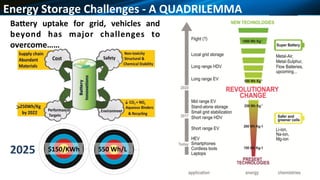
The document discusses how 2D materials can advance energy storage and discusses several research projects utilizing 2D materials for lithium and sodium-ion batteries. It summarizes that integrating selected 2D lithium host materials into 3D architectures can improve electrochemical performance through increased surface area and diffusion pathways. Composite 2D-3D microstructures incorporating graphene offer multiple functional enhancements for energy storage systems. There is a need to explore advanced manufacturing methods for nanostructured materials.