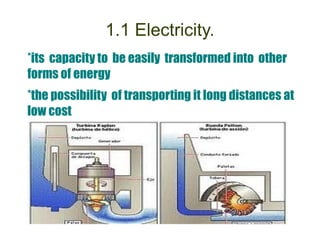
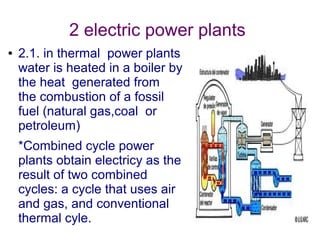
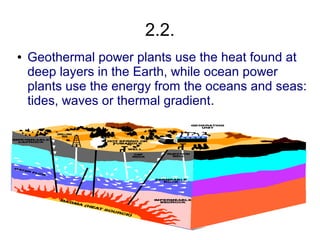
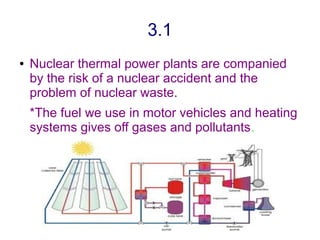
This document discusses different types of energy sources and power plants. It covers household and industrial energy uses, as well as renewable and non-renewable sources. It then describes various power plants in more detail, including thermal, nuclear, hydroelectric, wind, solar, biomass and geothermal plants. Finally, it discusses the environmental impacts of different energy sources and power plants, such as resource depletion, pollution, and solutions to reduce waste.