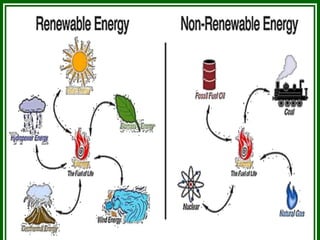
This document discusses energy conservation. It defines energy as the ability to do work and identifies renewable energy sources like solar and wind and non-renewable sources like fossil fuels. It explains that we need to conserve energy because resources are limited and demands are increasing. Some ways to conserve include recycling, turning off unused devices, and replacing old light bulbs. Specific tips provided include not leaving lights on unnecessarily and analyzing appliance energy efficiency. Energy conservation helps save money and reduce pollution. India relies heavily on fossil fuel imports for its energy needs and conservation can help address this.