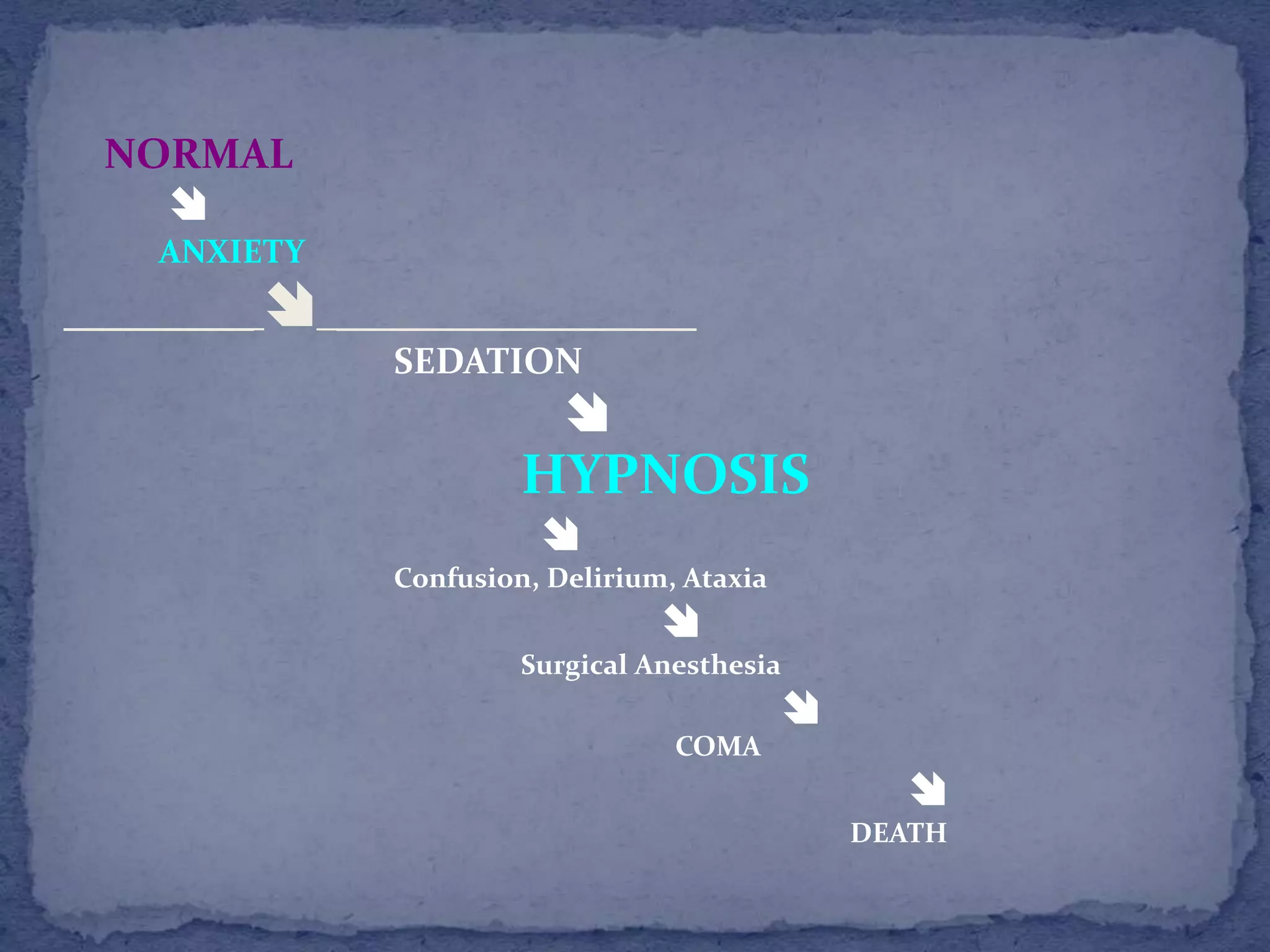
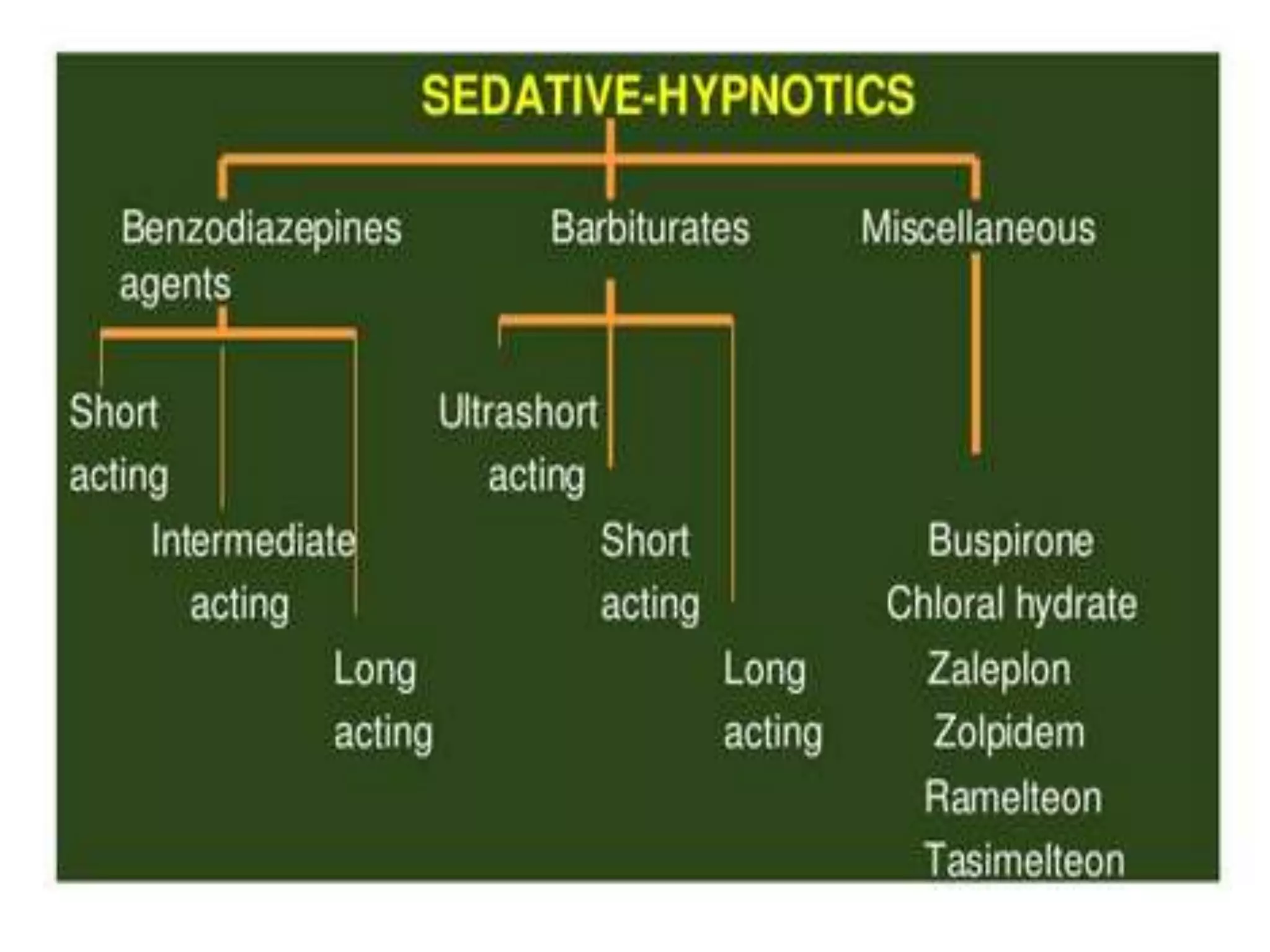
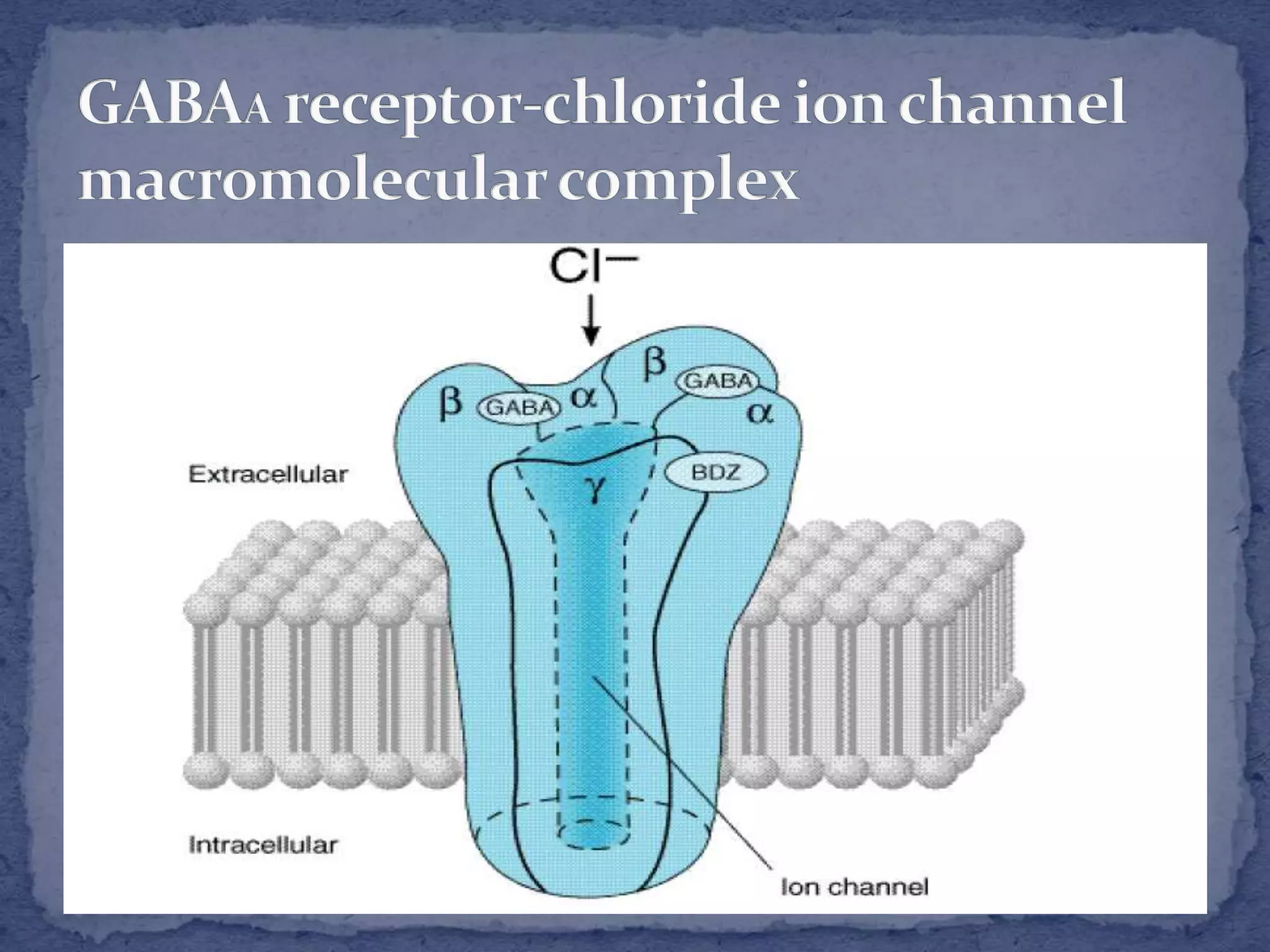
