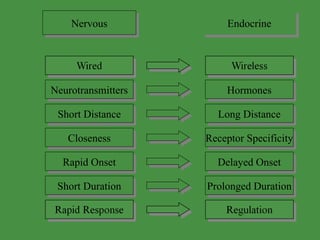
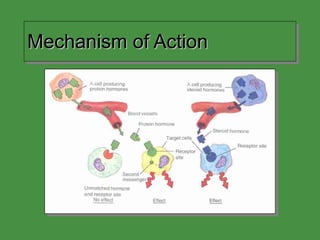
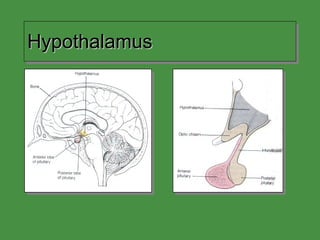
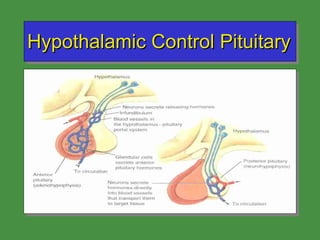
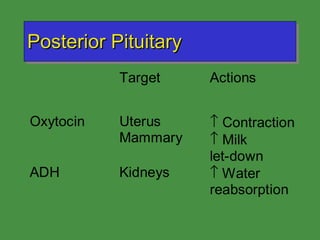
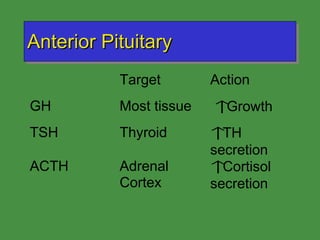
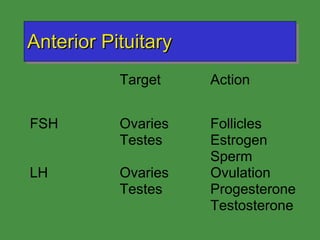
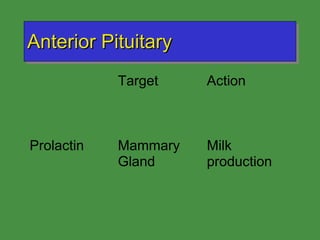
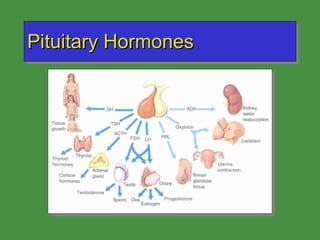
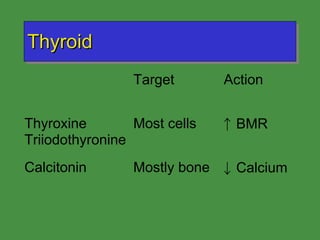
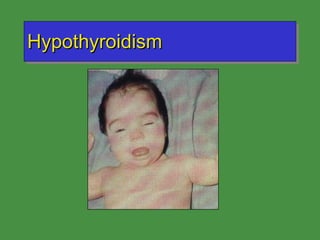
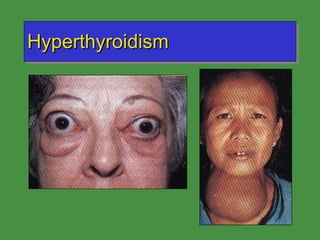
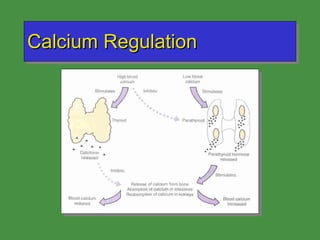
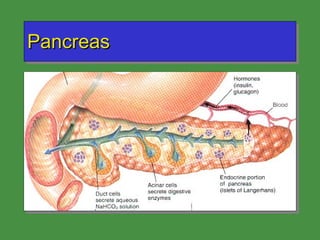
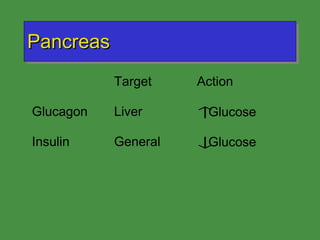
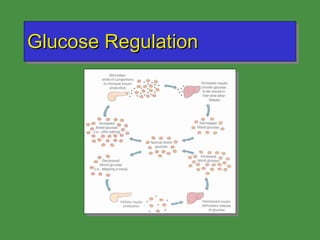
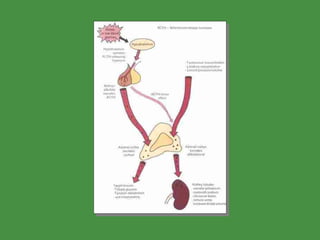
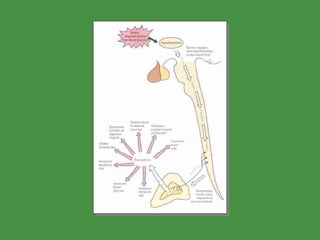
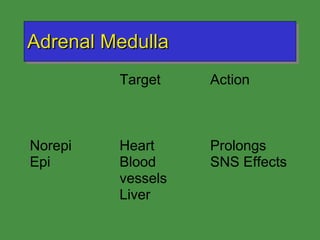
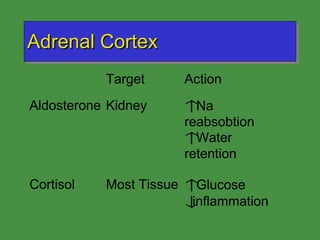
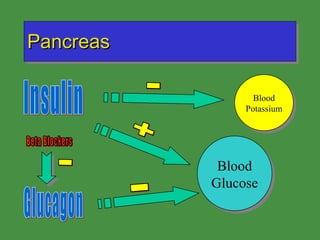
This document discusses various drugs that affect the endocrine system. It covers pituitary drugs, parathyroid/thyroid drugs, adrenal drugs, pancreatic drugs, reproductive drugs, and sexual behavior drugs. For each category, it provides examples of diseases or conditions treated and names brand name drugs used as treatment. It also discusses the basic functions and mechanisms of the endocrine system and how different glands are regulated.