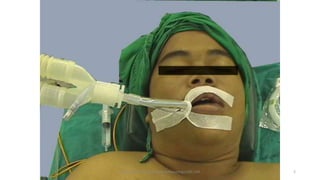
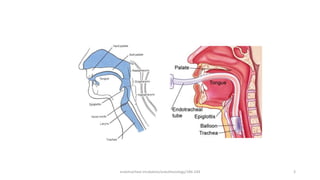
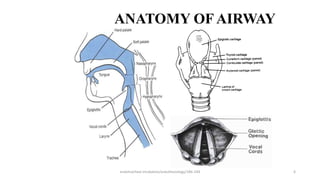
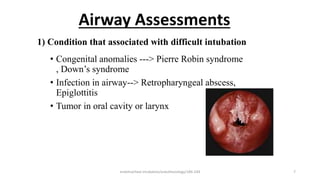
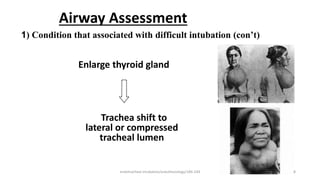
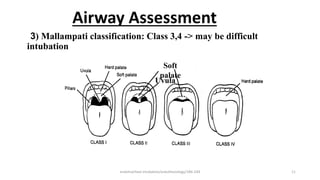
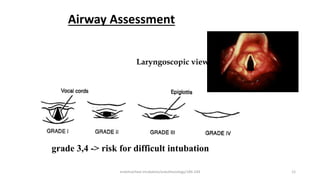
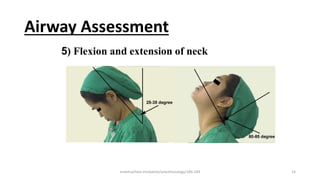
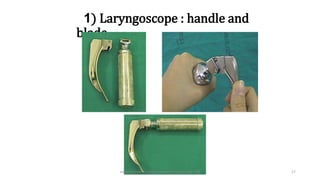
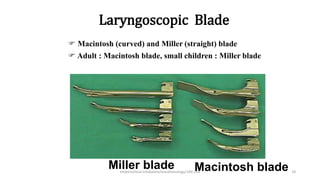
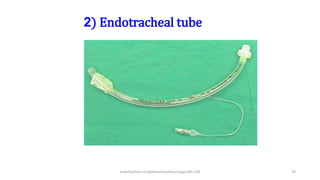
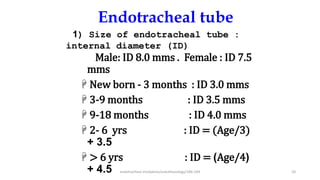
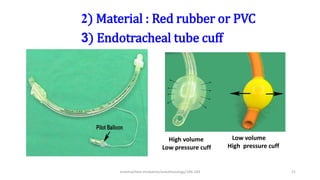
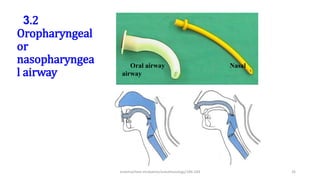
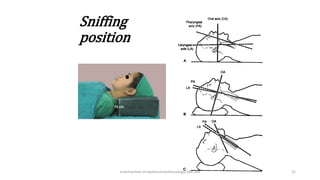
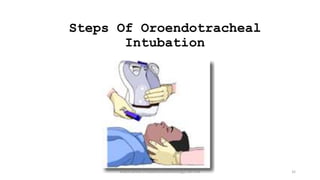
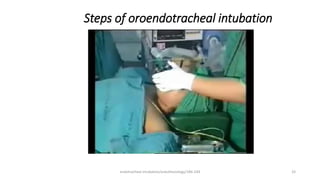
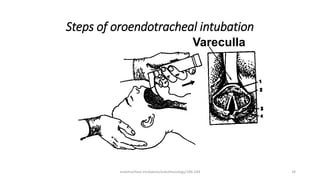
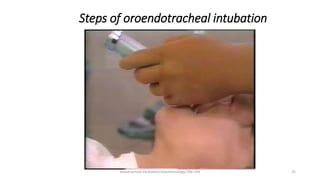
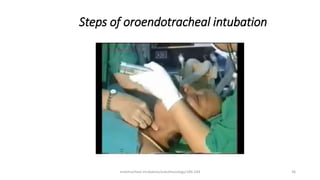
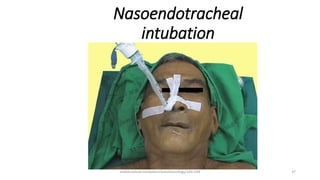
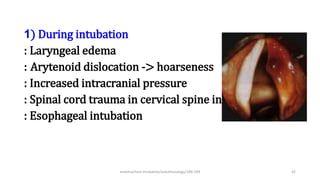
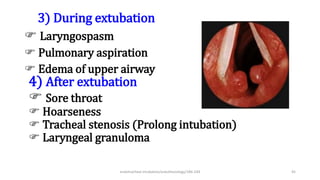
This document discusses endotracheal intubation, including indications, anatomy, equipment, techniques, and complications. Indications for intubation include supporting ventilation for respiratory diseases, anesthesia during surgery near the airway, and risk of aspiration. Airway assessments evaluate for conditions that could make intubation difficult, such as enlarged thyroid or cervical spine injuries. Equipment includes laryngoscopes, endotracheal tubes, suction catheters, and monitors to confirm proper placement. Techniques involve positioning the patient and inserting the tube through the vocal cords into the trachea. Complications can occur during or after intubation and intubation removal, such as trauma, aspiration, or laryngospasm.