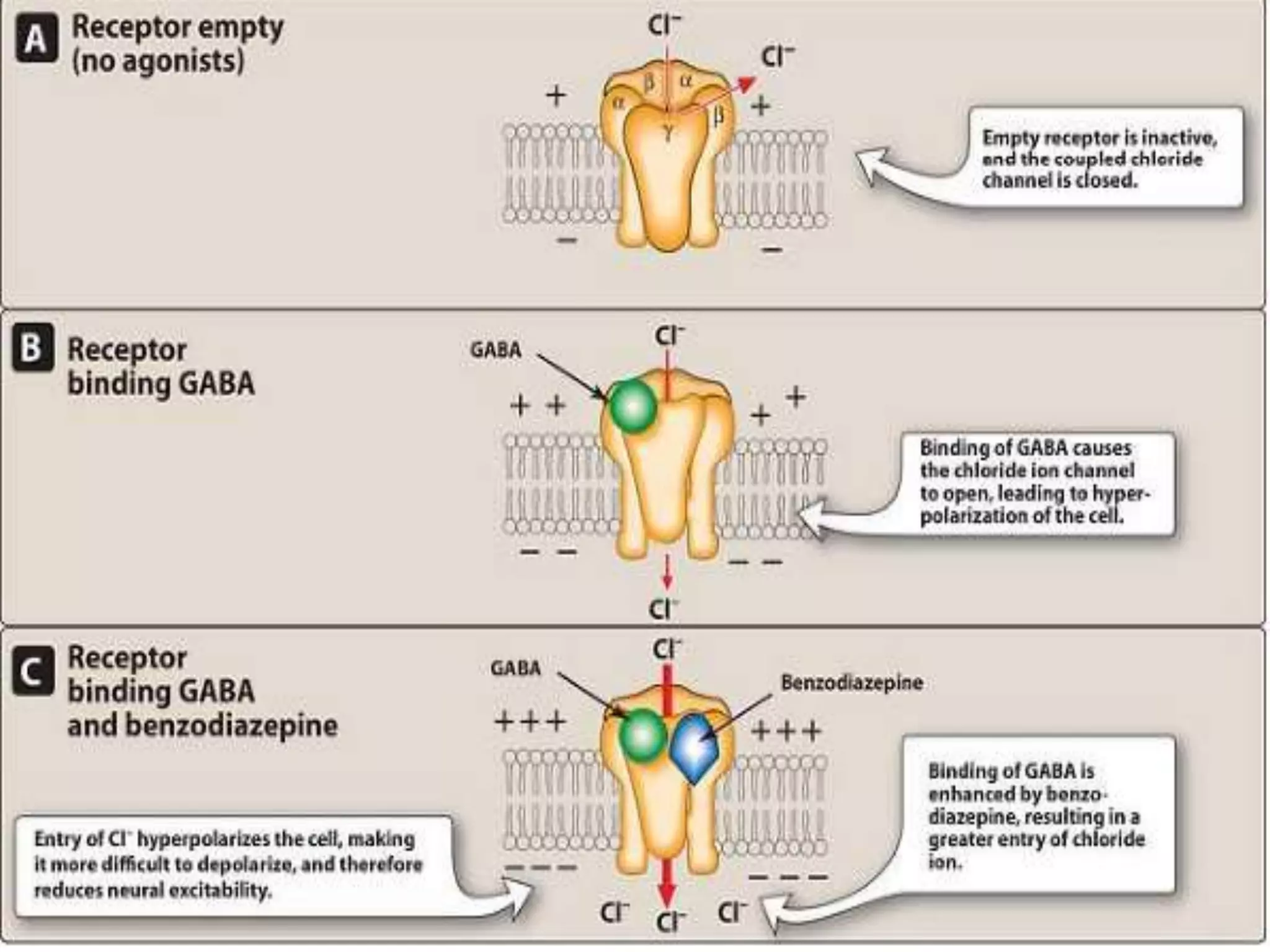
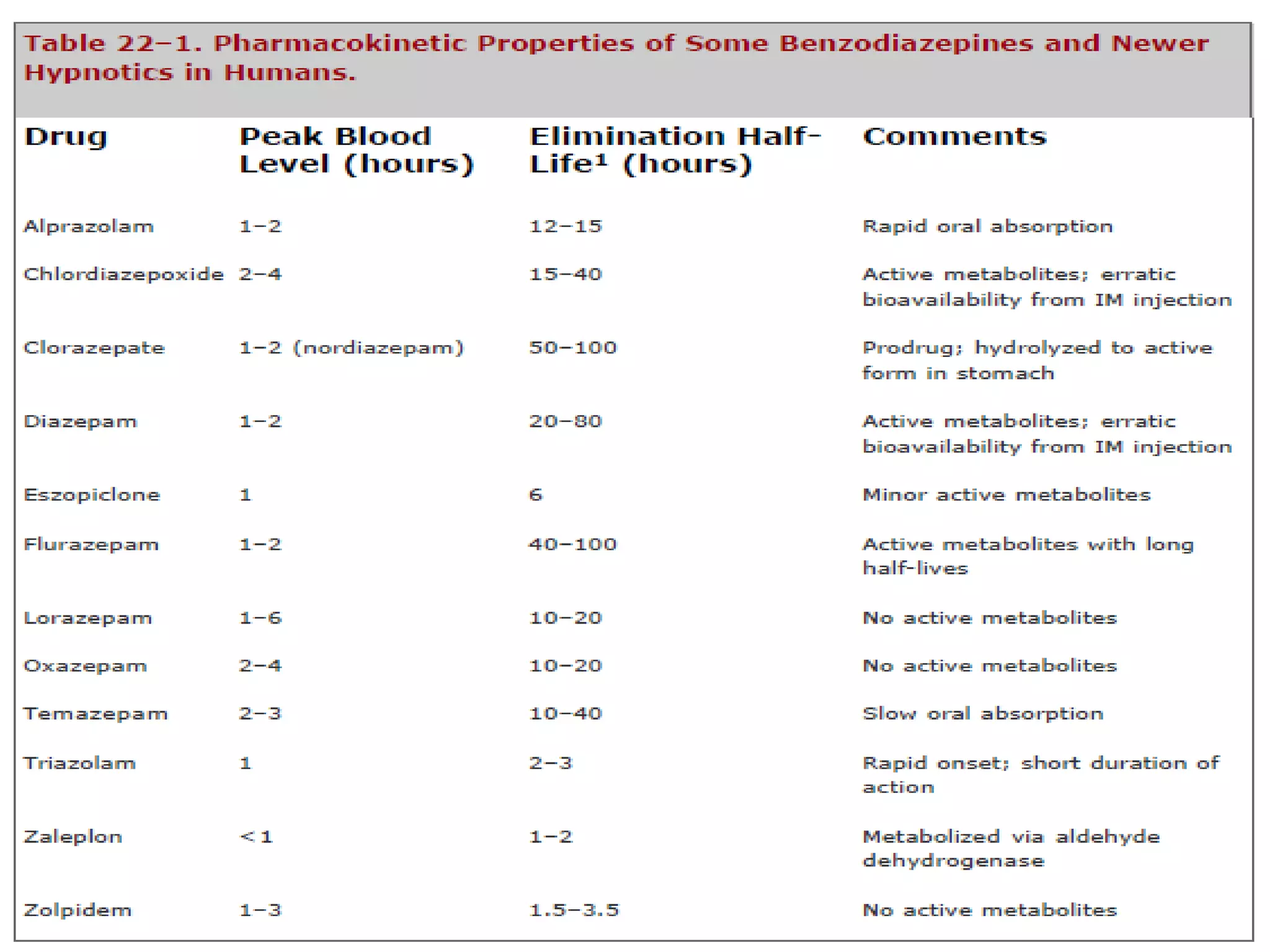
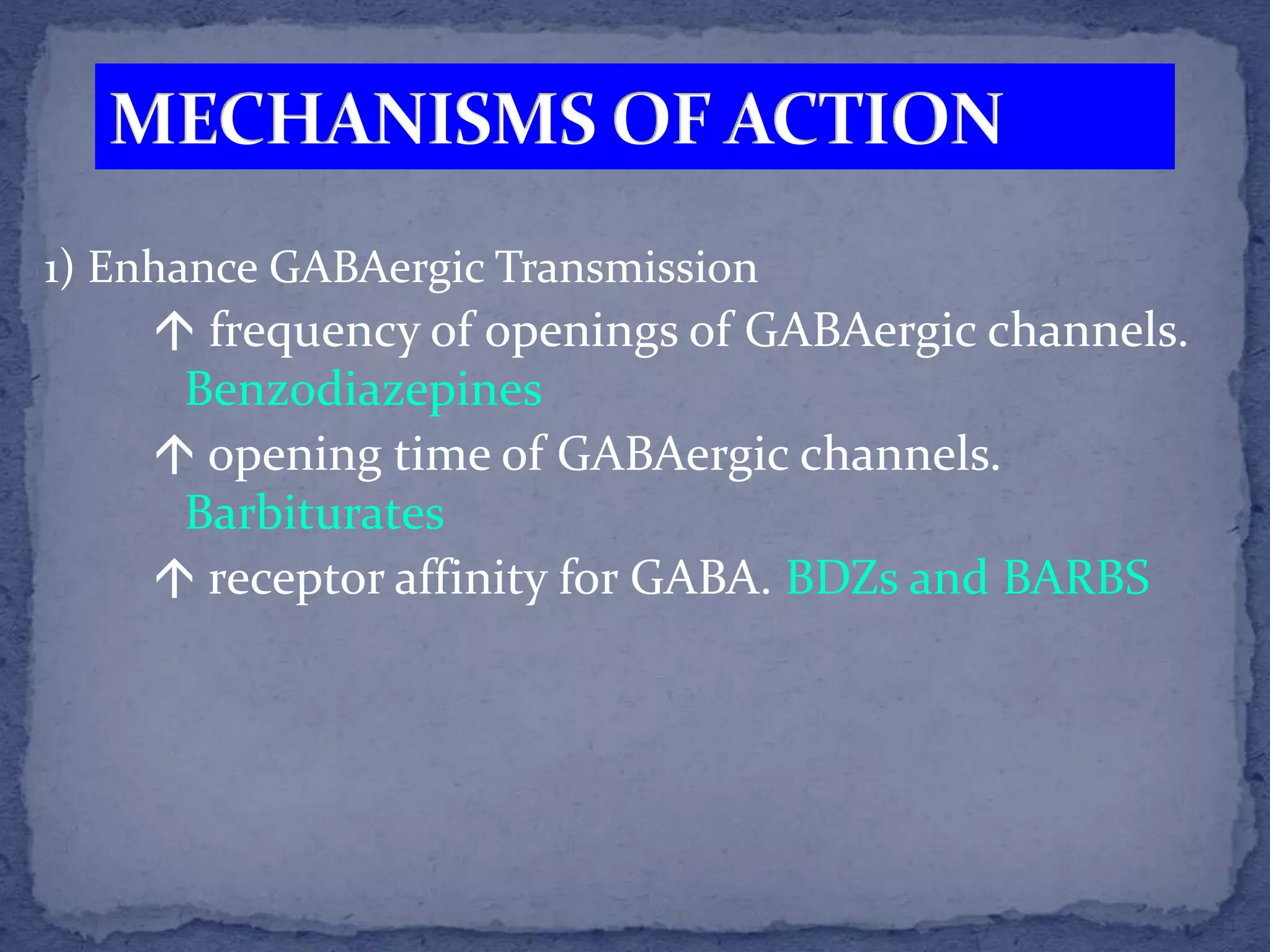
