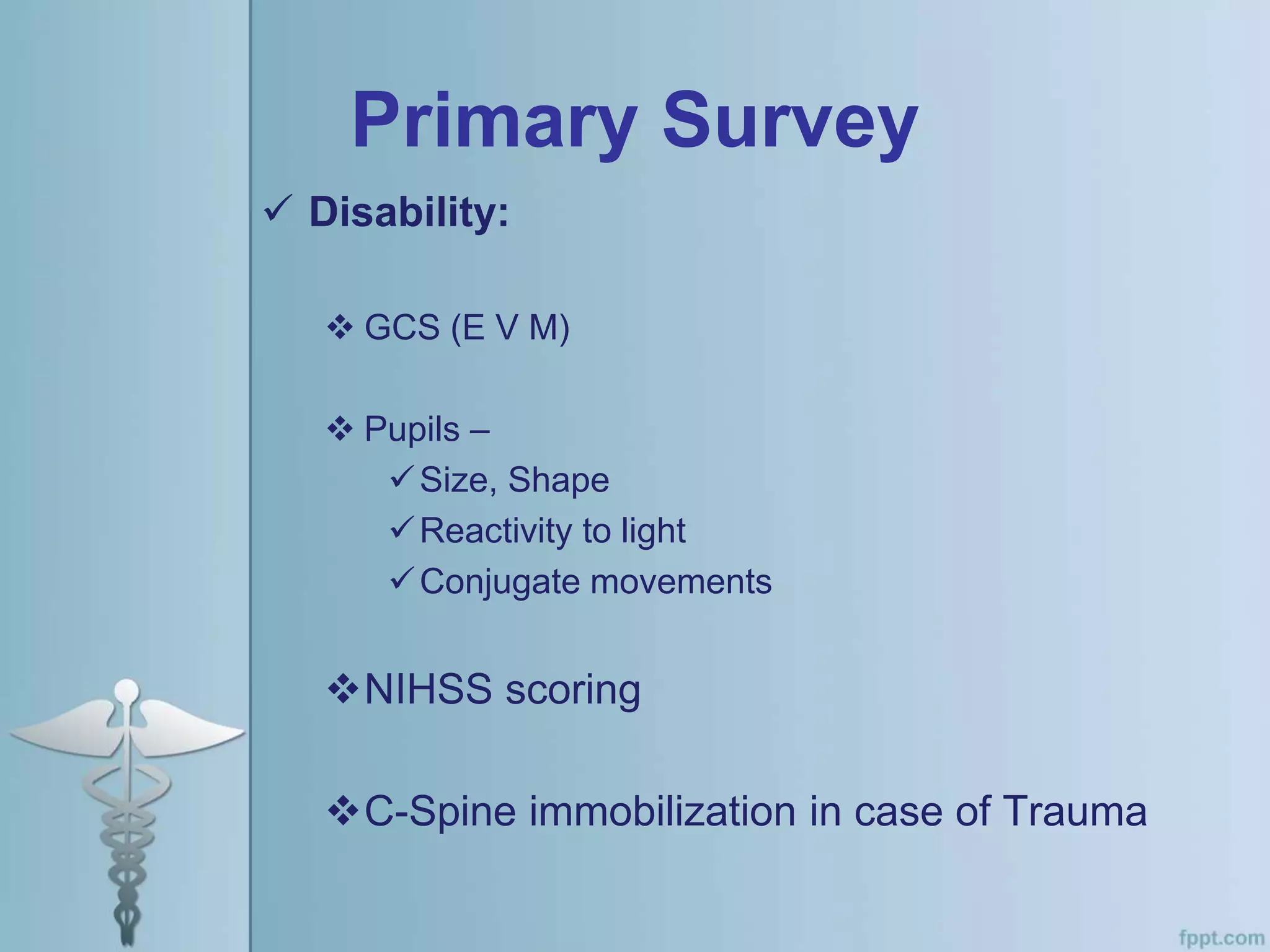
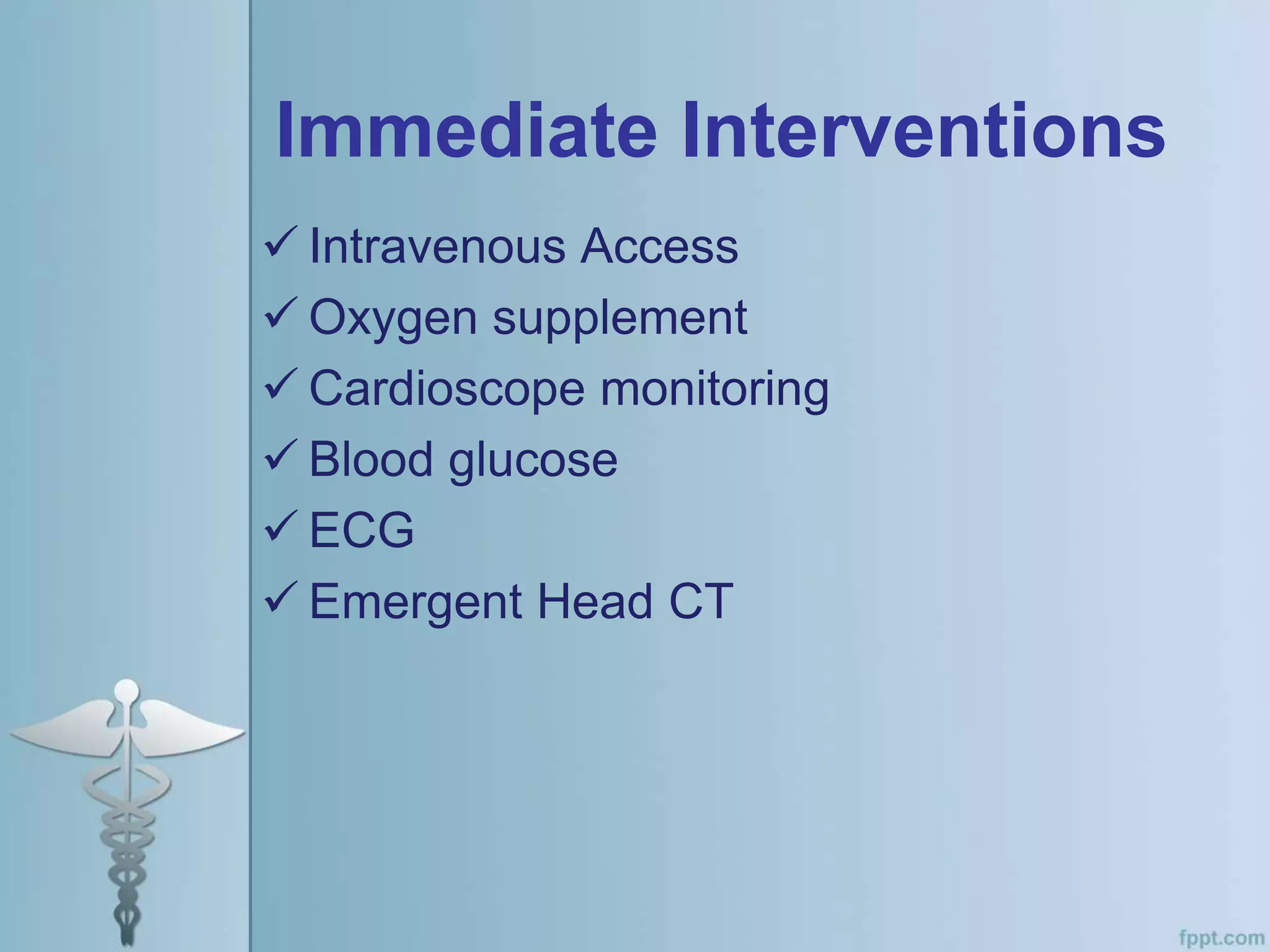
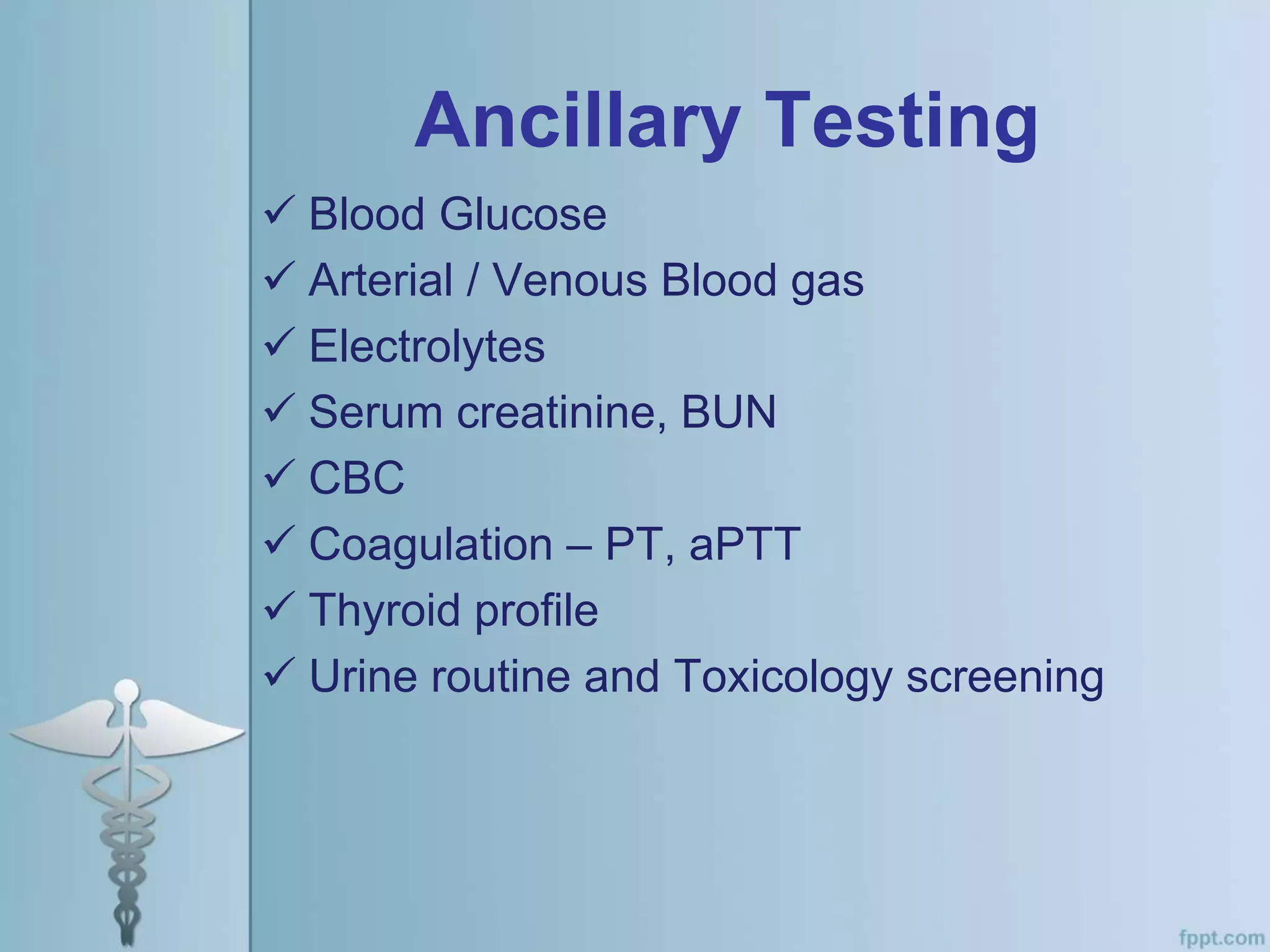
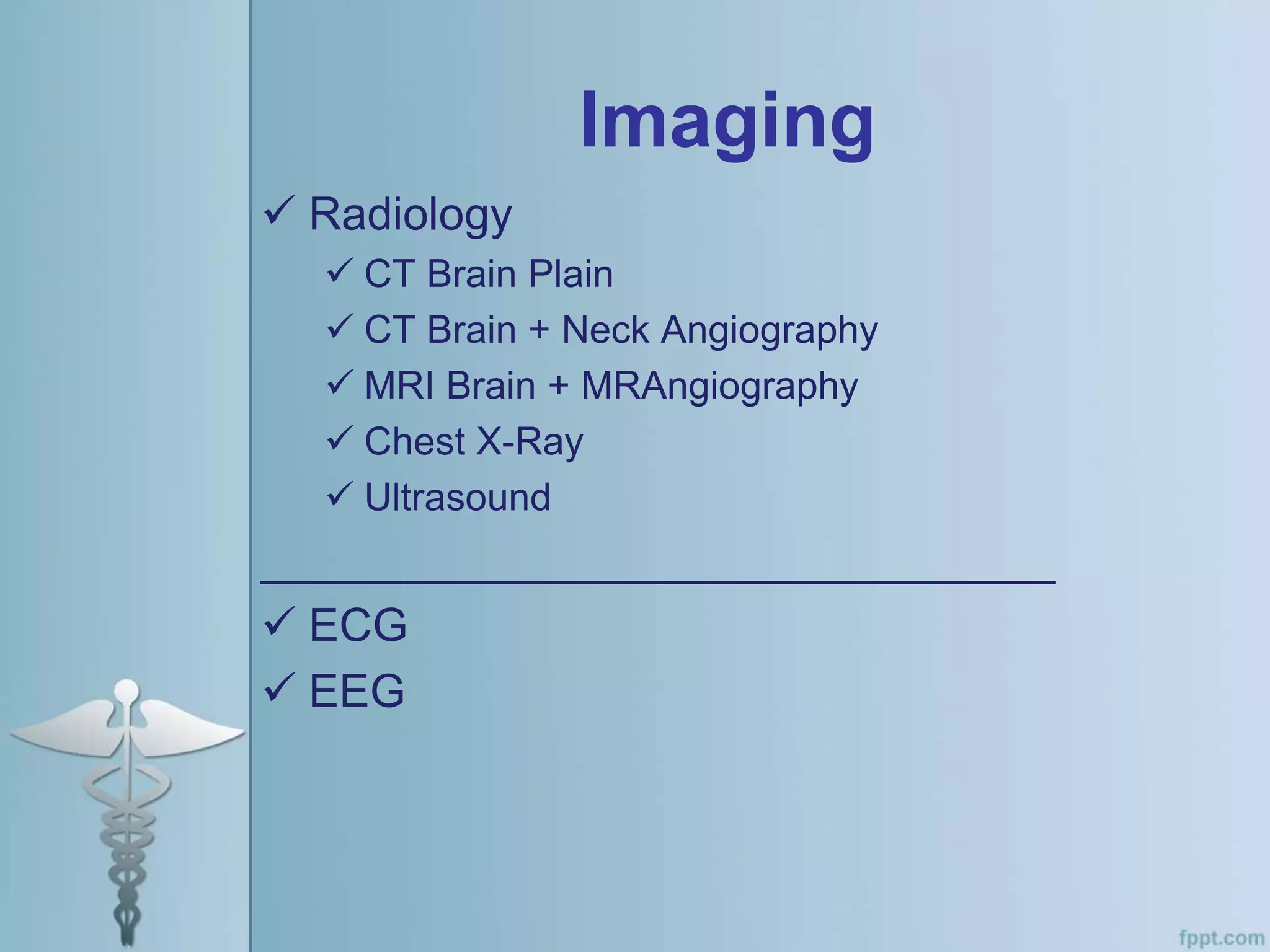
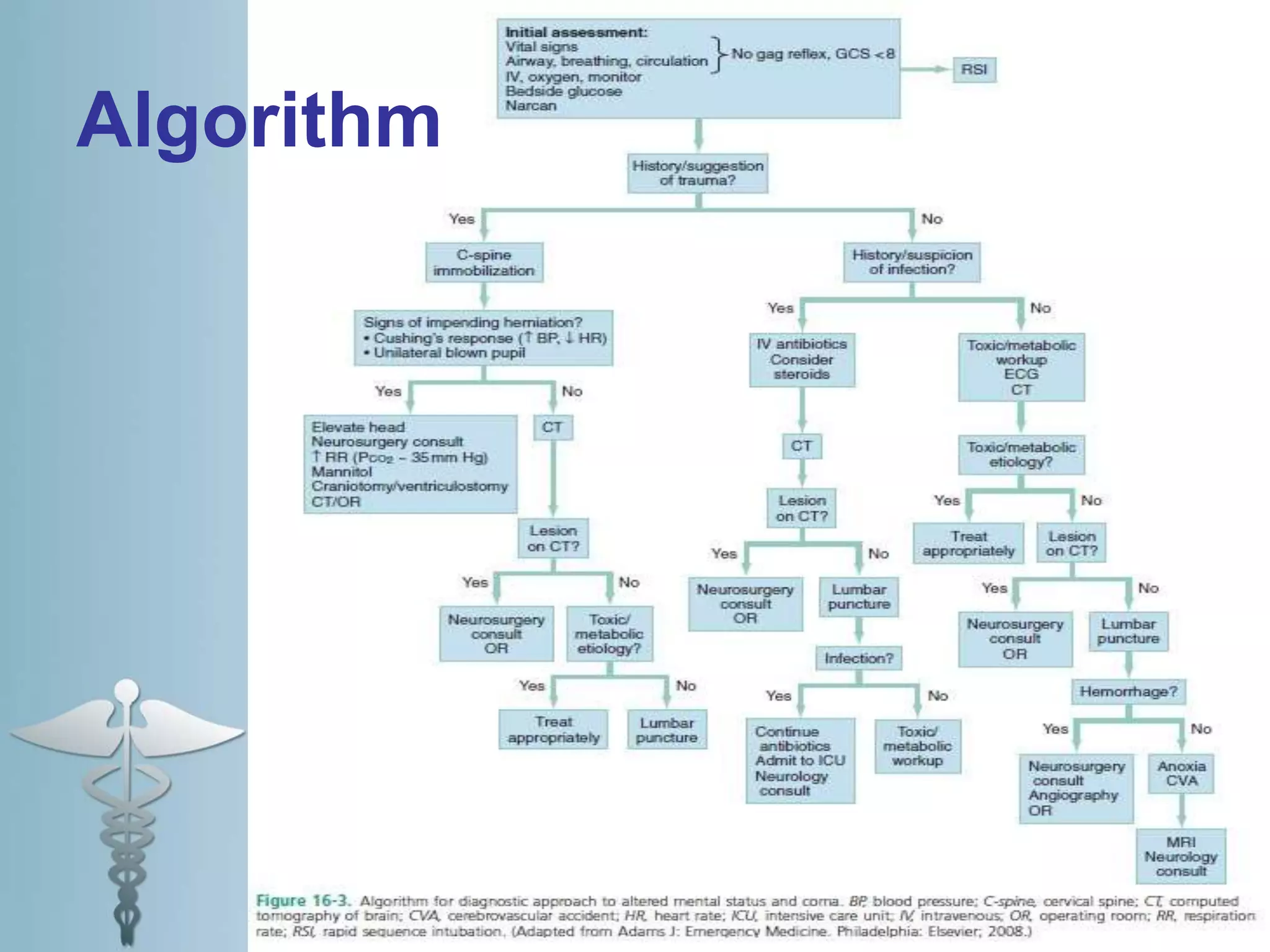
This document provides an overview of the approach to evaluating and managing a patient presenting with coma in the emergency department. It begins by defining coma and outlining the pathophysiology involving impaired arousal from damage to the brainstem arousal system or cerebral cortex. The primary and secondary surveys are described which involve assessing the airway, breathing, circulation, disability and exposure. Differential diagnosis, common etiologies, ancillary testing, imaging and disposition are discussed. The key steps in the emergency department include stabilizing the airway and breathing, obtaining vital signs, blood glucose, brief history, full examination, imaging of the head and further testing and treatment based on diagnosis.