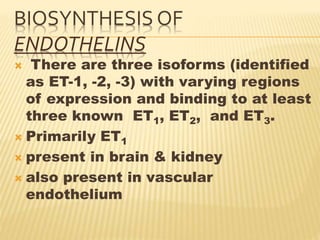
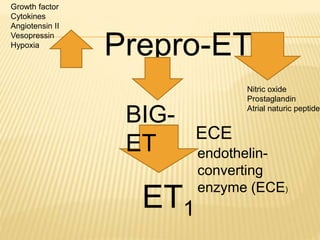
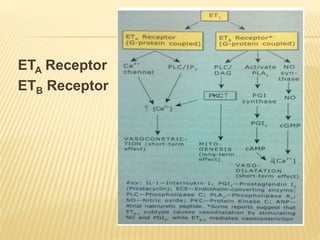
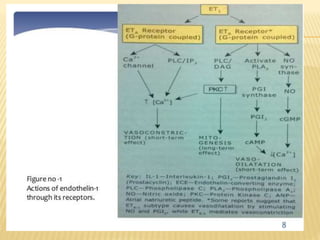
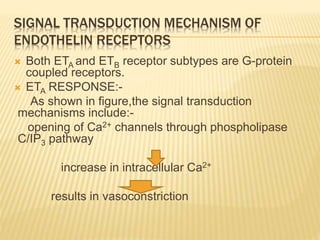
Vasactive peptides include vasoconstrictors like endothelin and vasodilators like nitric oxide. Endothelin is a potent vasoconstrictor peptide derived from endothelial cells. There are three endothelin isoforms, with ET-1 being the primary one found in vascular endothelium and brain. Endothelin receptors are classified as ETA and ETB, with ETA located on smooth muscle and ETB on endothelial cells. ETA activation causes vasoconstriction while ETB activation leads to vasodilation through nitric oxide release. Selective ETA antagonists are used to treat conditions involving endothelin overactivity.