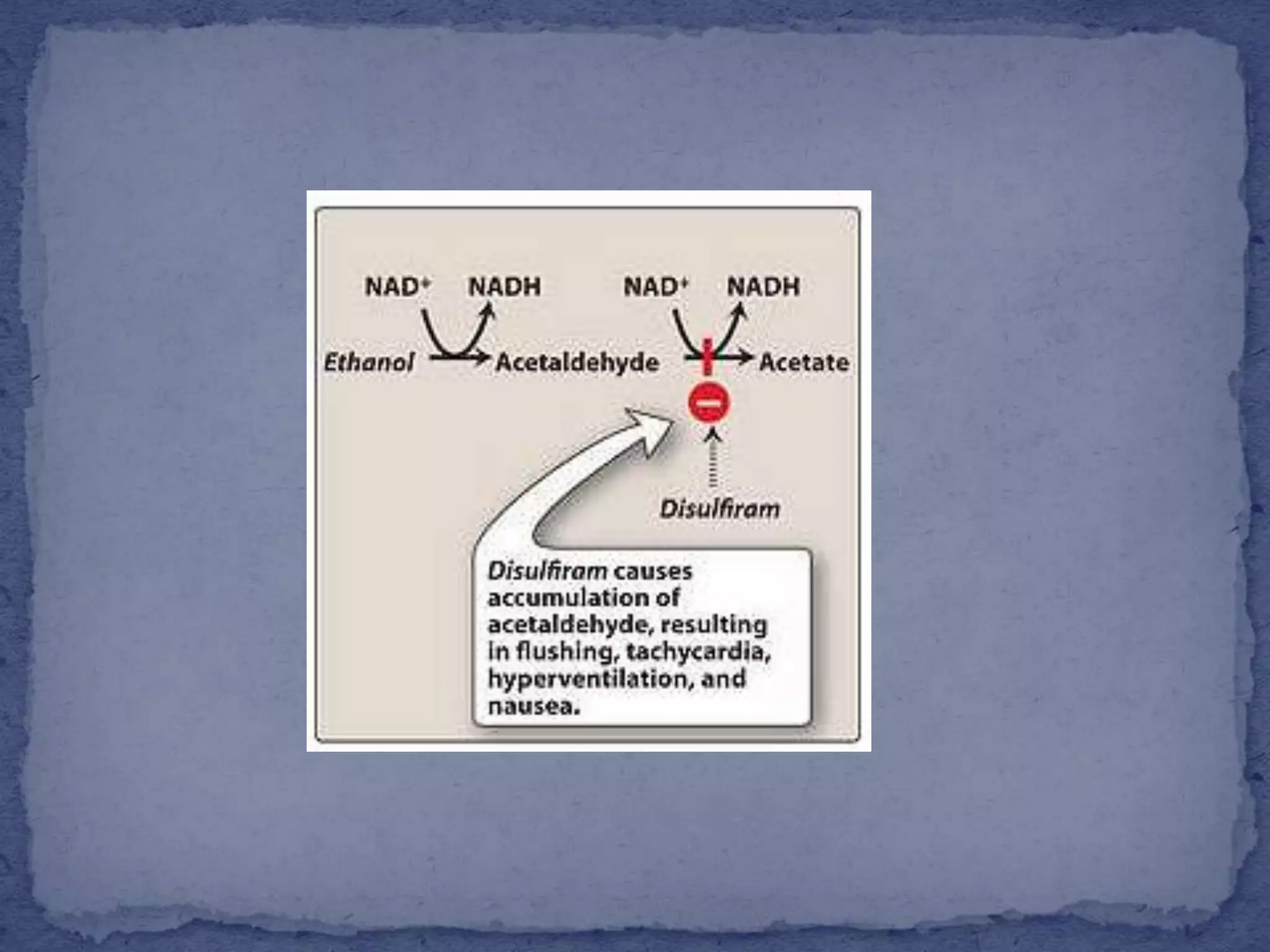
This document summarizes information about sedatives and hypnotics. It defines sedatives as drugs that reduce excitement and calm patients without inducing sleep, while hypnotics produce sleep resembling natural sleep. Both act by facilitating GABAergic transmission. Common classes discussed are benzodiazepines, barbiturates, antihistamines, and other sedative-hypnotics. Their mechanisms, clinical uses, and side effects are compared. Sedatives are used to relieve anxiety, while hypnotics induce sleep. Toxic doses can depress respiration and blood pressure, potentially causing death.